책 스프링부트와 AWS로 혼자 구현하는 웹서비스 따라하기
시작👊

어제에 이어 오늘은
수정 / 조회 기능을 만들어보자!
코드를 추가해준다.
PostsApiController에update,findById코드를 추가한다.
// PostsApicontroller.java
...
@PutMapping("/api/v1/posts/{id}")
public Long update(@PathVariable Long id,@RequestBody PostsUpdateRequestDto requestDto){
return postsService.update(id, requestDto);
}
@GetMapping("/api/v1/posts/{id}")
public PostsResponseDto findById (@PathVariable Long id){
return postsService.findById(id);
}
- dto 패키지에
PostsResponseDto클래스를 추가하고 코드를 추가해준다.
// PostsResponseDto.java
package com.prac.webservice.springboot.web.dto;
import com.prac.webservice.springboot.domain.posts.Posts;
import lombok.Getter;
@Getter
public class PostsResponseDto {
private Long id;
private String title;
private String content;
private String author;
public PostsResponseDto(Posts entity){
this.id = entity.getId();
this.title = entity.getTitle();
this.content = entity.getContent();
this.author = entity.getAuthor();
}
}
PostsResponseDto는 Entity의 필드 중 일부만 사용하므로 생성자로 Entity를 받아 필드에 값을 넣습니다. 모든 필드를 가진 생성자가 필요하지는 않으므로 Dto 는 Entity 를 받아 처리합니다.
- dto 패키지에
PostsUpdateRequestDto클래스를 만들고 코드를 추가해준다.
// PostsUpdateRequestDto.java
package com.prac.webservice.springboot.web.dto;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
public class PostsUpdateRequestDto {
private String title;
private String content;
@Builder
public PostsUpdateRequestDto(String title, String content){
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
}
}- Posts 클래스에
update메서드를 추가해준다.
// Posts.java
...
public void update(String title, String content){
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
}의문 : 왜 update 메서드를 Posts 클래스에 만들었지?!

에엥 왜지...?
controller 같은데 만들어야 하는 거 아닌가...?
- PostsService 클래스에
update,findById메서드를 추가해준다.
// PostsService.java
...
@Transactional
public Long update(Long id, PostsUpdateRequestDto requestDto) {
Posts posts = postsRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("해당 게시글이 없습니다. id = " + id));
posts.update(requestDto.getTitle(), requestDto.getContent());
return id;
}
public PostsResponseDto findById (Long id) {
Posts entity = postsRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("해당 게시글이 없습니다. id = " + id));
return new PostsResponseDto(entity);
}여기서 신기하느 것이 있습니다. update 기능에서 데이터베이스에 쿼리를 날리는 부분이 없습니다.
save 에는 있는 toEntity 가 없네!
이게 가능한 이유는 JPA의 영속성 컨텍스트 때문입니다.
영속성 컨텍스트란 Entity 를 영구저장하는 환경입니다. JPA의 핵심 내용은 Entity 가 영속성 컨텍스트에 포함되어 있느냐 아니냐로 갈립니다. JPA의 Entity Manager 가 활성화된 상태로 트랜잭션 안에서 데이터베이스의 데이터를 가져오면 이 데이터는 영속성 컨텍스트가 유지된 상태입니다.
이 상태에서 해당 데이터의 값을 변경하면 트랜잭션이 끝나는 시점에 해당 테이블에 변경분을 반영하니, 별도로 Update 쿼리를 날릴 필요가 없는 것이지요. 이 개념을 더티 체킹(dirty checking) 이라고 합니다.
헐 나 이거 들어본 거 같은데 수업하면서.
하나도 기억안나네.
수정과 조회 기능을 테스트해보자!
1.PostsApiControllerTest.java 에 코드를 추가해준다.
//PostsApiControllerTest.java
...
@Test
public void Posts_수정된다() throws Exception{
// given
Posts savedPosts = postsRepository.save(Posts.builder()
.title("title")
.content("content")
.author("author")
.build());
Long updateId = savedPosts.getId();
String expectedTitle = "title2";
String expectedContent = "content2";
PostsUpdateRequestDto requestDto = PostsUpdateRequestDto.builder()
.title(expectedTitle)
.content(expectedContent)
.build();
String url = "http://localhost:" + port + "/api/v1/posts/" + updateId;
HttpEntity<PostsUpdateRequestDto> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<>(requestDto);
// when
ResponseEntity<Long> responseEntity = restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.PUT,
requestEntity, Long.class);
// then
assertThat(responseEntity.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK);
assertThat(responseEntity.getBody()).isGreaterThan(0L);
List<Posts> all = postsRepository.findAll();
assertThat(all.get(0).getTitle()).isEqualTo(expectedTitle);
assertThat(all.get(0).getContent()).isEqualTo(expectedContent);
}근데 이 test 코드를 이해를 못하겠다..
이 테스트 코드를 이해해야 다음에 postman 같은 거 안 쓰고 바로 작동여부를 알 수 있을 텐데.. 처음 테스트 코드 작성하는 부분을 다시 한 번 살펴봐야겠다.
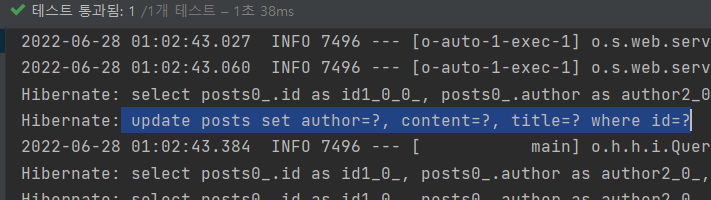
아무튼 잘 작동한다 !
책은 역시 두번 세번 읽어야 제 맛.
끝

