🤯 객체
키(key)와 값(value)으로 구성된 프로퍼티(Property)들의 집합
12_countNumberOfKeys
문제
객체를 입력받아 속성의 개수를 리턴
입출력 예시
const obj = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
c: 3,
};
let output = countNumberOfKeys(obj);
console.log(output); // --> 3나의 코드
function countNumberOfKeys(obj) {
let count = 0;
for(let prop in obj){
count++;
}
return count;
}✅ count 변수를 선언하며 숫자 0 할당
✅ for문으로 obj 안에 있는 property의 개수를 카운트하기 위해, for문이 1번씩 돌때마다 count 변수를 증가시킴
Reference
function countNumberOfKeys(obj) {
return Object.keys(obj).length;
}✅ ❗️Object.keys().length❗️
- 객체의 길이를 잴 수 있는 메소드
16_getLastElementOfProperty
문제
객체와 키를 입력받아 키에 해당하는 값이 배열인 경우, 마지막 요소를 리턴
주의 사항
- 주어진 키에 해당하는 값이 배열이고, 빈 배열이 아닌 경우에만 배열의 요소를 리턴
- 그 외의 경우, undefined를 리턴
입출력 예시
const obj = {
key: [1, 2, 5],
};
let output = getLastElementOfProperty(obj, 'key');
console.log(output); // --> 5나의 코드
function getLastElementOfProperty(obj, property) {
if(Array.isArray(obj[property])){
const index = obj[property].length - 1;
return obj[property][index];
}
}✅ 주의 사항에 배열이 아니거나 빈 배열인 경우 undefined를 리턴해주어야 한다고 명시되어 있었는데, 위의 코드가 문제 없이 잘 작동하였음
Reference
function getLastElementOfProperty(obj, property) {
let prop = obj[property];
if (!Array.isArray(prop) || prop.length === 0) {
return undefined;
}
return prop[prop.length - 1];
}✅ 레퍼런스 코드에는 if문으로 undefined되는 경우를 if문으로 작성함
❓
undefined가 되는 경우를 생각해서, 그 경우를 작성해주어야 하는걸까? 의문..
19_extend
문제
두 개의 객체를 입력받아 두번째 객체의 속성들을 첫번째 객체에 추가
입출력 예시
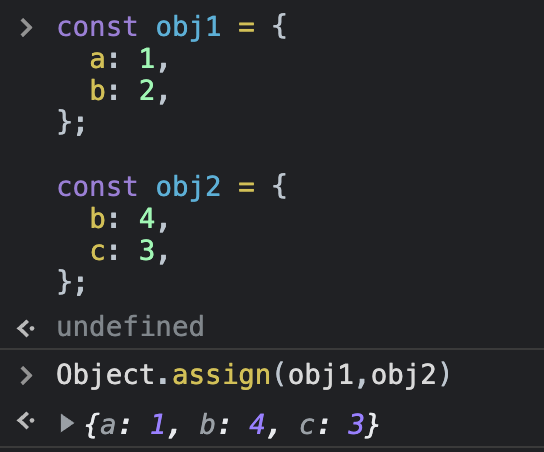
const obj1 = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
};
const obj2 = {
b: 4,
c: 3,
};
extend(obj1, obj2);
console.log(obj1); // --> {a: 1, b: 2, c: 3}
console.log(obj2); // --> {b: 4, c: 3}나의 코드
Object.assign()메소드 사용
- ojb1[b]의 값이 obj2[b]의 값으로 바뀌어 버려서 주의 사항 요건1 충족 못함
- for문과 if문 활용
function extend(obj1, obj2) {
for(let prop2 in obj2){
if(obj1[prop2] === undefined){
obj1[prop2] = obj2[prop2]
}
}
}✅ for문으로 obj2의 property들 돌리기
✅ obj1에 없는 프로퍼티가 들어가야 하므로 for문안에 if문 작성
Reference
function extend(obj1, obj2) {
for (let key in obj2) {
if (!(key in obj1)) {
obj1[key] = obj2[key];
}
}
}✅ ❗️for문에서 만든 변수를 if문에서 사용시, "~ in ~"으로 사용 가능❗️
20_countAllCharacters
문제
- 문자열을 입력받아 문자열을 구성하는 각 문자(letter)를 키로 갖는 객체를 리턴
- 각 키의 값은 해당 문자가 문자열에서 등장하는 횟수를 의미하는
number타입의 값이어야 함
입출력 예시
let output = countAllCharacters('banana');
console.log(output); // --> {b: 1, a: 3, n: 2}주의 사항
- 빈 문자열을 입력받은 경우, 빈 객체를 리턴
나의 코드
function countAllCharacters(str) {
const lettersArray = str.split("");
const letters = Array.from(new Set(lettersArray))
let result = {};
let count = 0;
for(let element of letters){
for(let i=0;i<lettersArray.length;i++){
if(element === lettersArray[i]){
count++;
}
}
result[element] = count;
count = 0;
}
return result;
}✅ string.split() 메소드를 이용해 단어 하나씩 잘라 배열로 변수 lettersArray에 할당
✅ Array.from(new Set()) 메소드를 이용하여 변수 lettersArray에 할당된 배열의 중복값 삭제 후 새로운 변수 letters에 할당
✅ for문에 문자열 중복값이 제거된 letters를 이용
✅ for문 안에 새로운 for문을 이용해(이중for문), letters 안의 element를 기준삼아 lettersArray에 element와 일치하는 알파벳을 카운트
✅ 카운트 된 값을 result 객체에 할당
✅ 다음 element로 for문이 돌기전에 count 값 0으로 초기화
Reference
function countAllCharacters(str) {
let obj = {};
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
if (obj[str[i]] === undefined) {
obj[str[i]] = 0;
}
obj[str[i]]++;
}
return obj;
}✅ 헐! 이렇게나 간단하게 할 수 있는 거였다니ㅠㅠ
21_mostFrequentCharacter
문제
문자열을 입력받아 가장 많이 반복되는 문자(letter)를 리턴
주의 사항
- 띄어쓰기 제외
- 가장 많이 반복되는 문자가 다수일 경우, 가장 먼저 해당 횟수에 도달한 문자를 리턴
- 빈 문자열을 입력받은 경우, 빈 문자열을 리턴
입출력 예시
let output = mostFrequentCharacter('apples not oranges');
console.log(output); // --> 'p'
output = mostFrequentCharacter('abba');
console.log(output); // --> 'b'나의 코드
function mostFrequentCharacter(str) {
const word = str.replace(/ /g, "");
let obj = {};
let max = 0;
let maxChar = "";
for(let i=0;i<word.length;i++){
if(obj[word[i]]){
obj[word[i]]++;
} else {
obj[word[i]] = 1;
}
if(obj[word[i]] > max){
max = obj[word[i]];
maxChar = word[i];
}
}
return maxChar;
}✅ String.replace() 메소드를 사용하여 str 공백제거 한 값을 변수 word에 할당
✅ if/else() 구문을 이용하여 word의 개수 카운트
✅ 카운트 된 값이 max의 값보다 크다면 그 값을 max와 maxChar에 할당
Reference
function mostFrequentCharacter(str) {
let obj = { mostCount: 0, mostFrequent: '' };
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
if (str[i] === ' ') {
continue;
}
if (obj[str[i]] === undefined) {
obj[str[i]] = 0;
}
obj[str[i]] += 1;
if (obj[str[i]] > obj['mostCount']) {
obj['mostCount'] = obj[str[i]];
obj['mostFrequent'] = str[i];
}
}
return obj['mostFrequent'];
}✅ for문 안에 continue 활용
-> if문의 조건식이 참일 경우에는 for문 적용을 건너뜀