최댓값 알고리즘
- 최댓값 알고리즘을 이용해서 숫자로 이루어진 리스트에서 최댓값과 최댓값의 개수를 찾는 모듈을 만들어보자.
코드1
class MaxAlgorithm:
def __init__(self, ns):
self.nums = ns
self.maxNum = 0
self.maxNumCnt = 0
def setMaxNum(self):
self.maxNum = 0
for n in self.nums:
if self.maxNum < n:
self.maxNum = n
return self.maxNum
def getMaxNum(self):
self.setMaxNum()
return self.maxNum
def setMaxNumCnt(self):
self.setMaxNum()
for n in self.nums:
if self.maxNum == n:
self.maxNumCnt += 1
def getMaxNumCnt(self):
self.setMaxNumCnt()
return self.maxNumCnt코드2
import random
import maxMod
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = []
for n in range(20):
nums.append(random.randint(1,50))
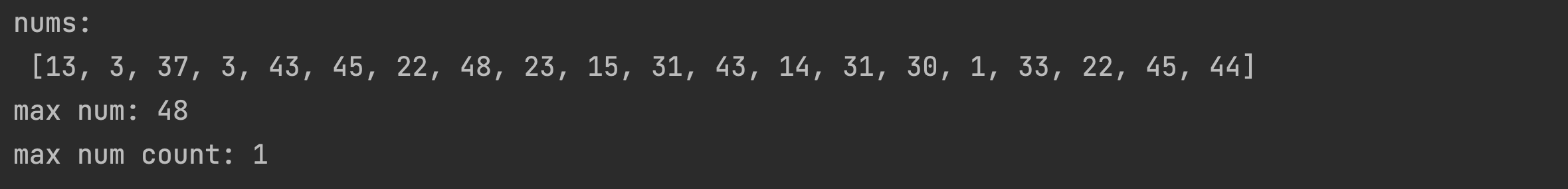
print(f'nums: \n {nums}')
ma = maxMod.MaxAlgorithm(nums)
print(f'max num: {ma.getMaxNum()}')
print(f'max num count: {ma.getMaxNumCnt()}')출력
최솟값 알고리즘
- 최솟값 알고리즘을 이용해서 숫자로 이루어진 리스트에서 최솟값과 최솟값의 개수를 찾는 모듈을 만들어보자.
코드1
class MinAlgorithm:
def __init__(self, ns):
self.nums = ns
self.minNum = 0
self.minNumCnt = 0
def setMinNum(self):
self.minNum = 51
for n in self.nums:
if self.minNum > n:
self.minNum = n
def getMinNum(self):
self.setMinNum()
return self.minNum
def setMinNumCnt(self):
self.setMinNum()
for n in self.nums:
if self.minNum == n:
self.minNumCnt += 1
def getMinNumCnt(self):
self.setMinNumCnt()
return self.minNumCnt코드2
import random
import minMod
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = []
for n in range(20):
nums.append(random.randint(1,50))
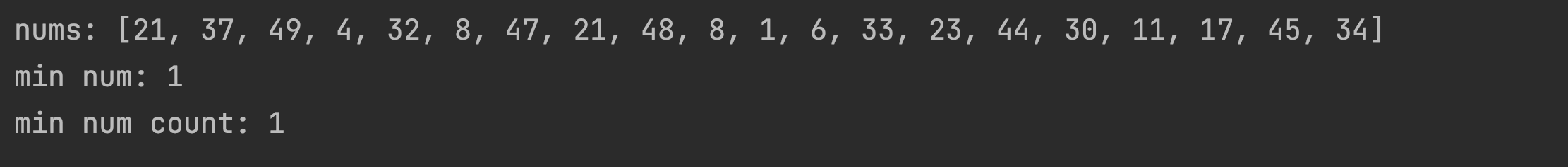
print(f'nums: {nums}')
ma = minMod.MinAlgorithm(nums)
print(f'min num: {ma.getMinNum()}')
print(f'min num count: {ma.getMinNumCnt()}')출력
최빈값 알고리즘
- 다음은 어떤 회사의 전직원 나이를 나타내는 리스트이다. 최빈값 알고리즘을 이용해서 나이 분포를 간단한 그래프로 출력하는 모듈을 만들어보자.
코드1
class MaxAlgorithm:
def __init__(self, ns):
self.nums = ns
self.maxNum = 0
self.maxNumIdx = 0
def setMaxIdxAndNum(self):
self.maxNum = 0
self.maxNumIdx = 0
for i, n in enumerate(self.nums):
if self.maxNum < n:
self.maxNum = n
self.maxNumIdx = i
def getMaxNum(self):
return self.maxNum
def getMaxIdx(self):
return self.maxNumIdx코드2
import maxMod
class ModeAlgorithm:
def __init__(self, ns, mn):
self.nums = ns
self.maxNum = mn
self.indexes = []
def setIndexList(self):
self.indexes = [0 for i in range(self.maxNum + 1)]
for n in self.nums:
self.indexes[n] = self.indexes[n] + 1
def getIndexList(self):
if sum(self.indexes) == 0:
return None
else:
return self.indexes
def printAges(self):
n = 1
while True:
maxAlo = maxMod.MaxAlgorithm(self.indexes)
maxAlo.setMaxIdxAndNum()
maxNum = maxAlo.getMaxNum()
maxNumIdx = maxAlo.getMaxIdx()
if maxNum == 0:
break
print(f'{n:0>3} {maxNumIdx}세 빈도수: {maxNum} \t',end='')
print('*' * maxNum)
self.indexes[maxNumIdx] = 0
n += 1코드3
import modeMod
import maxMod
ages = [25, 27, 27, 24, 31, 34, 33, 31, 29, 25,
45, 37, 38, 46, 47, 22, 24, 29, 33, 35,
27, 34, 37, 40, 42, 29, 27, 25, 26, 27,
31, 31, 32, 38, 25, 27, 28, 40, 41, 34]
print(f'employee cnt: {len(ages)}명')
maxAlo = maxMod.MaxAlgorithm(ages)
maxAlo.setMaxIdxAndNum()
maxAge = maxAlo.getMaxNum()
print(f'maxAge: {maxAge}세')
modAlo = modeMod.ModeAlgorithm(ages,maxAge)
modAlo.setIndexList()
print(f'IndexList: {modAlo.getIndexList()}')
modAlo.printAges()출력

근삿값 알고리즘
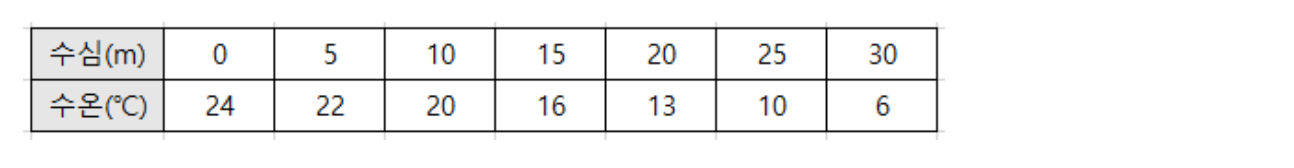
- 다음 표는 수심에 따른 수온을 나타내고 있다. 근사값 알고리즘을 이용해서 수심을 입력하면 수온을 출력하는 모듈을 만들어보자.
코드1
class NearAlgorithm:
def __init__(self, d):
self.temps = {0:24, 5:22, 10:20, 15:16, 20:13, 25:10, 30:6 }
self.depth = d
self.nearNum = 0
self.minNum = 24
def getNearNumbers(self):
for n in self.temps.keys():
absNum = abs(n - self.depth)
if absNum < self.minNum:
self.minNum = absNum
self.nearNum = n
return self.temps[self.nearNum]코드2
import nearMod
depth = int(float(input('input depth: ')))
print(f'depth: {depth}m')
na = nearMod.NearAlgorithm(depth)
temp = na.getNearNumbers()
print(f'water temperature: {temp}도')출력

재귀 알고리즘
- 다음은 ‘A상사’의 2021년 월별 매출을 나타내는 표이다. 재귀 알고리즘을 이용해서 1월부터 12월까지 전월대비 매출 증감액을 나타내는 프로그램을 만들어보자.

코드1
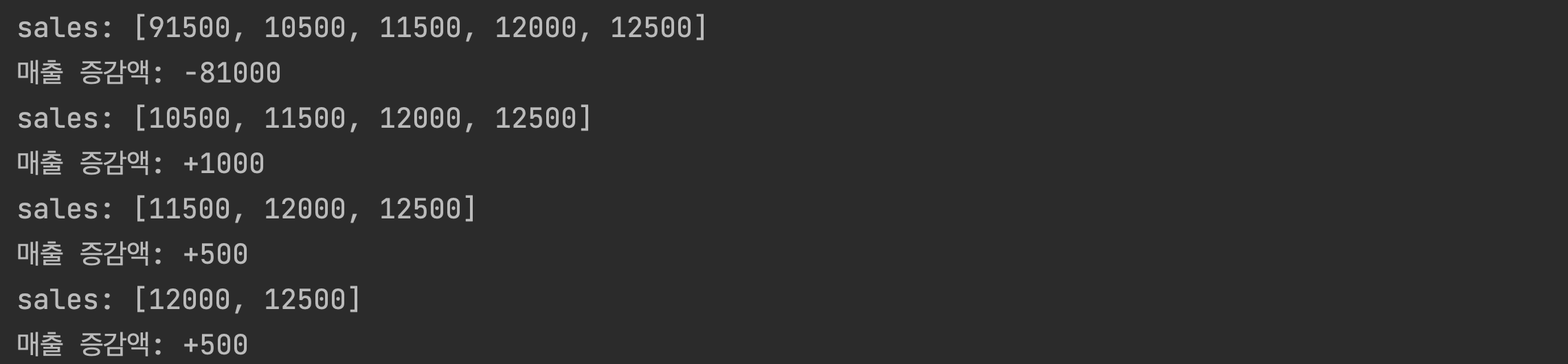
sales = [12000, 13000, 12500, 11000, 10500, 98000, 91000, 91500, 10500, 11500, 12000, 12500]
def salesUpAndDown(ss):
if len(ss) == 1:
return ss
print(f'sales: {ss}')
currentSales = ss.pop(0)
nextSales = ss[0]
increase = nextSales - currentSales
if increase > 0:
increase = '+' + str(increase)
print(f'매출 증감액: {increase}')
return salesUpAndDown(ss)
if __name__ == '__main__':
salesUpAndDown(sales)출력
평균 알고리즘
- 다음은 어떤 체조선수의 점수이다.평균을 구하고 순위를 정하는 알고리즘을 만들어보자.
코드1
class Top5Plyers:
def __init__(self, cs, ns):
self.currentScore = cs
self.newScore = ns
def setAlignScore(self):
nearInx = 0
nearScore = 0
minNum = 10.0
for i, s in enumerate(self.currentScore):
absNum = abs(self.newScore - s)
if absNum < minNum:
minNum = absNum
nearInx = i
nearScore = s
if self.newScore >= self.currentScore[nearInx]:
for i in range(len(self.currentScore) - 1,nearInx,-1):
self.currentScore[i] = self.currentScore[i-1]
self.currentScore[nearInx] = self.newScore
else:
for i in range(len(self.currentScore) - 1,nearInx + 1,-1):
self.currentScore[i] = self.currentScore[i-1]
self.currentScore[nearInx] = self.newScore
def getFinalTop5Scores(self):
return self.currentScore
코드2
import near
scores = [8.9, 7.6, 8.2, 9.1, 8.8, 8.1, 7.9, 9.4, 7.2, 8.7]
top5PlayerScores = [9.12, 8.95, 8.12, 7.90, 7.88]
print(f'top5PlayerScores: {top5PlayerScores}')
total = 0
average = 0
for n in scores:
total += n
average = total / len(scores)
print(f'total: {total}')
print(f'average: {average}')
tp = near.Top5Plyers(top5PlayerScores,average)
tp.setAlignScore()
top5PlayerScores = tp.getFinalTop5Scores()
print(f'top5PlayerScores: {top5PlayerScores}')출력


