[1]
- ( 2, 3, 4 ) 를 keepdims를 안했을경우 ( 3, 4 )
keepdims를 했을 경우 ( 1, 3, 4 )가 된다

a = np.arange(2*3*4).reshape((2,3,4))
sum_ = a.sum(axis = 0)
print("ndarray: {}\n{}".format(a.shape, a))
print("ndarray.sum(axis = 0): {}\n{}".format(sum_.shape, sum_))- (2,3,4) -> (2,4) or (2,1,4)
(2,4)일때는 브로드캐스팅 불가
(2,1,4)일때는 브로드캐스팅 가능
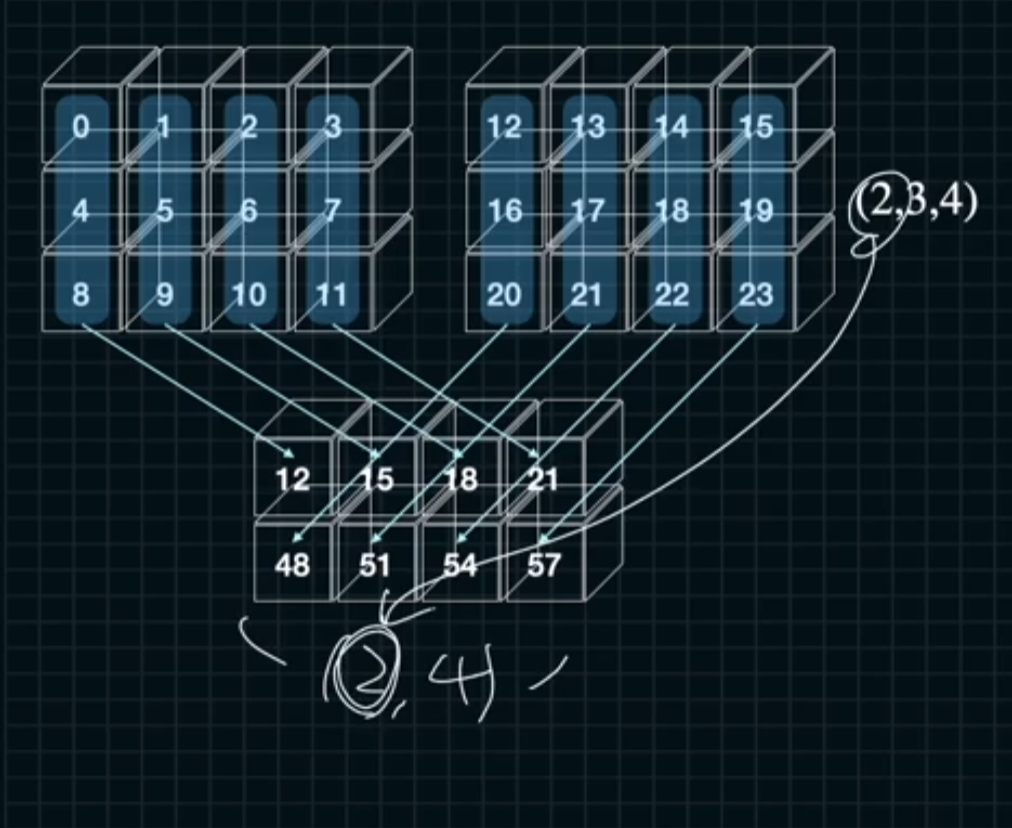
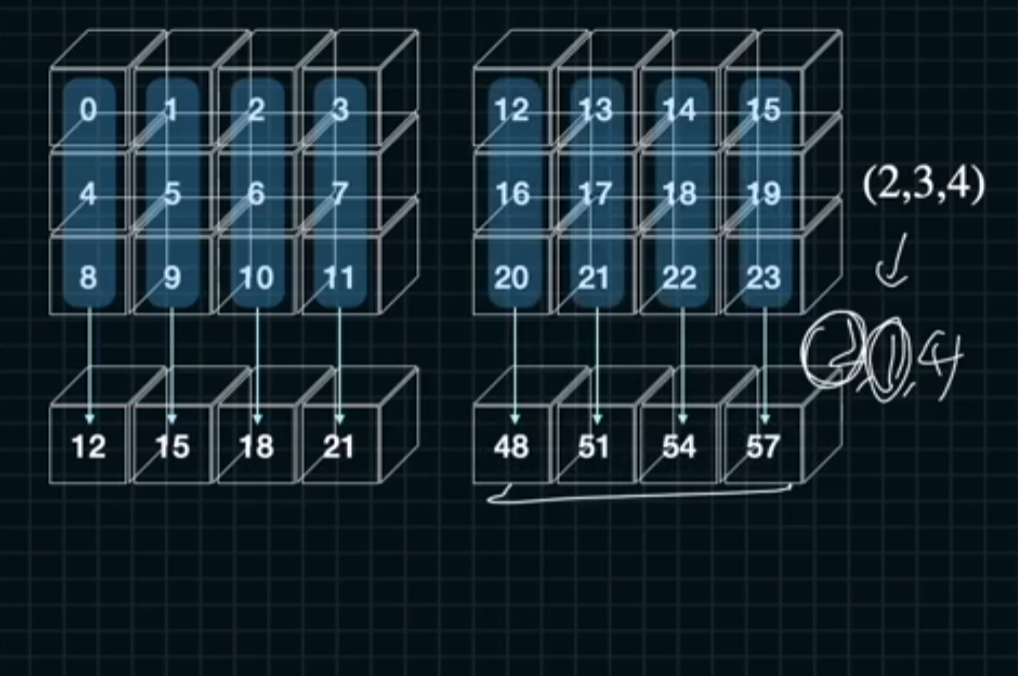
a = np.arange(2*3*4).reshape((2,3,4))
sum_ = a.sum(axis = 1)
sum_k = a.sum(axis = 1, keepdims = True)
print("ndarray: {}\n{}".format(a.shape, a))
print("axis = 1: {}\n{}".format(sum_.shape, sum_))
print("axis = 1, keepdims = True: {}\n{}".format(sum_k.shape, sum_k))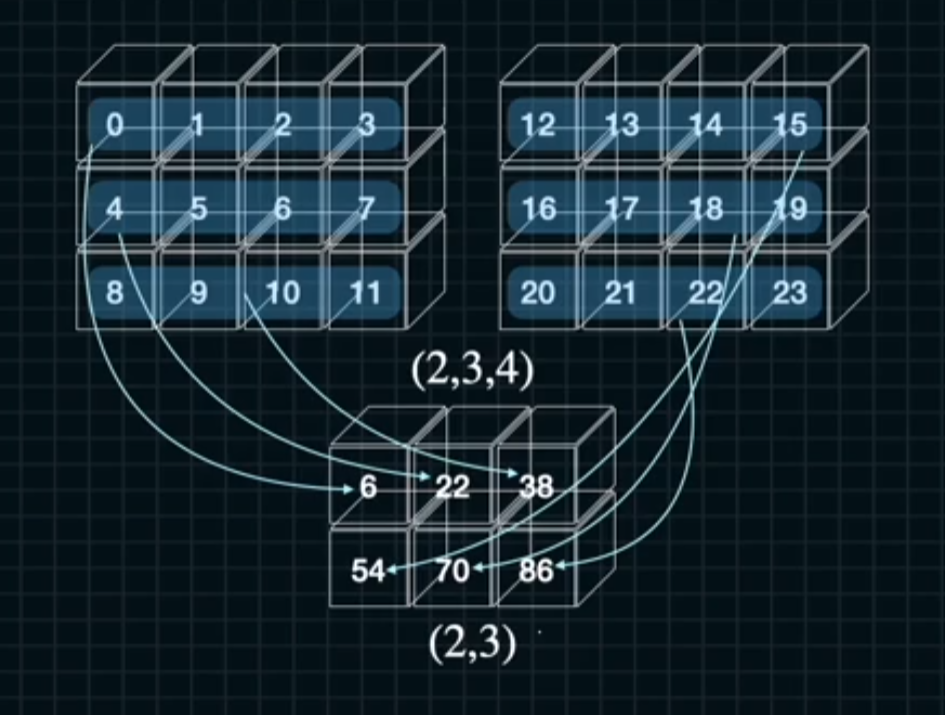
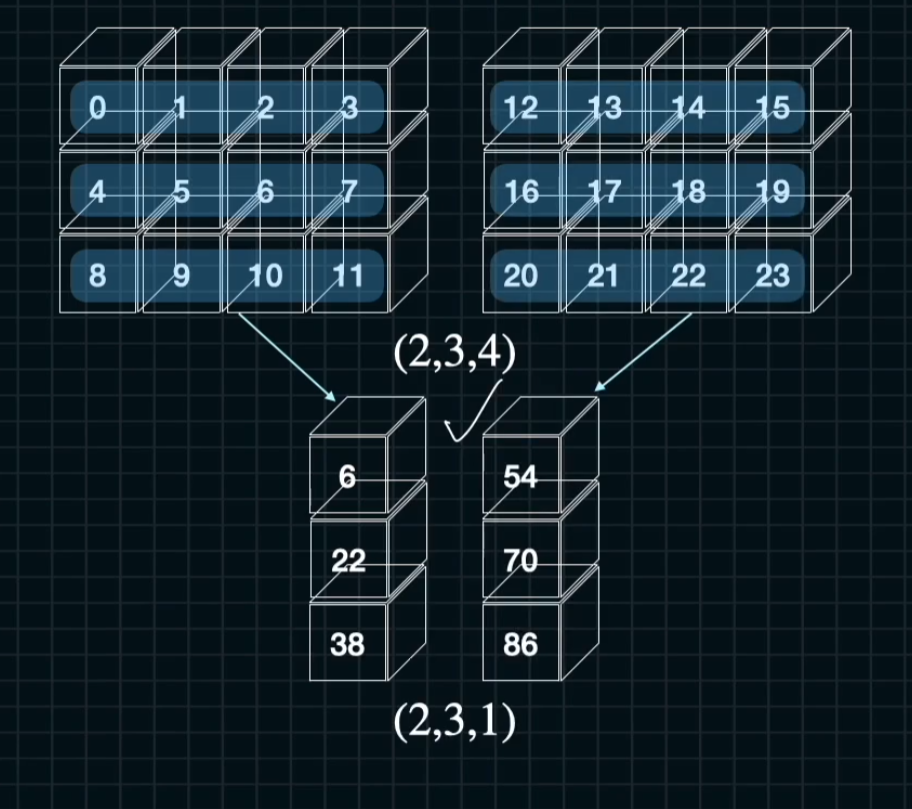
a = np.arange(2*3*4).reshape((2,3,4))
sum_ = a.sum(axis =2)
sum_k = a.sum(axis = 2, keepdims = True)
print("ndarray: {}\n{}".format(a.shape, a))
print("axis = 2: {}\n{}".format(sum_.shape, sum_))
print("axis = 2, keepdims = True: {}\n{}".format(sum_k.shape, sum_k))[2] 전체코드
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(2*3*4).reshape((2,3,4))
sum_ = a.sum(axis = 0)
print("ndarray: {}\n{}".format(a.shape, a))
print("ndarray.sum(axis = 0): {}\n{}".format(sum_.shape, sum_))
#
a = np.arange(2*3*4).reshape((2,3,4))
sum_ = a.sum(axis = 1)
sum_k = a.sum(axis = 1, keepdims = True)
print("ndarray: {}\n{}".format(a.shape, a))
print("axis = 1: {}\n{}".format(sum_.shape, sum_))
print("axis = 1, keepdims = True: {}\n{}".format(sum_k.shape, sum_k))
#
a = np.arange(2*3*4).reshape((2,3,4))
sum_ = a.sum(axis =2)
sum_k = a.sum(axis = 2, keepdims = True)
print("ndarray: {}\n{}".format(a.shape, a))
print("axis = 2: {}\n{}".format(sum_.shape, sum_))
print("axis = 2, keepdims = True: {}\n{}".format(sum_k.shape, sum_k))
#
n_test_time, n_student, n_class = 4, 3, 4
m_score, M_score = 0, 100
scores = np.random.randint(low = m_score, high = M_score, size = (n_test_time, n_student, n_class))
print("scores: \n", scores)
score_mean = np.mean(scores, axis = 0)
print("score mean: ", score_mean.shape, '\n', score_mean)
score_mean = np.mean(scores, axis = 1)
print("score mean: ", score_mean.shape, '\n', score_mean)
C, H, W = 3, 100, 200
# (C, H, W) case
images = np.random.randint(0, 256, size = (C, H, W))
print("Shape of original image:", images.shape)
gray_image = np.mean(images, axis = 0)
print("Shape of gray-scaled image:", gray_image.shape, '\n')
# (H, W, C) case
images = np.random.randint(0, 256, size = (H, W, C))
print("Shape of original image:", images.shape)
gray_image = np.mean(images, axis = -1)
print("Shape of gray-scaled image:", gray_image.shape, '\n')