Problem
You are given the head of a singly linked-list. The list can be represented as:
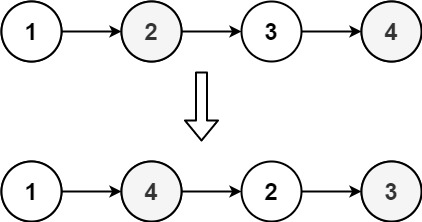
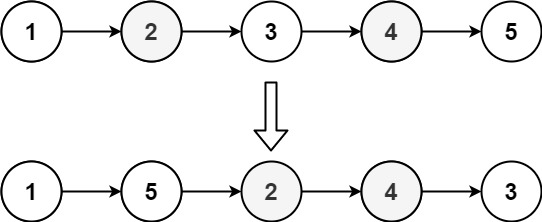
L0 → L1 → … → Ln - 1 → LnReorder the list to be on the following form:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln - 1 → L2 → Ln - 2 → …You may not modify the values in the list's nodes. Only nodes themselves may be changed.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4] Output: [1,4,2,3]Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: [1,5,2,4,3]Constraints:
・ The number of nodes in the list is in the range [1, 5 * 10⁴]. ・ 1 <= Node.val <= 1000
Idea
Queue와 Stack을 이용해서 풀면 쉽다.
처음에 리스트를 탐색하면서 크기를 구하고, 리스트의 처음 절반은 queue에, 나머지 절반은 stack에 쌓는다.
이후 queue에서 한 번, stack에서 한 번 번갈아 가면서 node를 꺼내고 그 때마다 나온 노드의 포인터를 바꿔주기만 하면 된다.
하지만 이렇게 풀면 결과가 2ms가 나와 상위 50% 밖에 되지 않는다.
다른 좋은 풀이 방법을 검색하니 자료구조 없이 포인터만 조정해서 풀 수가 있었다.
처음에 한 칸씩 넘어가는 포인터와 두 칸씩 넘어가는 포인터를 설정하면 middle 포인터를 구할 수 있다.
middle 포인터를 기점으로 리스트의 후반부를 역순으로 바꾼다. 역순으로 바꾼 다음 head와 middle 포인터를 번갈아가면서 연결하면 원하는 형태의 리스트가 만들어진다.
Solution
아래는 직관적이지만 느린 풀이 방법 (자료 구조 이용)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
Queue<ListNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode node = head;
int size = 0;
while (node != null) {
size++;
node = node.next;
}
int index = 0;
int border = (size + 1) / 2;
node = head;
while (node != null) {
if (index < border) {
queue.add(node);
} else {
stack.add(node);
}
index++;
node = node.next;
}
boolean flip = true;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
node = dummy;
while (size > 0) {
if (flip) {
node.next = queue.poll();
} else {
node.next = stack.pop();
}
node = node.next;
flip ^= true;
size--;
}
node.next = null;
}
}아래는 포인터만 이용해서 푸는 효율적인 방법이다.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null) return;
//Find the middle of the list
ListNode p1=head;
ListNode p2=head;
while(p2.next!=null&&p2.next.next!=null){
p1=p1.next;
p2=p2.next.next;
}
//Reverse the half after middle 1->2->3->4->5->6 to 1->2->3->6->5->4
ListNode preMiddle=p1;
ListNode preCurrent=p1.next;
while(preCurrent.next!=null){
ListNode current=preCurrent.next;
preCurrent.next=current.next;
current.next=preMiddle.next;
preMiddle.next=current;
}
//Start reorder one by one 1->2->3->6->5->4 to 1->6->2->5->3->4
p1=head;
p2=preMiddle.next;
while(p1!=preMiddle){
preMiddle.next=p2.next;
p2.next=p1.next;
p1.next=p2;
p1=p2.next;
p2=preMiddle.next;
}
}
}