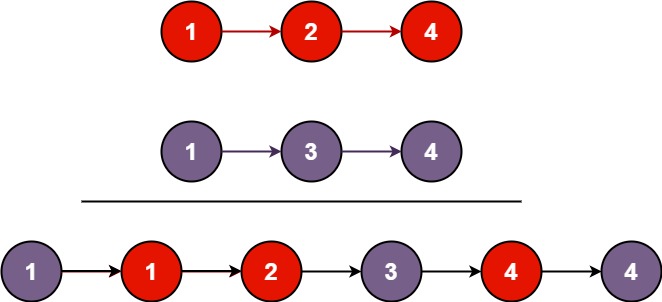
Problem
You are given the heads of two sorted linked lists list1 and list2.
Merge the two lists in a one sorted list. The list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
Return the head of the merged linked list.
Example 1:
Input: list1 = [1,2,4], list2 = [1,3,4] Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4]Example 2:
Input: list1 = [], list2 = [] Output: []Example 3:
Input: list1 = [], list2 = [0] Output: [0]Constraints:
・ The number of nodes in both lists is in the range [0, 50]. ・ -100 <= Node.val <= 100 ・ Both list1 and list2 are sorted in non-decreasing order.
Idea
자료구조 중 List를 다루는 간단한 문제다. 정렬되어 있는 두 List를 하나의 정렬된 List로 만들라는 문제다.
각 List를 탐색하면서 새로운 노드를 만들어 풀면 간단하겠지만, 쓸 데 없이 메모리를 낭비할 필요 없이 포인터만 잘 조정해주는 편이 낫다.
우선 두 List 중 하나가 null이면 다른 리스트를 그대로 리턴한다.
두 List가 모두 빈 List가 아니라면 더 작은 값을 가진 List의 첫 노드를 head 노드로 정한다.
이후 두 리스트를 탐색하면서 더 작은 값을 가진 노드를 현재 노드 (cur)의 다음 노드로 지정하고, 현재 노드를 해당 노드로 바꾸어 준다. 지정이 된 List의 노드는 List의 다음 노드로 바꾼다.
두 리스트 중 하나가 끝에 다다랐다면 남은 리스트를 끝에 붙여주면 된다.
Solution
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null) {
return list2;
}
if (list2 == null) {
return list1;
}
ListNode head = null;
if (list1.val <= list2.val) {
head = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
head = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val <= list2.val) {
cur.next = list1;
cur = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
cur.next = list2;
cur = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
if (list1 != null) {
cur.next = list1;
}
if (list2 != null) {
cur.next = list2;
}
return head;
}
}