Problem
Given the head of a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places.
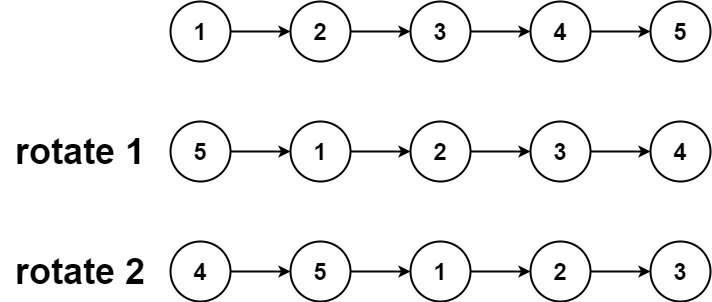
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output: [4,5,1,2,3]Example 2:
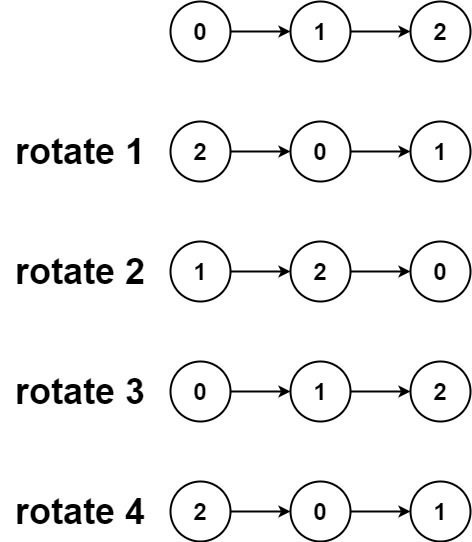
Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4 Output: [2,0,1]Constraints:
・ The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 500]. ・ -100 <= Node.val <= 100 ・ 0 <= k <= 2 * 10⁹
Idea
주어진 리스트를 k번만큼 회전시킨 결과를 구하는 문제다.
우선 head가 null이면 곧바로 head를 반환하면 된다.
이후 리스트의 길이 (len)를 측정하고, len - (k % len)를 기준으로 새로운 head와 end를 정한다. k가 리스트의 길이보다 길 수 있으므로 나머지 연산은 필수다.
move = len - (k % len)rotate시킨 뒤, 새로운 end (newEnd)는 새로운 head (newHead)의 바로 뒤 노드이다. 따라서 newEnd는 head에서 (move - 1)만큼, newHead는 head에서 move만큼 떨어져 있다.
두 노드를 찾으면 새로운 end의 next 포인터를 null로, 기존 end의 next 포인터를 head로 가리키게 한다.
만약 k == len이라면 새로운 head가 null이 될 수 있으므로 head를 반환하고, 아니라면 새로운 head를 반환한다.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Solution
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode end = head;
int len = 1;
while (end.next != null) {
end = end.next;
len++;
}
int move = len - (k % len);
ListNode newHead = head;
ListNode newEnd = head;
for (int i=0; i < move - 1; i++) {
newEnd = newEnd.next;
}
for (int i=0; i < move; i++) {
newHead = newHead.next;
}
if (newHead != null) {
newEnd.next = null;
end.next = head;
}
return newHead == null ? head : newHead;
}
}