Problem
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum width of the given tree.
The maximum width of a tree is the maximum width among all levels.
The width of one level is defined as the length between the end-nodes (the leftmost and rightmost non-null nodes), where the null nodes between the end-nodes are also counted into the length calculation.
It is guaranteed that the answer will in the range of 32-bit signed integer.
Example 1:
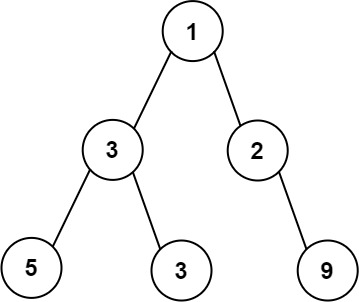
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9] Output: 4 Explanation: The maximum width existing in the third level with the length 4 (5,3,null,9).Example 2:
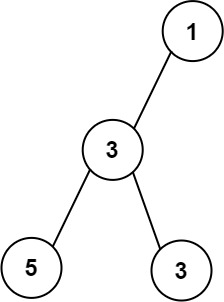
Input: root = [1,3,null,5,3] Output: 2 Explanation: The maximum width existing in the third level with the length 2 (5,3).Example 3:
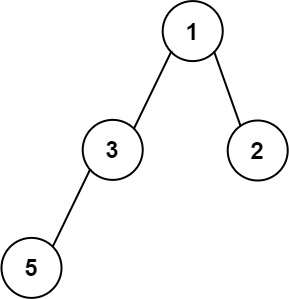
Input: root = [1,3,2,5] Output: 2 Explanation: The maximum width existing in the second level with the length 2 (3,2).Constraints:
・ The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 3000]. ・ -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Idea
주어진 Binary Tree의 가장 큰 너비를 구하는 문제다. Tree 문제니 탐색을 어떻게 하느냐에 따라 두 가지 방법으로 풀 수 있다.
나에게 익숙한 DFS 방식으로 풀었더니 long→int 변환도 해야 하고 시간도 BFS보다 더 걸리길래 BFS로 다시 풀었다.
DFS로 푸는 법은 각 높이의 최소값과 최대값을 저장하는 배열을 먼저 만들고 노드를 탐색할 때마다 해당 level의 최소값과 최대값을 바꾸는 것이다. 모든 노드를 탐색하고 난 후 저장된 값으로 너비를 계산하고 가장 큰 값을 리턴한다.
BFS로 풀 때는 deque를 사용하면 쉽다. 처음에 주어진 root 노드를 deque에 넣고 탐색을 시작한다. 왼쪽 자식 노드가 있으면 해당 노드의 값을 현재 노드의 값의 두 배로, 오른쪽 자식 노드가 있으면 해당 노드의 값을 현재 노드의 값의 두 배 + 1로 설정한다. 자식 노드들은 deque에 넣는다. deque에서 각 level을 탐색할 때 마지막 노드의 값을 right로 설정하고 너비를 right - left + 1로 계산하면 된다. 이렇게 계산한 너비 중 최대값을 리턴한다.
Solution
BFS
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new ArrayDeque<TreeNode>();
root.val = 0;
deque.add(root);
return bfs(deque);
}
private int bfs(Deque<TreeNode> deque) {
int res = 0;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
int s = deque.size();
int left = deque.peek().val;
int right = left;
for (int i=0; i < s; i++) {
TreeNode node = deque.removeFirst();
if (node.left != null) {
node.left.val = node.val * 2;
deque.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
node.right.val = node.val * 2 + 1;
deque.add(node.right);
}
if (i == s - 1) {
right = node.val;
}
}
res = Math.max(res, right - left + 1);
}
return res;
}
}DFS
class Solution {
long[][] width;
int maxLevel;
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
width = new long[3000][2];
maxLevel = 0;
for (int i=0; i < 3000; i++) {
width[i][0] = Long.MAX_VALUE;
width[i][1] = Long.MIN_VALUE;
}
traverseTree(root, 0, 0);
long res = 0;
for (int i=0; i <= maxLevel; i++) {
res = Math.max(res, width[i][1] - width[i][0] + 1);
}
return Long.valueOf(res).intValue();
}
private void traverseTree(TreeNode node, int level, long num) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
maxLevel = Math.max(maxLevel, level);
if (num < width[level][0]) {
width[level][0] = num;
}
if (num > width[level][1]) {
width[level][1] = num;
}
traverseTree(node.left, level + 1, num * 2);
traverseTree(node.right, level + 1, num * 2 + 1);
}
}