Problem
You are given a string s of lowercase English letters and an integer array shifts of the same length.
Call the shift() of a letter, the next letter in the alphabet, (wrapping around so that 'z' becomes 'a').
For example, shift('a') = 'b', shift('t') = 'u', and shift('z') = 'a'.
Now for each shifts[i] = x, we want to shift the first i + 1 letters of s, x times.Return the final string after all such shifts to s are applied.
Example 1:
Input: s = "abc", shifts = [3,5,9] Output: "rpl" Explanation: We start with "abc". After shifting the first 1 letters of s by 3, we have "dbc". After shifting the first 2 letters of s by 5, we have "igc". After shifting the first 3 letters of s by 9, we have "rpl", the answer.Example 2:
Input: s = "aaa", shifts = [1,2,3] Output: "gfd"Constraints:
・ 1 <= s.length <= 10⁵ ・ s consists of lowercase English letters. ・ shifts.length == s.length ・ 0 <= shifts[i] <= 10⁹
Idea
shifts에 주어진 값만큼 주어진 string의 각 알파벳 문자를 shift시키면 되는 문제다. 대신 shifts의 index보다 작은 index의 문자 전부를 shift 시켜야 한다. 따라서 shifts를 뒤에서부터 runningSum한 array를 만든 뒤 runningSum한 값만큼 input의 각 문자를 shift시키면 된다.
알고리즘은 다음과 같다.
- shifts array의 runningSum을 역순으로 구한다.
- input으로 주어진 string s의 각 문자에 runningSum값을 더해 shift한다.
- shift된 string을 리턴한다.
Solution
class Solution { public String shiftingLetters(String s, int[] shifts) { // 1. get running sum long[] runningSum = new long[shifts.length]; long sum = 0; for (int i=shifts.length-1; i >= 0; i--) { sum += shifts[i]; runningSum[i] = sum; } // 2. transform long to char StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (int i=0; i < s.length(); i++) { sb.append((char)(((long) (s.charAt(i) - 'a') + runningSum[i]) % 26 + 'a')); } return sb.toString(); } }
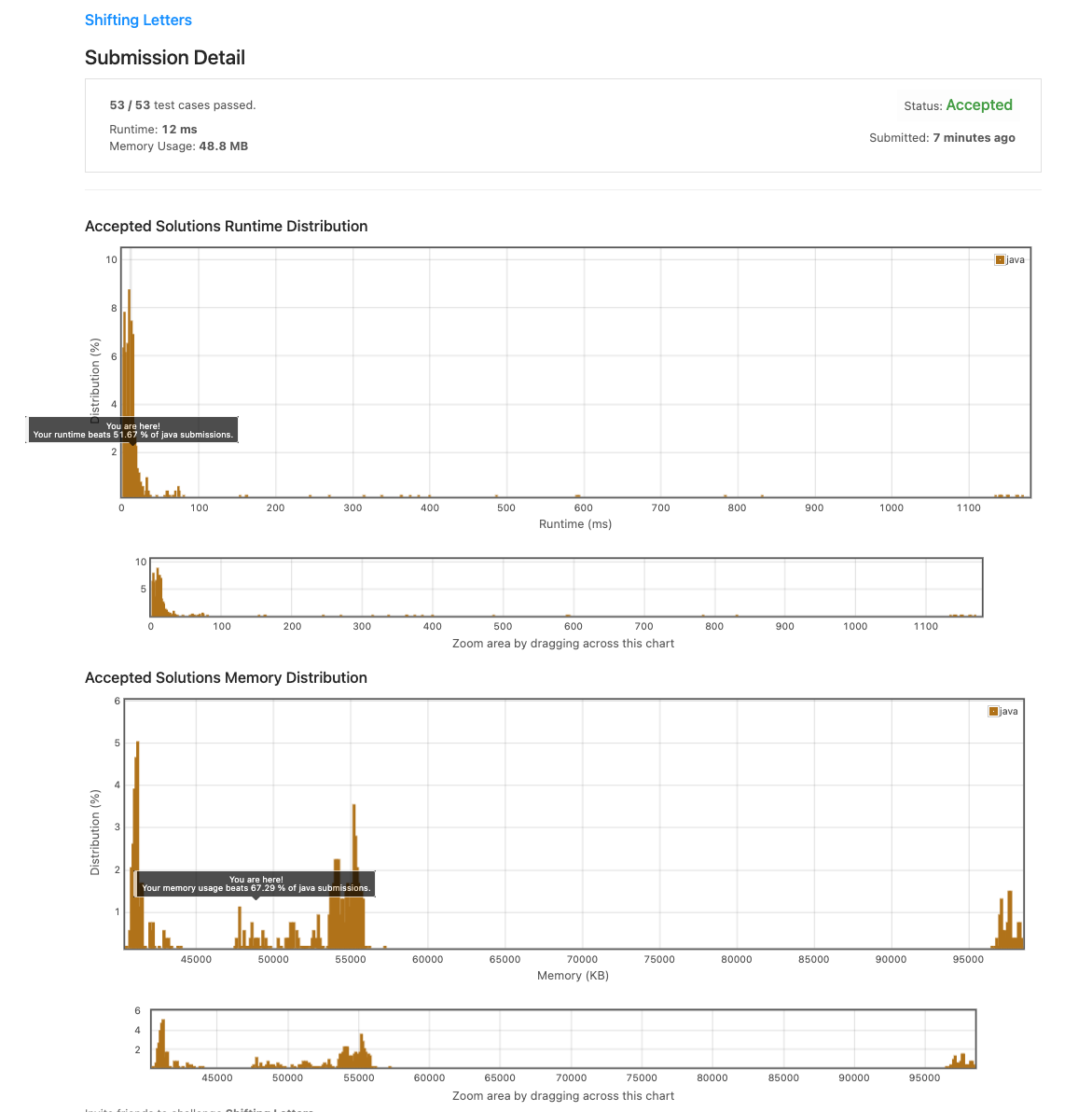
좋지도 나쁘지도 않은 결과가 나왔다.