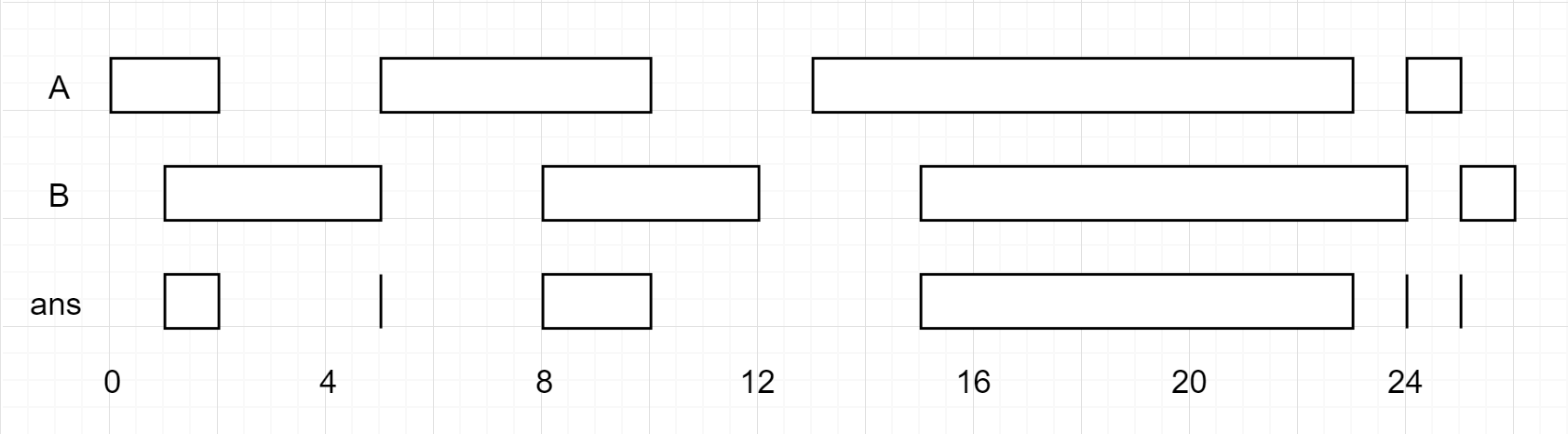
Problem
You are given two lists of closed intervals, firstList and secondList, where firstList[i] = [starti, endi] and secondList[j] = [startj, endj]. Each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order.
Return the intersection of these two interval lists.
A closed interval [a, b] (with a <= b) denotes the set of real numbers x with a <= x <= b.
The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that are either empty or represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].
Example 1:
Input: firstList = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], secondList = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]] Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]Example 2:
Input: firstList = [[1,3],[5,9]], secondList = [] Output: []Example 3:
Input: firstList = [], secondList = [[4,8],[10,12]] Output: []Example 4:
Input: firstList = [[1,7]], secondList = [[3,10]] Output: [[3,7]]Constraints:
・ 0 <= firstList.length, secondList.length <= 1000 ・ firstList.length + secondList.length >= 1 ・ 0 <= startᵢ < endᵢ <= 10⁹ ・ endᵢ < startᵢ₊₁ ・ 0 <= startʲ < endʲ <= 10⁹ ・ endʲ < startʲ₊₁
Idea
iteration만 잘 하면 쉽게 풀 수 있는 문제다.
주어진 array A와 B를 돌면서 겹치는 영역을 확인하고 list에 더하기만 하면 된다. A와 B의 index는 각각 i와 j로 관리되며, 두 index 중 하나라도 범위를 벗어나면 탐색은 중단된다.
겹치는 영역을 구할 때는 A의 현재 array의 첫 번째 값과 B의 현재 array의 첫 번째 값의 최대값을 low로, A의 현재 array의 두 번째 값과 B의 현재 array의 두 번째 값의 최소값을 high로 정한다. low가 high보다 작거나 같으면 겹치는 영역이 있다는 뜻이므로 ans list에 low와 high를 array로 만들어 추가해준다.
탐색이 끝나면 list를 array로 변경해 리턴한다.
내가 짠 코드는 너무 지저분해 solution에 있는 코드 그대로 옮겨왔다. 🥲
Solution
class Solution {
public int[][] intervalIntersection(int[][] A, int[][] B) {
List<int[]> ans = new ArrayList();
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < A.length && j < B.length) {
// Let's check if A[i] intersects B[j].
// lo - the startpoint of the intersection
// hi - the endpoint of the intersection
int lo = Math.max(A[i][0], B[j][0]);
int hi = Math.min(A[i][1], B[j][1]);
if (lo <= hi)
ans.add(new int[]{lo, hi});
// Remove the interval with the smallest endpoint
if (A[i][1] < B[j][1])
i++;
else
j++;
}
return ans.toArray(new int[ans.size()][]);
}
}