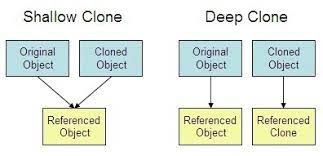
깊은 복사(Deep copy) vs 얕은 복사(Shallow copy)
우선 깊은 복사와 얕은 복사의 차이를 그림으로 보면 아래와 같다.
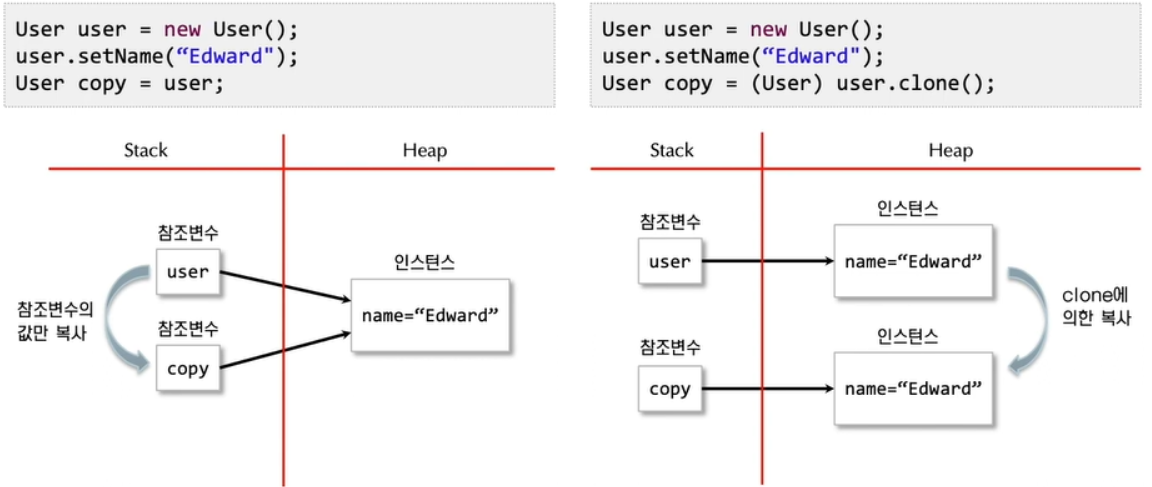
깊은 복사(오른쪽)는 2개의 참조 변수가 각각의 다른 Object를 가르키고 있고, 얕은 복사(왼쪽)는 2개의 참조 변수가 공통의 Object를 가르키고 있는 상황이다.
다시 말해, 깊은 복사는 새로운 객체에 Heap 데이터를 복사하는 것을 말하고, 얕은 복사는 Stack에 참조하고 있는 단순 주소값을 복제하는 것이다.
따라서 복제를 할 때는 아래 코드와 같이 주의할 점이 필요하다.
class Book implements Cloneable {
String name;
String author;
public Book(String name, String author) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
}
public void showInfo() {
System.out.println("Name : " + name + ", Author : " + author);
}
@Override // 공변 반환 타입을 이용한 오버라이딩
public Book clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Book) super.clone();
}
}public static void main(String[] args) {
Book[] library = new Book[3];
Book[] copyLibrary = new Book[3];
library[0] = new Book("Clean Code", "Robert");
library[1] = new Book("Sapience", "James");
library[2] = new Book("2011", "John");
System.arraycopy(library, 0, copyLibrary, 0, copyLibrary.length); //얕은 복사
copyLibrary[0].setAuthor("Lina"); //library[0]도 바뀜
System.out.println(" == Library == ");
for(Book book : library) {
book.showInfo();
}
System.out.println("\n == Copied Library == ");
for(Book book : copyLibrary) {
book.showInfo();
}
}
/* 실행 결과 */
== Library ==
Name : Clean Code, Author : Lina
Name : Sapience, Author : James
Name : 2011, Author : John
== Copied Library ==
Name : Clean Code, Author : Lina
Name : Sapience, Author : James
Name : 2011, Author : John위 코드를 그림으로 보현하자면 아래의 상황과 같다.

따라서, 깊은 깊은 복사를 이용하여 다시 바꾸면 아래와 같다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book[] library = new Book[3];
Book[] copyLibrary = new Book[3];
library[0] = new Book("Clean Code", "Robert");
library[1] = new Book("Sapience", "James");
library[2] = new Book("2011", "John");
for(int i=0; i<library.length; i++) //**바뀐 부분**
copyLibrary[i] = library[i].clone(); //깊은 복사
copyLibrary[0].setAuthor("Lina"); //library[0]도 바뀜
System.out.println(" == Library == ");
for(Book book : library) {
book.showInfo();
}
System.out.println("\n == Copied Library == ");
for(Book book : copyLibrary) {
book.showInfo();
}
}
/* 실행 결과 */
== Library ==
Name : Clean Code, Author : Robert
Name : Sapience, Author : James
Name : 2011, Author : John
== Copied Library ==
Name : Clean Code, Author : Lina
Name : Sapience, Author : James
Name : 2011, Author : Johnequals(), == 차이
/* equals(), == 차이 */
String str1 = new String("abc"); //String str = "abc";는 Heap메모리가 아닌 Literal Pool에 저장된다.
String str2 = new String("abc");
String str3 = str2;
System.out.println(str1==str2); //false
System.out.println(str2==str3); //true
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); //true
System.out.println(str2.equals(str3)); //true
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(str1)); //885284298
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(str2)); //1389133897
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(str3)); //1389133897== : 주소(해시 값)비교
equals() : 논리적인 비교로, override하여 재정의할 수 있음
/* equals() 재정의 */
public class Student implements Cloneable {
public int num;
public String name;
public Student(int num, String name) {
this.num = num;
this.name = name;
}
public String toString() {
return num + " , " + name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj instanceof Student) {
Student std = (Student)obj;
if( this.num == std.num) return true;
else return false;
}
return super.equals(obj);
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return (Student)super.clone();
}
}Student std1 = new Student(1, "Kim");
Student std2 = new Student(1, "Kim");
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(std1)); //2129789493
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(std2)); //668386784
System.out.println(std1 == std2); //false
System.out.println(std1.equals(std2)); //true
Student copyStd = (Student)std1.clone();
System.out.println(copyStd); //1 , Kim
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(copyStd)); //317574433std1, std2, copyStd 모두 다른 주소값을 가르키지만, 논리적 비교는 모두 같다.
