✨ 스프링 입문 - 코드로 배우는 스프링 부트, 웹 MVC, DB 접근 기술
🔅 목차
✅프로젝트 환경설정
#1 프로젝트 생성
#2 라이브러리 살펴보기
✔#3 view 환경설정
#4 빌드하고 실행하기
🔅 Welcome Page 만들기 (정적 페이지 ver)
Welcome Page 란 도메인(인터넷 사이트 주소)을 치고 들어 왔을 때 첫 화면을 뜻한다.
스프링부트는 resources/static 폴더에 index.html이라고 넣어두면 그 페이지는 Welcome Page로 인식한다. 다음 그림은 스프링 부트 공식 문서에 나와있는 설명이다.

정적 페이지로 Welcome Page를 만들어보자.
📌 정적 페이지의 특징
- 정적 페이지는 html 파일을 웹 서버가 웹 브라우저에게 그대로 넘겨주는 것을 뜻함
- 프로그래밍을 하지 않고, 파일을 그대로 넘겨주는 것
📌 정적 페이지 소스 ( index.html )
- 경로 : /src/main/resources/static/index.html
- 파일명 : index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
Hello
<a href="/hello">hello</a>
</body>
</html>📌 정적 페이지 소스 실행 결과
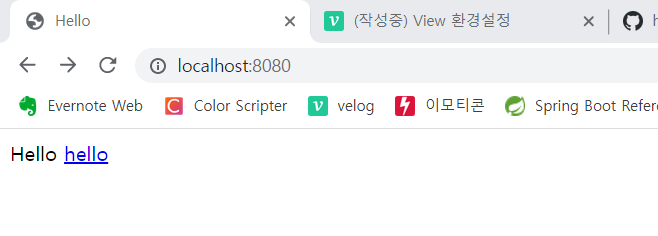
📌 정적 페이지 소스 설명 ( index.html )
<!DOCTYPE>-문서 형식 선언
-특정 문서 형식의 정의를 따르겠다고 선언한 것
<!DOCTYPE html>-선언한 페이지의 HTML 버전이 무엇인지를 웹 브라우저에 알려주는 역할을 하는 선언문
-대소문자 구분 없음
<html>-HTML 문서의 루트 요소(root element)를 정의
<head>-해당 문서에 대한 정보인 메타데이터(metadata)의 집합을 정의.
<title>-웹 페이지의 제목을 나타내는 태그
-head 태그 안에서 쓰임
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="texl/html; charset=UTF-8" />-해당 문서에 대한 정보인 메타데이터(metadata)를 정의
-head 태그 안에서 쓰임
-(속성) http-equiv
- content 속성에 명시된 값에 대한 HTTP 헤더를 제공
- 만약 http-equiv 속성이 명시되어 있다면, 반드시 content 속성도 함께 명시되어야 함
- content-type : 해당 문서의 문자 인코딩 방식을 명시함
<body>-해당 문서의 콘텐츠 영역을 정의함
-화면에 직접 출력되는 부분
<a href="/hello">hello</a>-하나의 페이지에서 다른 페이지를 연결할 때 사용하는 하이퍼링크(hyperlink)를 정의할 때 사용
-(속성) href
- 링크된 페이지의 url을 명시함
- 나의 경우, /hello라고 명시했으므로, hello라는 경로로 이동함
> localhost:8080/hello
🔅 Welcome Page 만들기 (동적 페이지 ver)
Thymeleaf 템플릿 엔진을 이용하여, 동작하고 프로그래밍하는 화면을 만들어보자.
이는 다음 2개의 파일을 만들어 실현 할 것이다.
- HelloController.java
- hello.html
📌 동적 페이지 소스 실행 결과
검색 창에 localhost:8080/hello 를 작성하면 다음 화면이 뜬다
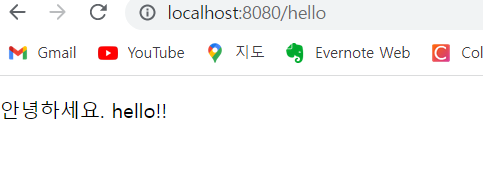
📌 동적 페이지 소스 및 설명 1 ( HelloController.java )
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("hello")
public String hello(Model model){
model.addAttribute("data","hello!!");
return "hello";
}
}@Controller-컨트롤러를 지정해주기 위한 어노테이션
-View에 표시될 데이터가 있는 Model 객체를 만들고, 올바른 View를 선택하는 일을 담당
@GetMapping("hello")-@GetMapping 어노테이션은 HTTP GET 요청을 처리하는 메서드를 맵핑(@RequestMapping)하는 어노테이션으로, 주어진 URL 표현식과 일치하는 HTTP GET 요청을 처리한다.
ex) http://localhost:8080/hello-위와 같이 웹 어플리케이션에서 /hello라고 들어오면 @GetMapping("hello")를 보고 해당 메소드로 이동한다.
Spring의 Model 객체-Spring에서 Controller의 메서드를 작성할 때는 Model이라는 타입을 파라미터로 지정할 수 있다
-Model 객체는 JSP에 Controller에서 생성된 데이터를 담아서 전달하는 역할을 하는 존재다.
-Model은 HashMap 형태를 가지고 있으며, key-value 값을 가지고 있다.
Model addAttribute(String name, Object value)-addAttribute()와 같은 기능을 통해 value 객체를 name 이름으로 View에 데이터를 전달할 수 있다
// Controller에서 Model 객체를 통해 데이터를 View에 전달해보는 예시
// Controller
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("hello")
public String hello(Model model){
model.addAttribute("data","hello!!");
return "hello";
}
}
-메소드에 매개변수를 Model 타입의 model 변수를 선언
-addAttribute()를 이용하여 data는 변수명에 hello!!라는 데이터 값을 담아 넘긴다.
<!-- view-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Hello</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="'안녕하세요. ' + ${data}">안녕하세요. 손님</p>
</body>
</html>-view에서는 설정한 name인 data로 데이터를 받는다. 형식은 ${data}와 같다.
Return "hello";-resource/templates/hello.html 이 있는데 여기에서 렌더링해라랑 같은 말이다. 즉, 이 화면을 실행시키라는 의미.
-Resource/templates/hello를 찾는다. (Thymeleaf 템플릿 엔진 처리)
cf. 자바의 메소드 형식

📌 동적 페이지 소스 및 설명 2 ( hello.html )
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Hello</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="'안녕하세요. ' + ${data}">안녕하세요. 손님</p>
</body>
</html><html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">- Thymeleaf 문법의 기본적인 특징은 html 태그 안에 th 문법을 추가하는 형태
- 표현식 : <div th:[속성]="서버에서 받는 값 및 조건식">
- 태그는 div가 아니여도 html 에서 지원하는 태그면 상관 없다
<!-- 서버에서 data라는 변수가 있을 경우, "손님"의 자리를 변수값으로 대체하게 됨 -->
<p th:text="'안녕하세요. ' + ${data}">안녕하세요. 손님</p>- p 태그 : paragraph. 하나의 문단을 만들 때 쓰임
- th:text : 태그 안의 텍스트를 서버에서 전달 받은 값에 따라 표현하고자 사용
📌 스프링의 동작 원리
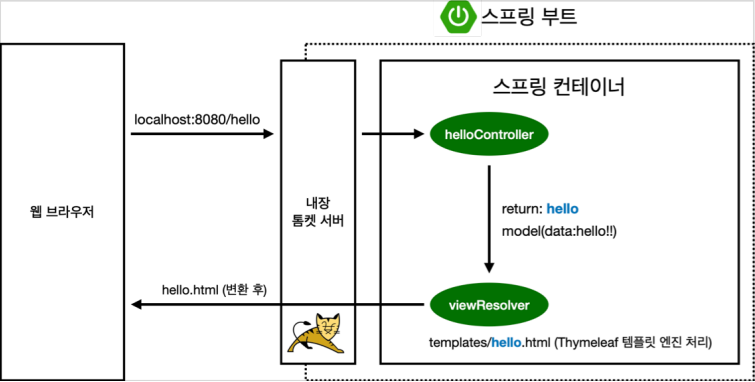
-
웹 브라우저에서 localhost:8080/hello 를 스프링 부트로 보낸다.
-
톰캣 서버를 내장하고 있는 스프링 부트는 이를 받아서 helloController에 있는 hello로 매핑된 메소드로 감
-
컨트롤러에서 리턴 값으로 문자를 반환하면 뷰 리졸버( viewResolver )가 화면을 찾아서 처리한다.
- 스프링 부트 템플릿엔진 기본 viewName 매핑
resources:templates/ +{ViewName}+ .html
- 스프링 부트 템플릿엔진 기본 viewName 매핑
