정의
- 동일한 타입의 데이터 0개 이상을 하나의 연속된 메모리 공간에서 관리하는 것
선언
//초기화생략
int[] arr1 = new int[10];
int arr2[] = new int[10];
//초기화
int[] numbers = new int[] {10, 20, 30}; //개수 생략해야 함
int[] numbers = {10, 20, 30}; // new int[] 생략 가능
int[] ids;
ids = new int[] {10, 20, 30}; // 선언후 배열을 생성하는 경우는 new int[] 생략할 수 없음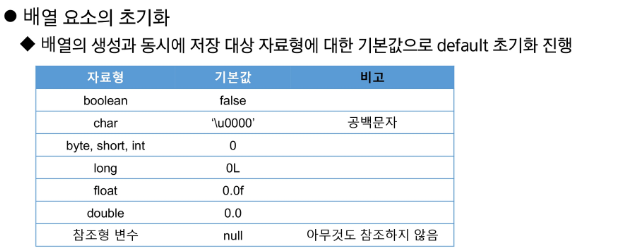
메서드
- Arrays.toString()-배열 안의 모든 요소를 char 리스트 반환한다.
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class ArrayTest_03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr1=new int[10];
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
}
}[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]*string-length(),toCharArray()
public class ArrayTest_04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String org = "SSAFY";
//length()는 string자료형의 길이를 반환
char[] chars=new char[org.length()];
for(int i=0;i<chars.length;i++) {
chars[i]=org.charAt(i);
}
for(int i=0;i<chars.length;i++) {
System.out.print(chars[i]);
}
//toCharArray()는 String 자료형을 char[]로 변환 후 반환
chars=org.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<chars.length;i++) {
System.out.print(chars[i]);
}
}
}SSAFYSSAFY배열의 접근
public class ArrayTest_07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int intArray[]= {1,3,5,7,9};
for(int x:intArray) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}1
3
5
7
9사용
public class ArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr1=new int[10];
int arr2[]=new int[10];
int[] numbers= {1,2,3,4,5};
//배열의 요소를 인덱스로 출력
for(int i=0;i<numbers.length;i++) {
System.out.println(numbers[i]);
}
int[] ids;
ids=new int[] {10,20,30,40,50};
//python의 for i in arrays와 비슷함
for(int id:ids) {
System.out.println(id);
}
int[] arr=new int[10];
//배열에 수를 초기화
for (int i=0,num=1;i<arr.length;i++) {
arr[i]=num;
}
int total=0;
//배열의 모든 합 구하기
for (int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
total+=arr[i];
}
System.out.println(total);
//문자배열 다루기
char[] alphas=new char[26];
char ch='A';
for (int i=0;i<alphas.length;i++) {
alphas[i]=ch++;
}
for(char alpha : alphas) {
System.out.print(alpha+" ");
}
}
}1
2
3
4
5
10
20
30
40
50
10
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 객체배열
- 기본 자료형 배열은 선언과 동시에 배열의 크기만큼의 메모리가 할당되지만,
객체 배열의 경우엔 요소가 되는 객체의 주소가 들어갈(4바이트, 8바이트) 메모리만 할당되고(null) 각 요소 객체는 생성하여 저장해야 함
Book.java
public class Book {
private String title;
private String author;
public Book() {
}
public Book(String title,String author) {
this.title=title;
this.author=author;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public void showBookInfo() {
System.out.println(author+" "+title);
}
}BookTest.java
public class BookTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book[] books=new Book[5];
for (int i=0;i<books.length;i++) {
books[i]=new Book("태백산맥"+i,"사용자"+i);
}
for (Book book:books) {
book.showBookInfo();
System.out.println(book);
}
}
}사용자0 태백산맥0
ch23.Book@7c30a502
사용자1 태백산맥1
ch23.Book@49e4cb85
사용자2 태백산맥2
ch23.Book@2133c8f8
사용자3 태백산맥3
ch23.Book@43a25848
사용자4 태백산맥4
ch23.Book@3ac3fd8b복사
- 얕은 복사
객체 주소만 복사되어 한쪽 배열의 요소를 수정하면 같이 수정 됨
즉, 두 배열이 같은 객체를 가리킴
public class BookCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//주소만 복사하는 얕은 복사이다.
Book[] books=new Book[5];
for (int i=0;i<books.length;i++) {
books[i]=new Book("태백산맥"+i,"사용자"+i);
}
Book[] copyBooks=new Book[books.length];
System.arraycopy(books, 0, copyBooks, 0, books.length);
for (Book book:books) {
System.out.println(book);
}
for (Book copybook:copyBooks) {
System.out.println(copybook);
}
}
}ch23.Book@7c30a502
ch23.Book@49e4cb85
ch23.Book@2133c8f8
ch23.Book@43a25848
ch23.Book@3ac3fd8b
ch23.Book@7c30a502
ch23.Book@49e4cb85
ch23.Book@2133c8f8
ch23.Book@43a25848
ch23.Book@3ac3fd8b- 깊은 복사
각각의 객체를 생성하여 그 객체의 값을 복사하여 배열이 서로 다른 객체를 가리키도록 함
public class CopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book[] books=new Book[5];
for (int i=0;i<books.length;i++) {
books[i]=new Book("태백산맥"+i,"사용자"+i);
}
Book[] copyBooks=new Book[books.length];
for (int i=0;i<books.length;i++) {
copyBooks[i]=new Book();
copyBooks[i].setAuthor(books[i].getAuthor());
copyBooks[i].setTitle(books[i].getTitle());
}
for (Book book:books) {
book.showBookInfo();
}
System.out.println("============================");
for (Book copyBook:copyBooks) {
copyBook.showBookInfo();
}
}
}사용자0 태백산맥0
사용자1 태백산맥1
사용자2 태백산맥2
사용자3 태백산맥3
사용자4 태백산맥4
============================
사용자0 태백산맥0
사용자1 태백산맥1
사용자2 태백산맥2
사용자3 태백산맥3
사용자4 태백산맥42차원 배열
- 이차원 이상으로 구현 된 배열
- 평면 (이차원 배열) 이나 공간(삼차원 배열)을 활용한 프로그램 구현
public class TwoArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr= {{1,2,3},{4,5,6}};
System.out.println(arr.length);
System.out.println(arr[0].length);
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
for (int j=0;j<arr[i].length;j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}2
3
1 2 3
4 5 6 ArrayList
- 기존의 배열 선언과 사용 방식은 배열의 길이를 정하고 요소의 개수가 배열의 길이보다 커지면 배열을 재할당하고 복사해야 했음
- 배열의 요소를 추가하거나 삭제하면 다른 요소들의 이동에 대한 구현을 해야 함
- ArrayList는 객체 배열을 좀더 효율적으로 관리하기 위해 자바에서 제공해 주는 클래스
- 이미 많은 메서드들이 최적의 알고리즘으로 구현되어 있어 각 메서드의 사용 방법만 익히면 유용하게 사용할 수 있음
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
//요소 추가
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
list.add(i);
}
//배열 길이
System.out.println(list.size());
System.out.println("===================");
//인덱스로 요소 조회
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
System.out.println("===================");
//요소 삭제
list.remove(0);
for (int ele:list) {
System.out.println(ele);
}
System.out.println("===================");
//특정 위치에 요소 삽입
list.add(0,100);
for (int ele:list) {
System.out.println(ele);
}
}
}5
===================
0
1
2
3
4
===================
1
2
3
4
===================
100
1
2
3
4