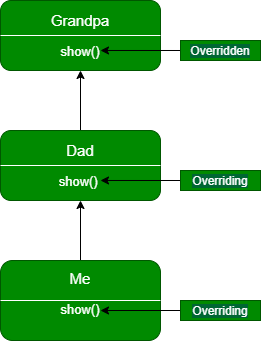
오버라이딩
- 상속 관계에 있는 부모 클래스에서 이미 정의된 메소드를 자식 클래스에서 같은 시그니쳐를 갖는 메소드로 다시 정의하는 것
class Robot:
population = 10
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
Robot.population += 1
def die(self):
print(f"{self.name} is being destroyed!")
Robot.population -= 1
if Robot.population == 0:
print(f"{self.name} was the last")
else:
print(f"there are still {Robot.population} remain")
def say_hi(self):
print(self)
print(f"my master call me {self.name}")
def cal__add(self, a, b):
return a + b
@classmethod
def how_many(cls):
return f"we have {cls.population} robots"
class Siri(Robot):
age = 10
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name=name
self.age = age
def say_hi(self):
print(f"my master call me {self.name} by apple")
@classmethod
def how_many(cls):
return f"we have {cls.population} robots by apple"
siri = Siri("iphone7", 20)
siri.say_hi()
print(Siri.how_many())
my master call me iphone7 by apple
we have 11 robots by apple
super
- 부모클래스의 임시적인 객체를 반환하여 부모클래스의 메소드를 사용할 수 있게 하는 것
class Robot:
population = 10
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
Robot.population += 1
def die(self):
print(f"{self.name} is being destroyed!")
Robot.population -= 1
if Robot.population == 0:
print(f"{self.name} was the last")
else:
print(f"there are still {Robot.population} remain")
def say_hi(self):
print(f"my master call me {self.name}")
def cal__add(self, a, b):
return a + b
@classmethod
def how_many(cls):
return f"we have {cls.population} robots"
class Siri(Robot):
age = 10
def __init__(self, name, age):
super().__init__(name)
self.age = age
def say_hi(self):
super().say_hi()
print(f"my master call me {self.name} by apple")
@classmethod
def how_many(cls):
return super().how_many()
siri = Siri("iphone7", 20)
siri.say_hi()
print(Siri.how_many())
my master call me iphone7
my master call me iphone7 by apple
we have 11 robots