객체의 상태 정보를 가지는 클래스를 따로 생성하여, 객체의 상태를 저장하거나 이전 상태로 복원할 수 있게 해주는 패턴
Intro
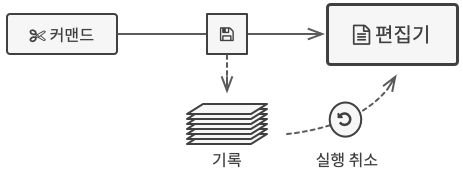
텍스트 에디터를 사용시 기존 작업을 취소하고 이전 버전으로 돌려야할 때가 있다
이때, 용자가 작업을 실행 취소하기로 하면 앱은 기록에서 가장 최신 스냅샷을 가져와 모든 객체의 상태를 복원하는 데 사용한다
문제점
객체의 필드에 대한 액세스 문제 - 캡슐화의 파괴
- 대부분의 실제 객체들은 중요한 데이터를 비공개 필드에 숨김
- 그러나, 스냅샷을 하려면 필드를 다 공개해야함(비공개포함)
- 객체 필드 변경시 미러링 하고있는(객체의 상태를 복사하는) 클래스들 죄다 변경해야함
클래스 내부의 세부 정보를 모두 공개하면 클래스가 너무 취약해진다. 하지만, 클래스의 상태에 접근하지 못하게 하면 스냅샷을 생성할 수 없다
Memento Pattern
설명
- 이 게임은 자동적으로 진행됩니다.
- 게임의 주인공은 주사위를 던져 나온 수가 다음 상태를 결정합니다.
- 좋은 수가 나오면 주인공의 돈이 증가합니다.
- 나쁜 수가 나오면 돈이 감소합니다.
- 특별히 좋은 수가 나오면 주인공이 과일을 받습니다.
- 돈이 없어지면 종료합니다. -> 돈이 절반으로 떨어지면 이전 상태로 복구함
구조
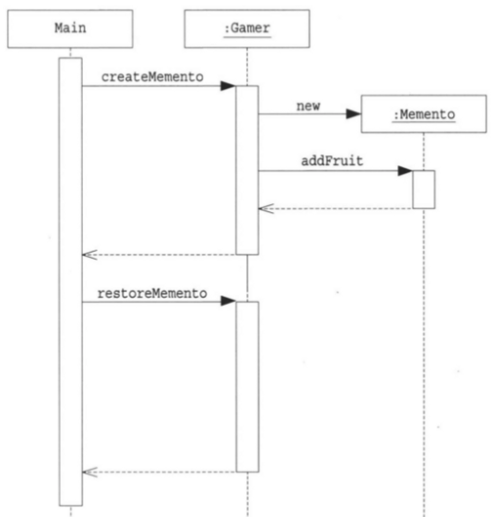
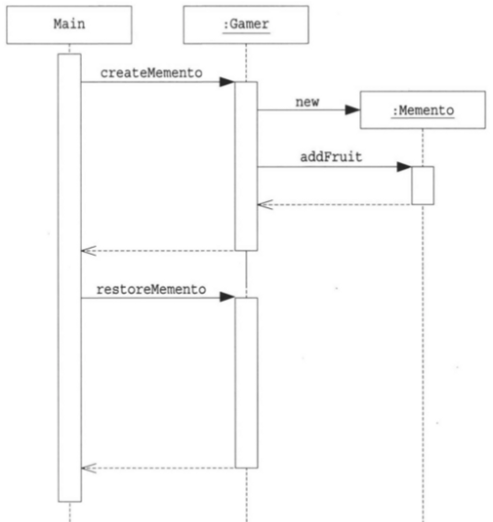
| 패키지 | 클래스 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| game | Memento | Gamer의 상태를 나타내는 클래스 |
| game | Gamer | 게임을 실행하는 주인공의 클래스. Memento의 인스턴스를 만든다 |
| client | Main | 게임을 진행시키는 클래스. Memento의 인스턴스를 저장해 두고, 필요에 따라 Gamer의 상태를 복원한다. |
코드
Memento.class
public class Memento {
int money; // 가진 돈
ArrayList fruits; // 과일
// 돈을 얻는다
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
Memento(int money) {
this.money = money;
this.fruits = new ArrayList();
}
// 과일을 추가한다
void addFruit(String fruit) {
fruits.add(fruit);
}
// 과일을 얻는다
List getFruit() {
return (List)fruits.clone();
}
}- gamer의 상태를 나타내는 클래스
- memento의 필드는(인스턴스, 메소드, 생성자) 모두 default(같은 패키지내 gamer 클래스들만 자유로운 액세스 가능)
Gamer.class
public class Gamer {
private int money; // 소지금
private List fruits = new ArrayList(); // 과일개수
private static final ThreadLocalRandom random = ThreadLocalRandom.current();
private static String[] fruitsname = {
"사과", "포도", "바나나", "귤",
};
public Gamer(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void bet() {
int dice = random.nextInt(6) + 1;
if (dice == 1) {
money += 100;
System.out.println("소지금이 증가했습니다.");
} else if (dice == 2) {
money /= 2;
System.out.println("소지금이 절반이 되었습니다.");
} else if (dice == 6) {
String f = getFruit();
System.out.println("과일(" + f + ")을 받았습니다.");
fruits.add(f);
}
}
// 스냅샷을 찍는 메소드
public Memento createMemento() {
Memento m = new Memento(money);
for (Object o : fruits) {
String f = (String) o;
if (f.startsWith("맛있는 ")) {
m.addFruit(f);
}
}
return m;
}
// 찍었던 스냅샷을 기초로 자신의 상태를 복원함
public void restoreMemento(Memento memento) {
this.money = memento.money;
this.fruits = memento.fruits;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[money = " + money + ", fruit = " + fruits + "]";
}
// 과일을 얻는다
private String getFruit() {
String prefix = "";
if (random.nextBoolean()) {
prefix = "맛있는 ";
}
return prefix + fruitsname[random.nextInt(fruitsname.length)];
}
}- 중심 메소드는 bet(내기하다)로 주인공이 파산하지 않았다면 주사위를 던지고 그 눈에 따라 돈과 과일개수를 변화시킴
Main.class
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Gamer gamer = new Gamer(100); // gamer 생성
Memento memento = gamer.createMemento(); // 최초 상태 저장
// 게임 시작
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("=== " + i); // 횟수
System.out.println("상태:"+gamer);
gamer.bet(); // 게임 진행
System.out.println("소지금은"+gamer.getMoney()+"원이 되었습니다.");
//Memento의 취급 결정
if (gamer.getMoney() > memento.getMoney()) {
System.out.println("(많이 증가했으므로 현재의 상태를 저장합니다.)");
memento = gamer.createMemento();
} else if (gamer.getMoney() < memento.getMoney() / 2) {
System.out.println("(많이 감소했으므로 이전의 상태로 복원하자)");
gamer.restoreMemento(memento);
}
}
// 잠시 대기
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(InterruptedException ignored){
// InterruptedException ignore..
}
System.out.println("");
}
}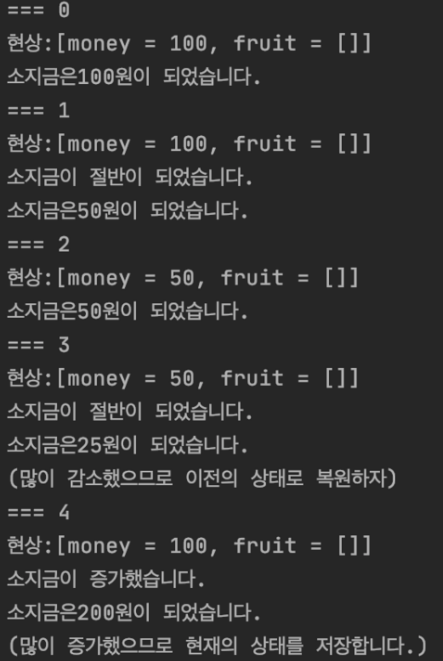
실행 흐름
결론
- 캡슐화를 유지하며 스냅샷 생성가능
- 객체 상태가 바뀌어도 client(main)의 코드는 변경 x
- 객체의 필드들/게터들/세터들을 직접 접근하는 것이 해당 객체의 캡슐화를 위반할 때 사용하자
