import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static int[] arr;
static int n, m;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
n = Integer.parseInt(bf.readLine());
arr = new int[n];
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i<n; i++) {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
Arrays.sort(arr);
m = Integer.parseInt(bf.readLine());
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i<m; i++) {
int checkNum = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int result = upperBound(checkNum) - lowerBound(checkNum);
sb.append(result+" ");
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
static int lowerBound(int checkNum) {
int hi = n;
int lo = 0;
while (lo < hi) {
int mid = (hi+lo) / 2;
if (checkNum <= arr[mid]) {
hi = mid;
}
else {
lo = mid + 1;
}
}
return lo;
}
static int upperBound(int checkNum) {
int hi = n;
int lo = 0;
while (lo < hi) {
int mid = (hi + lo) / 2;
if (checkNum < arr[mid]) {
hi = mid;
} else {
lo = mid+1;
}
}
return hi;
}
}풀이
숫자 카드 1에 이어서 업그래이드 되서 숫자가 있는지 없는지에 더해 몇개 있는지 까지 판별하는 문제다.
이 문제는 lowerBound upperBound 개념을 알면 쉽게 풀수 있다.
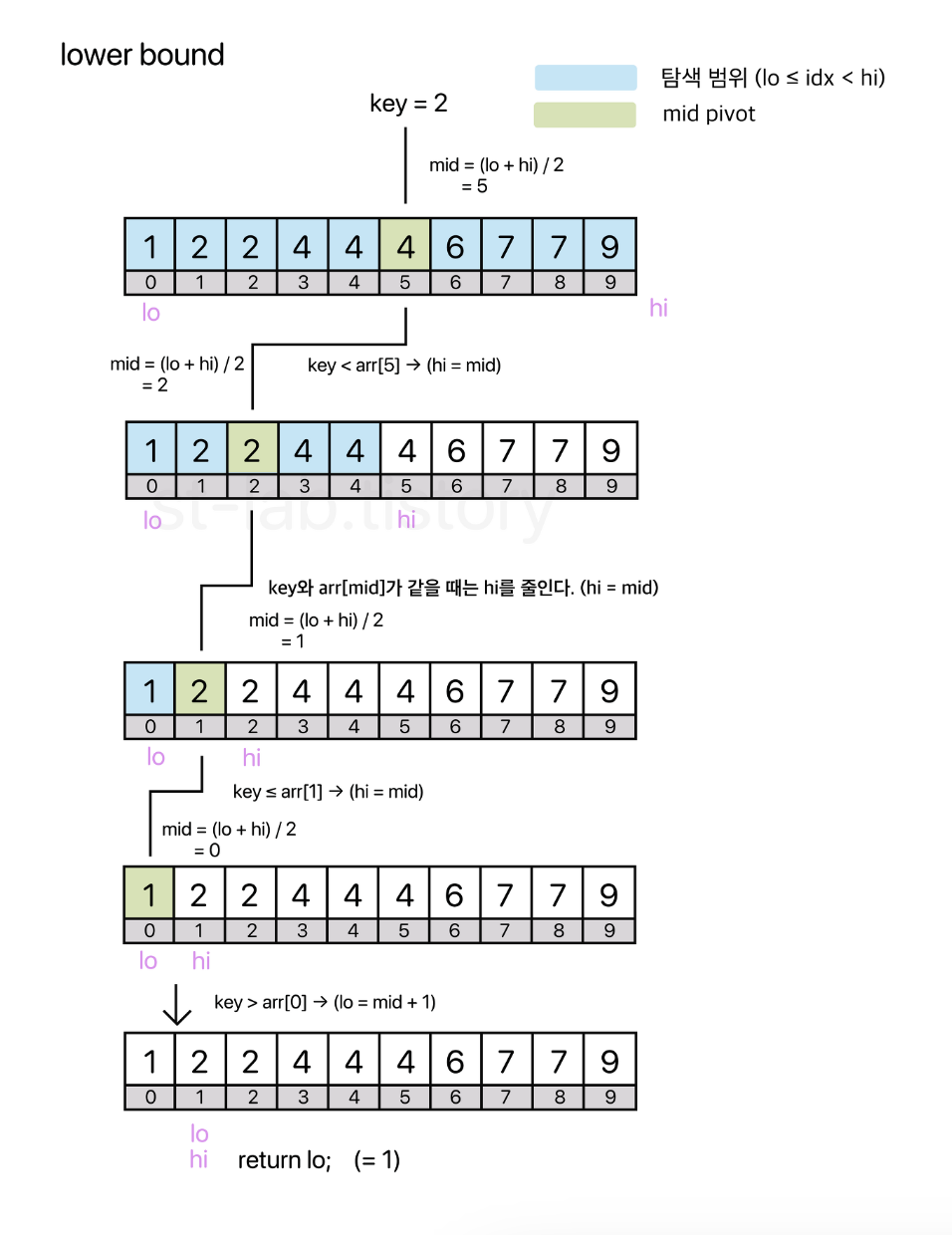
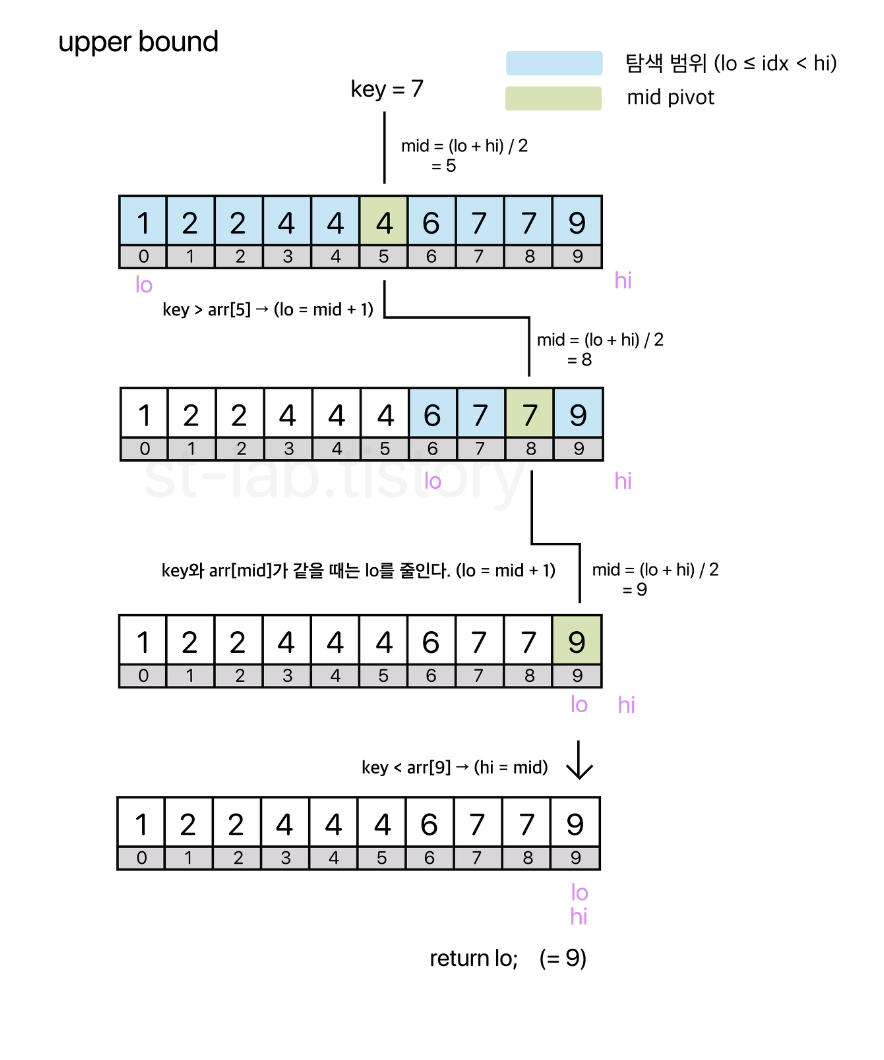
upperBound - lowerBound = 해당 숫자가 몇개있는지 알 수 있다.
https://st-lab.tistory.com/267
