SQL
- null 값 제외하는 방법
- 기존에 left join 을 사용하였을 때 null값이 존재한다면 그대로 나타나는 문제점이 있었다. 그것을 해결하기 위해 사용
select a.order_id,
a.customer_id,
a.restaurant_name,
a.price,
b.name,
b.age,
b.gender
from food_orders a left join customers b on a.customer_id=b.customer_id
where b.customer_id is not null - is not null을 붙혀 사용한다면 null값이 아닌 데이터들만 나오게 된다.
다른 방법 또한 존재한다
- null 값 변경하는 방법
- 제외하는 방법과 달리 null값을 다른 값으로 대체하여 임의로 값을 넣어 줄 수 있다
select a.order_id,
a.customer_id,
a.restaurant_name,
a.price,
b.name,
b.age,
coalesce(b.age, 20) "null 제거",
b.gender
from food_orders a left join customers b on a.customer_id=b.customer_id
where b.age is null보는 것과 같이 코드를 작성할 경우 where문에 의해서 b.age가 null 값인 경우에 데이터만 나오게 되는데 coalesce(b.age, 20)을 사용하여 b.age에 null인 값을 20이라는 대체 값으로 대체할 수 있다.
RANK
- 이름 그대로 랭킹을 구할 수있다.
문제) 음식 타입별로 주문 건수가 가장 많은 상점 3개씩 조회하기
SELECT cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
cnt_order,
ranking
FROM
( //subquery b
SELECT cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
cnt_order,
rank() over (partition by cuisine_type order by cnt_order desc) ranking
FROM
( //subquery a
SELECT cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
count(1) cnt_order
FROM food_orders
group by 1,2
) a
) b
where ranking<=3- 설명
- 복잡하게 생각하지 말자! 천천히 팡가하면 다 알 수 있다.
우선 subquery a 부분부터 파악하자면
1. 음식타입(cuisine_type), 상점 이름, 그리고 그 두개의 데이터 개수를 알아야 어느 곳이 주문 건수가 가장 많은 곳인지 알 수 있으므로 count(1) cnt_order를 사용해준다.
여기서 where절에 group_by 1,2를 쓰는 이유는 차이를 보면 확연히 알 수 있다.
group by 1,2를 썼을때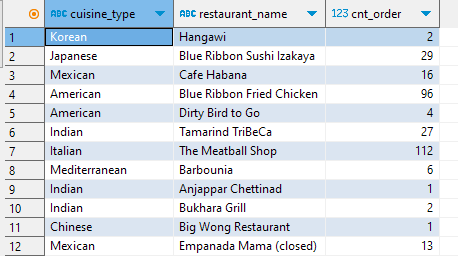
- 모든 음식타입과, 상점 이름이 나옴
group by 1만 썼을때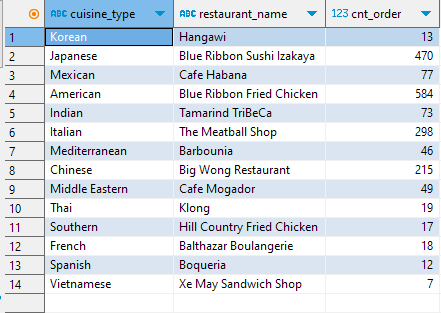
- cuisine_type에만 group by 가 걸렸으므로 각 지역별로 하나씩만 나옴
group by 사용 X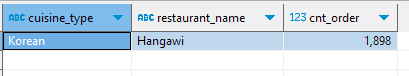
- 하나만 나옴
다음으로 b절을 살펴보자
rank() over (partition by cuisine_type order by cnt_order desc) ranking- 요놈이 핵심이다. 우선 rank() over 까지는 고정적으로 사용한다.
그 뒤에 partition by는 그룹을 나누기 위해 사용한다고 생각한다. ex)파티션 벽
그리고 내가 나누고 싶은 그룹을 써주고 (cuisine_type)
order by를 통하여 정렬 기준을 정한다.( cnt_order 기준으로 desc(내림차순))
이렇게 subquery a,b 구성이 끝나면 where문에서 ranking <= 3 을 통해 조건을 설정해주면 끝이다.
format
- SQL의 연산은 날짜도 가능하다.
- 날짜를 나타내는 함수는 date(칼럼명)
select date,
date(date) date_type,
date_format(date(date), '%Y') "년",
date_format(date(date), '%m') "월",
date_format(date(date), '%d') "일",
date_format(date(date), '%w') "요일"
from payments /*payments는 date를 가지고있음*/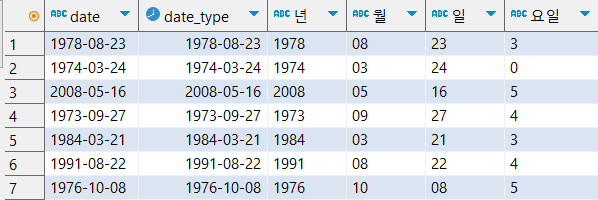
- date와 date_type 앞부분을 보면 date는 ABC, date_type은 시계로 아이콘이 나타나 있는 것이 보인다.
- 참고로 요일에 0은 일요일을 나타낸다 순서(1 : 월, 2 : 화 ~~ 6 : 토, 0 : 일)
- 나머지는 개인이 응용하기
실습
- 문제
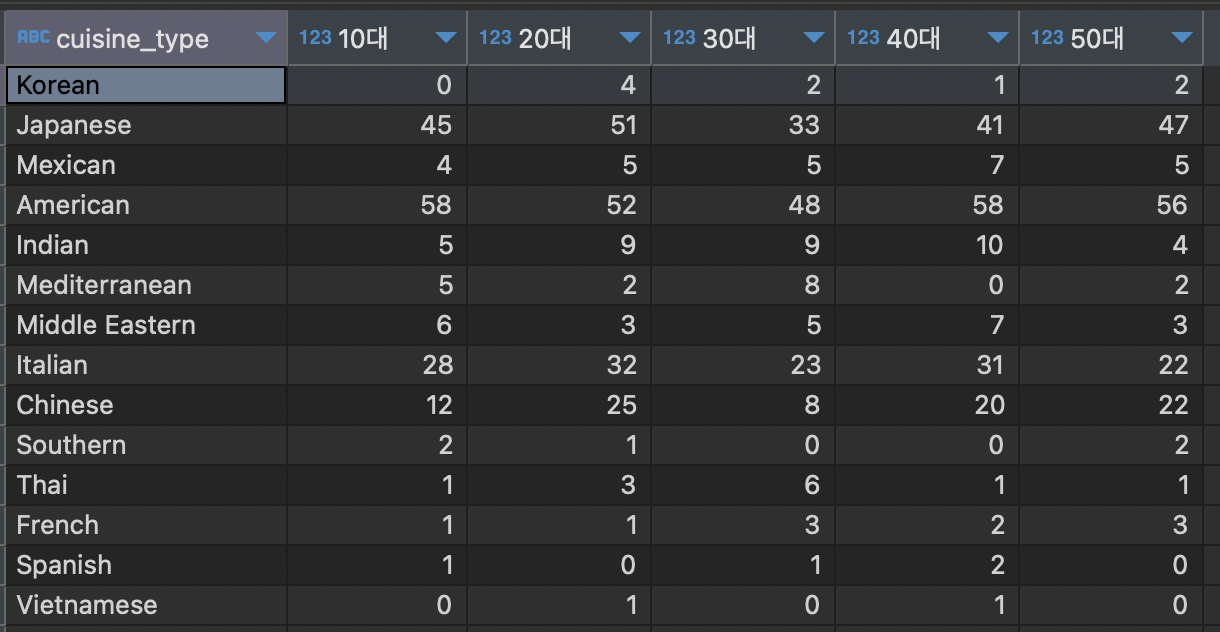
음식 타입별, 연령별 주문건수 pivot view 만들기 (연령은 10~59세 사이)
SELECT cuisine_type,
sum(if(age=10,age_count,0)) "10대",
sum(if(age=20,age_count,0)) "20대",
sum(if(age=30,age_count,0)) "30대",
sum(if(age=40,age_count,0)) "40대",
sum(if(age=50,age_count,0)) "50대"
FROM
(
SELECT f.cuisine_type,
case when 10 < age and age <=19 then 10
when 20 < age and age <=29 then 20
when 30 < age and age <=39 then 30
when 40 < age and age <=49 then 40
when 50 < age and age <=59 then 50 end age,
count(1) age_count
FROM customers c inner join food_orders f on c.customer_id = f.customer_id
where age BETWEEN 10 and 60
group by 1,2
) a
group by 1설명할게 많이 없다.
subquery에 case문을 이용하여 age값의 범위를 설정하여 then을 통해 값을 반환하여 주고 count(1) 문을통해 age_count에 10,20,30,40,50의 개수를 넣어주고
sum(if(age=10,age_count,0)) "10대"를 통하여 age가 10인경우 age_count를 할당하여 계산할 수 있게 하였다.