동시성 문제 해결하기
문제 상황
@Override
@Transactional
public PostRepDto getPostById(Long postId, Member member) {
Post post = postRepository.findById(postId).orElseThrow(PostNotFoundException::new);
if(reportRepository.existsByPostAndReporter(post,member)){
throw new ReportedPostAccessDeniedException();
}
if(blockRepository.existsByMemberAndBlockedMember(member, post.getWriter())){
throw new BlockedMemberPostAccessDeniedException();
}
// 조회수 증가
post.increaseView();
log.info("게시글 조회 성공, postId = {}", postId);
return post.toPostRepDto(scrapRepository.existsByMemberIdAndItemIdAndItemType(member.getId(),post.getId(), POST));
}
// Post.java
public void increaseView() {
this.view++;
}게시글 조회 시 게시글의 조회수를 증가시키는 로직을 구현함.
toBuilder()를 이용하여 조회 수를 증가시킨 후 다시 저장하는 방식.
하지만 여러 명이 동시에 조회 시 조회 수가 제대로 증가하지 못하는 문제 발생.
PostViewConcurrencyTest.java
하나의 게시글을 생성하고, 여러 명의 사용자(멀티 쓰레드 1000개)가 게시글 조회 API 요청 시 조회수가 1000이 되는지 확인하는 테스트 구현.
원래 MySQL 데이터베이스를 사용하지만 테스트 환경과의 분리를 위해 h2 데이터베이스 사용
@Test
@DisplayName("게시글 조회 수 증가 동시성 문제 테스트")
void successPostViewConcurrencyTest() throws InterruptedException {
// given
Member writer = memberRepository.save(Member.builder()
.username("member1")
.role(Role.USER)
.build());
Post post = postRepository.save(Post.builder()
.title("post1")
.writer(writer)
.view(0L)
.contents(List.of(Content.builder().content(CONTENT).type(ContentType.TEXT).build()))
.build());
int threadCount = 1000;
// when
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadCount);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
executorService.execute(() -> {
try {
postReadService.getPostById(post.getId(), writer);
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
});
}
latch.await();
Post updatedPost = postRepository.findById(post.getId()).orElseThrow();
assertThat(updatedPost.getView()).isEqualTo(threadCount);
System.out.println("게시글 조회수" + " " + updatedPost.getView());
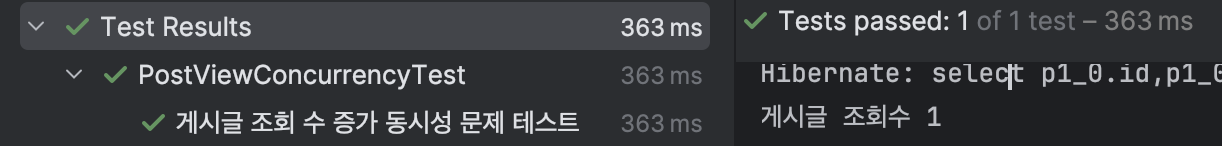
}한번 조회 시(threadCount : 1)
여러 번 조회 시(threadCount : 1000)
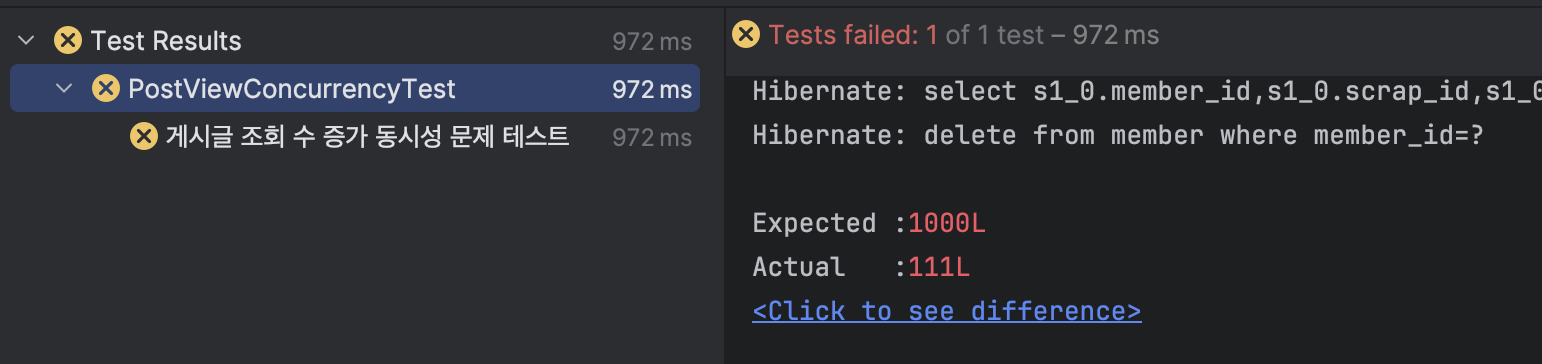
위와 같이 멀티 쓰레드로 테스트 시 1000번 조회가 되면 조회수는 1000이 되어야하는데 111만 증가된 모습 확인
문제 원인
공유 자원의 동시 접근
여러 스레드가 동시에 하나의 변수를 수정하게 되면서 레이스 컨디션이 발생함.
- 스레드 A가 count 값을 읽고 있을 때, 스레드 B도 같은 값을 읽음
- 각각 1을 더한 후 저장하면 결과적으로 1번만 증가한 것처럼 됨
➔ 서로의 연산이 덮어쓰기 때문에 예상한 만큼 증가하지 않는 것
레이스 컨디션이란?
동시에 실행되는 여러 작업이 동일한 자원에 접근하여, 실행 순서나 타이밍에 따라 결과가 달라지는 상황
해결 방법
1. synchronized 키워드 사용?
public synchronized void increaseView() {
this.view++;
}단일 JVM 내에서 한 번에 하나의 쓰레드만 해당 메서드에 접근하도록 동기화하는 방법
동시에 여러 요청이 들어와도 한 번에 하나만 처리하므로 Race Condition 방지 가능
장점
구현이 간단하다, 별도의 라이브러리나 DB 등이 필요하지 않음
단점
여러 서버 환경에서 무효함
- 하나의 JVM안에서만 동작하므로 서버가 여러 개인 경우 서버마다 값이 달라짐
- 즉, 데이터베이스 레벨에서는 동시성 보장이 안됨.
- 성능 저하(멀티 쓰레드 환경에서 병렬 처리 불가)
가장 간편한 방법이지만 성능 저하 등 프로젝트의 확장성을 해치는 단점이 존재함.
2. 락을 거는 방식
1. 비관적 락 (Pessimistic Lock)
- 동시 수정 가능성을 높게 봄 → 미리 락을 걸어 충돌 방지
- 데이터를 조회할 때부터 락을 걸어 다른 트랜잭션이 수정하지 못하게 함
- 데이터베이스 레벨의 락 (SELECT ... FOR UPDATE 등)을 많이 사용
@Transactional
public void increaseViewCount(Long id) {
Post post = PostRepository.findByIdWithLock(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new NotFoundException());
post.increaseView();
// 트랜잭션 종료 시 update 자동 수행
}
// Repository
@Lock(LockModeType.PESSIMISTIC_WRITE)
@Query("SELECT p FROM Post p WHERE p.id = :id")
Optional<Post> findByIdWithLock(@Param("id") Long id);단점
- 성능 저하 : 매 조회 시 락을 걸기 때문에 동시 요청들이 대기하게 됨
- 데드락 발생 가능성
- 낙관적 락 (Optimistic Lock)
- 충돌 가능성을 낮게 보고 → 수정 시점에 검증
- 버전 필드(version)를 이용하여 변경 시점에 충돌 여부 확인
- 충돌 발생 시 ObjectOptimisticLockingFailureException 예외 발생 → 다시 시도 필요
단점
- 충돌 시 예외 발생 : 재시도 로직을 구현해야하고 복잡해짐
- 충돌이 자주 발생하게 될 경우 비용, 성능 문제
3. 직접 쿼리 수정 방식
@Modifying + @Query 를 이용하여 한번의 쿼리로 바로 수정하는 방식.
- 영속성 컨텍스트에 저장하지 않고, DB에 바로 반영함
단점
- 영속성 컨텍스트를 무시함, 엔티티 조회 없이 바로 수정 -> 영속성 컨텍스트와 상태 불일치 발생
- version 기반 검증, 락 기반의 충돌 방지 기능이 없음
최종 해결 방법
Redis를 이용한 방법
Redis를 이용하여 동시성 문제를 해결하는 방법은 크게 2가지가 존재
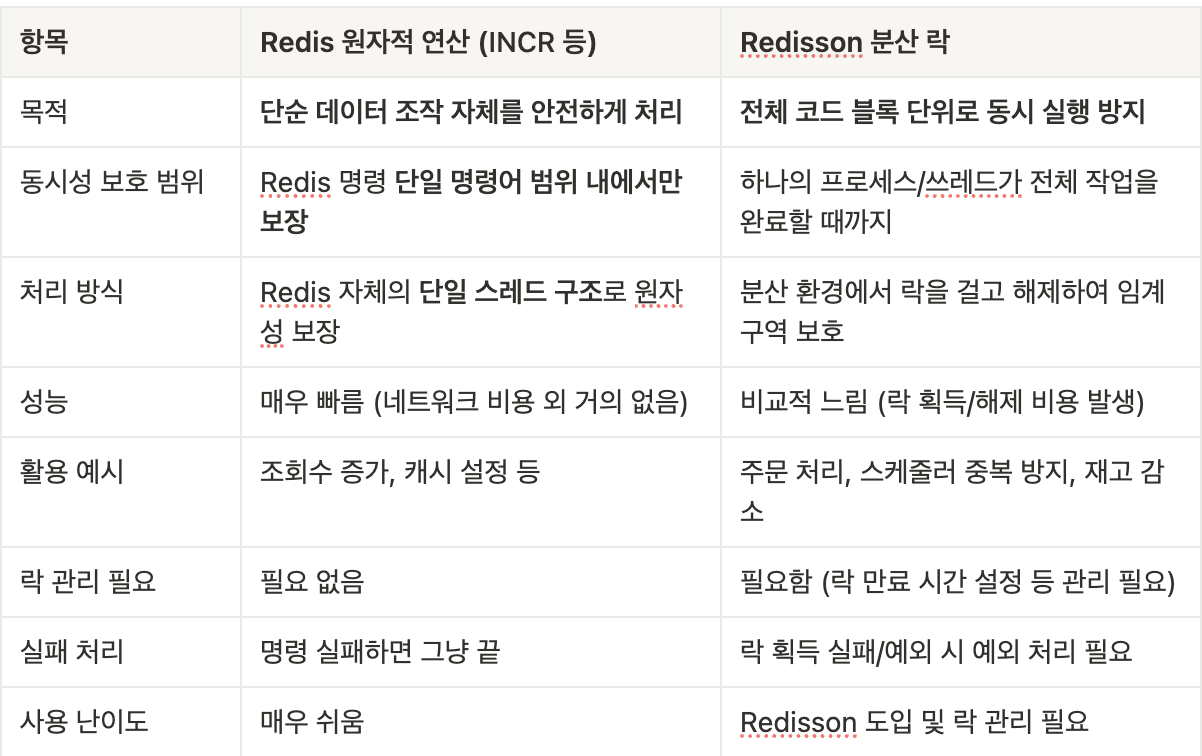
- 원자적 연산과 분산 락 처리
- 조회수 증가 연산은 재고 감소, 주문 처리, 예약과 같이 데이터의 손실이나 정합성이 매우 중요한 경우와는 다름
- 게시글 조회는 매우 빈번하게, 동시에 일어날 가능성이 높고 조회수가 매우 중요한 데이터는 아니기 때문에 속도가 빠르고 비용이 낮은 원자적 연산 방법이 더 적합함.
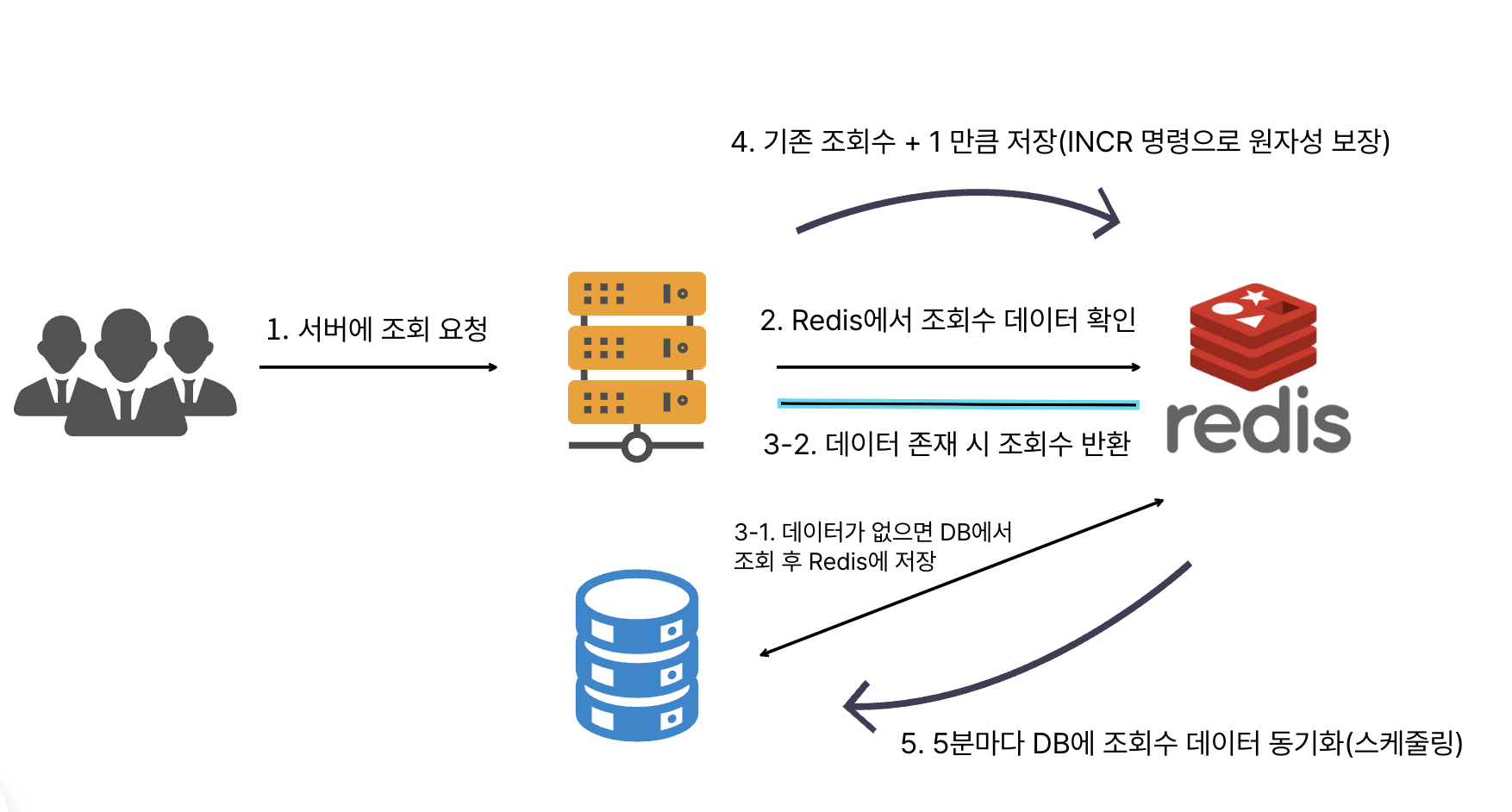
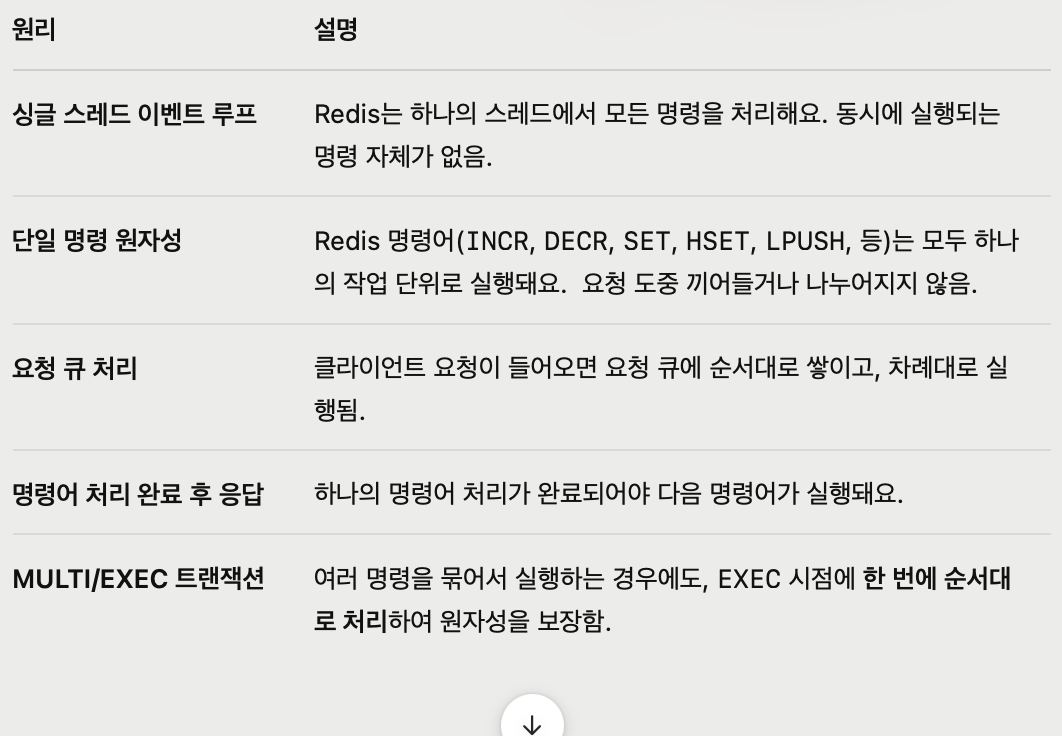
Redis 원자적 연산
단일 명령어 실행이 절대 끊기지 않고 완전히 실행되는 것을 보장
build.gradle
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-redis'
RedisConfig.java
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
return new LettuceConnectionFactory("localhost", 6379);
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate() {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory());
template.setKeySerializer(new org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer());
template.setValueSerializer(new org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer());
return template;
}
}RedisUtil.java
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class RedisUtil {
private final RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
// 키에 해당하는 조회수 1 증가
public void increaseView(String key){
redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(key, 1L);
}
// 키에 해당하는 조회수 반환
public Long getViewCount(String key){
String value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
return value == null ? null : Long.parseLong(value);
}
// 저장된 모든 키, 값 쌍을 map으로 반환
public Map<String, Long> getAllViewCount(String prefix) {
Set<String> keys = redisTemplate.keys(prefix + "*");
if (keys == null || keys.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyMap();
}
List<Object> values = redisTemplate.executePipelined((RedisCallback<Object>) connection -> {
for (String key : keys) {
connection.stringCommands().get(redisTemplate.getStringSerializer().serialize(key));
}
return null;
});
Map<String, Long> result = new HashMap<>();
int index = 0;
for (String key : keys) {
String value = (String) values.get(index++);
result.put(key, value != null ? Long.parseLong(value) : null);
}
return result;
}
public void setView(String key, Long viewCount) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, String.valueOf(viewCount));
}
}이때 실제 운영 환경에서는 많은 조회수 키값이 저장되기 때문에 좀 더 효율적으로 조회하고자 executePipeLined를 사용
- RedisTemplate이 제공하는 “파이프라인 처리”용 메서드
- 여러 요청을 한 번에 처리해서 네트워크 왕복 비용(RTT)을 줄이는 기술
- Redis는 원래 하나의 명령을 보내고 → 결과를 받고 → 다음 명령을 보내는 방식
- Pipeline은 명령 여러 개를 한꺼번에 서버에 보내고, 서버도 응답을 모아서 한꺼번에 반환함
List<Object> values = redisTemplate.executePipelined((RedisCallback<Object>) connection -> {
for (String key : keys) {
connection.stringCommands().get(redisTemplate.getStringSerializer().serialize(key));
}
return null;
});PostReadServiceImpl.java
public void increaseViewCount(Long postId, Post post) {
String key = VIEW_COUNT_PREFIX + postId;
// Redis의 INCR → 원자적 증가 연산
if(redisUtil.getViewCount(key) == null){
redisUtil.setView(key, post.getView());
}
redisUtil.increaseView(key);
}조회수 증가 함수
- 키에 해당하는 조회수 데이터가 존재하지 않으면 먼저 DB값으로 세팅 후 증가시킴
/** 게시글, 리뷰 상세 조회 */
@Override
@Transactional
public PostRepDto getPostById(Long postId, Member member) {
Post post = postRepository.findById(postId).orElseThrow(PostNotFoundException::new);
if(reportRepository.existsByPostAndReporter(post,member)){
throw new ReportedPostAccessDeniedException();
}
if(blockRepository.existsByMemberAndBlockedMember(member, post.getWriter())){
throw new BlockedMemberPostAccessDeniedException();
}
// 조회수 증가
increaseViewCount(post.getId(), post);
String key = VIEW_COUNT_PREFIX + postId;
Long viewCount = redisUtil.getViewCount(key);
if(viewCount == null){
viewCount = post.getView() + 1;
}
log.info("게시글 조회 성공, postId = {}", postId);
return post.toPostRepDto(scrapRepository.existsByMemberIdAndItemIdAndItemType(member.getId(),post.getId(), POST), viewCount);
}게시글 상세 조회 메서드 수정
- 조회수 증가시킨 후 게시글 아이디에 해당하는 조회수를 가져와서 응답에 반영
@Override
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 300000) // 5분
public void allViewCountFlush(){
log.info("게시글 조회수 flush 작업 수행");
// Redis에 저장된 조회수 값 모두 가져오기
Map<String, Long> views = redisUtil.getAllViewCount(VIEW_COUNT_PREFIX);
// 키값 해당하는 게시글 데이터 모두 조회
List<Long> postIds = views.keySet().stream()
.map(key -> key.substring(VIEW_COUNT_PREFIX.length()))
.map(Long::valueOf).toList();
List<Post> postList = postRepository.findAllById(postIds);
List<Post> updatedPostList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Post post : postList) {
Long view = views.get(VIEW_COUNT_PREFIX + post.getId());
if (view != null) {
updatedPostList.add(post.toBuilder().view(view).build());
}
}
// 한번에 처리
postRepository.saveAll(updatedPostList);
}Redis에 존재하는 조회수 데이터를 일정 주기로 DB에 반영하는 작업
- 5분마다 수행
- Redis에서 게시글 조회수에 해당하는 모든 키, 값 쌍을 가져옴
- 해당 키(게시글 아이디 추출)들에 속하는 게시글 데이터 조회
- redis에 저장된 조회수 값을 DB에 반영
PostViewConcurrencyTest.java
@Test
@DisplayName("게시글 조회 수 증가 동시성 문제 테스트")
void successPostViewConcurrencyTest() throws InterruptedException {
// given
Member writer = memberRepository.save(Member.builder()
.username("member1")
.role(Role.USER)
.build());
Post post = postRepository.save(Post.builder()
.title("post1")
.writer(writer)
.view(0L)
.contents(List.of(Content.builder().content(CONTENT).type(ContentType.TEXT).build()))
.build());
int threadCount = 1000;
// when
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadCount);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
executorService.execute(() -> {
try {
postReadService.getPostById(post.getId(), writer);
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
});
}
latch.await();
postReadService.allViewCountFlush();
Post updatedPost = postRepository.findById(post.getId()).orElseThrow();
assertThat(updatedPost.getView()).isEqualTo(threadCount);
System.out.println("게시글 조회수" + " " + updatedPost.getView());
}기존 테스트 메서드에 DB반영 메서드 호출 로직 추가
테스트 결과
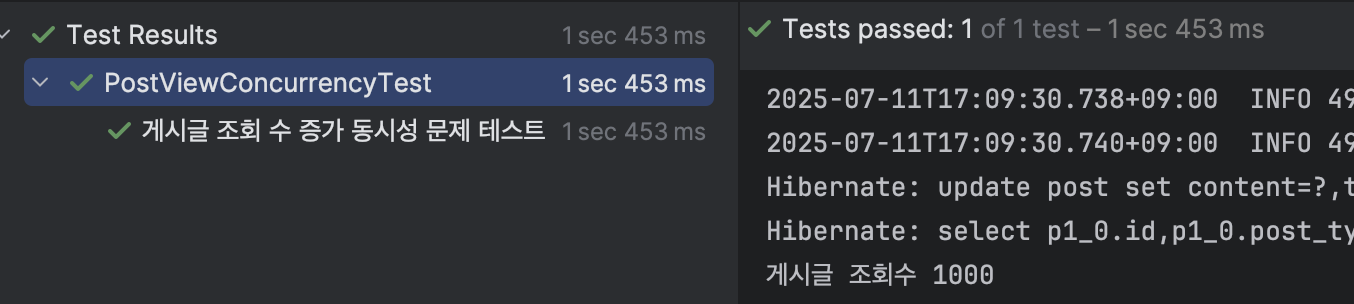
이전과 달리 조회수가 1000회로 잘 나오는 모습
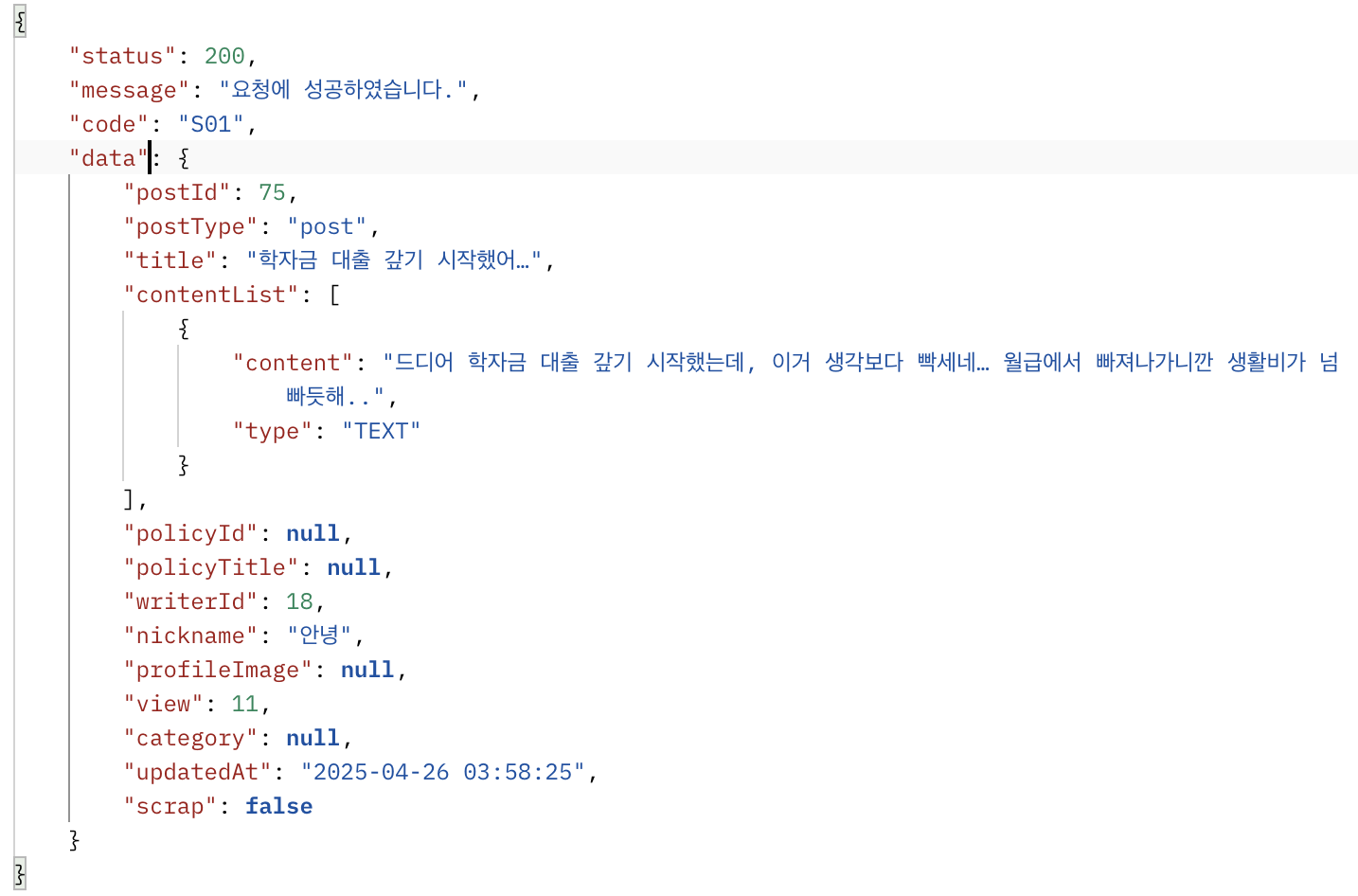

5분 후


update문이 실행 후 DB에 반영되는 모습을 확인 가능
