1. Comparable , Comparator
- 객체를 정렬하기 위한 용도로 사용하는 인터페이스이다
- 단순히 정렬만 하는것이 아니라 객체를 비교할 수 있도록 만들어주는 인터페이스임
primitive타입(byte,int,long)의 변수들은 쉽게 부등호를 이용해 비교가 가능하다
public class PrimitiveTypeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int t1 = 100;
int t2 = 200;
if(a>b) System.out.println("a가 b보다 큼");
}
}-
이런식으로
primitive타입은 비교가 그냥 기본적으로 자바에서 처리가 가능하기 때문에 아무 생각없이 사용하기가 가능하다. -
만약, String 같은 객체나 , 혹은 우리가 만든 객체를 비교하려면 어떻게 해야할까
- 이때 사용하는 것이
Comparator , Comparable이다
- 이때 사용하는 것이
public class ClassExample{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Score studentA = new Score(80, 90,100);
Score studentB = new Score(75, 85,95);
Score studentC = new Score(10, 100,70);
//if (studentA > studentB ) primitive에서 했던것처럼 부등호로 비교가 안됨
}
}
class Score {
int koreanScore; // 국어 점수
int englishScore; // 영어 점수
int mathScore; // 수학 점수
Score(int koreanScore, int englishScore, int mathScore) {
this.koreanScore = koreanScore;
this.englishScore = englishScore;
this.mathScore = mathScore;
}
}- 이런식으로 객체를 생성할 때, 어떤 것을 기준으로 정렬을 해야할지 기준이 없다
- 우선 순위를 우리가 정해줘야한다. 바로
Comparator , Comparable를 이용해서 말이다.
- 우선 순위를 우리가 정해줘야한다. 바로
2. Comparable
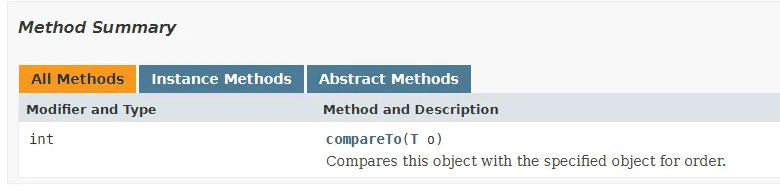
Comparable (Java Platform SE 8 )
- API 공식 문서에 보면 Comparable 인터페이스에는
compareTo (T o)메서드 하나가 선언 되어있다.- 즉, 우리가 사용하기 위해서는 저걸 오버라이드해서 작성해줘야한다.
Comparable은 자기 자신과 매개변수 객체를 비교하는 인터페이스이다.
public class ClassName implements Comparable<객체 타입> {
// 로직
// 필수로 작성해야하는 부분
@Override
public int compareTo(Type o) {
// 비교 부분
}
}- 실제로 사용하는 방법은 위처럼
Comparable인터페이스를 구현해주면 된다- 이때 ,
compareTo부분은 반드시 작성해 줘야하는 부분이다
- 이때 ,
class Score implements Comparable<Score> {
int koreanScore; // 국어 점수
int englishScore; // 영어 점수
int mathScore; // 수학 점수
Score(int koreanScore, int englishScore, int mathScore) {
this.koreanScore = koreanScore;
this.englishScore = englishScore;
this.mathScore = mathScore;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Score o) {
if (this.koreanScore > o.koreanScore) { // 자기 자신이 더 크다면 양수
return 1; //892374 로 적어도 문제없음
} else if (this.koreanScore == o.koreanScore) { // 자기 자신과 같다면 0
return 0;
} else { // 자기 자신보다 작다면 음수
return -1; // -203948 로 적어도 문제없음
}
}
}compareTo는 정수를 반환하도록 되어있는데 자기자신과 객체값이 들어오면 그 값과 비교하여 양수 , 0 , 음수를 반환해줘야한다.- 이때, 값의 크기는 상관이 없고 양수인지 음수인지 0인지가 중요하다 .
class Score implements Comparable<Score> {
int koreanScore; // 국어 점수
int englishScore; // 영어 점수
int mathScore; // 수학 점수
Score(int koreanScore, int englishScore, int mathScore) {
this.koreanScore = koreanScore;
this.englishScore = englishScore;
this.mathScore = mathScore;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Score o) {
// 자기 자신과 파라미터값의 차를 이용해서
// 자기 자신이 더 크면 양수 , 같으면 0 작으면 음수로 표현이 가능하다
return this.koreanScore - o.koreanScore;
}
}- -1 ,1 , 0 을 꼭 반환하는 것이 아니라, 양수인지 음수인지 0인지가 중요하다면 if문을 여러개 써서 복잡하게 할 것이 아니라 단순히 차이를 비교해서 값이 리턴되도록해 간단하게 표현이 가능하다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Score studentA = new Score(80, 90,100);
Score studentB = new Score(75, 85,95);
Score studentC = new Score(10, 100,70);
int test = studentA.compareTo(studentB);
if (test>0) {
System.out.println("studentA의 국어 점수가 더 높습니다");
} else if (test ==0) {
System.out.println("국어 점수가 서로 같습니다");
} else {
System.out.println("studentB의 국어 점수가 더 높습니다");
}
}
}
class Score implements Comparable<Score> {
int koreanScore; // 국어 점수
int englishScore; // 영어 점수
int mathScore; // 수학 점수
Score(int koreanScore, int englishScore, int mathScore) {
this.koreanScore = koreanScore;
this.englishScore = englishScore;
this.mathScore = mathScore;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Score o) {
return this.koreanScore - o.koreanScore;
}
}
//결과 : studentA의 국어 점수가 더 높습니다3.Comparator
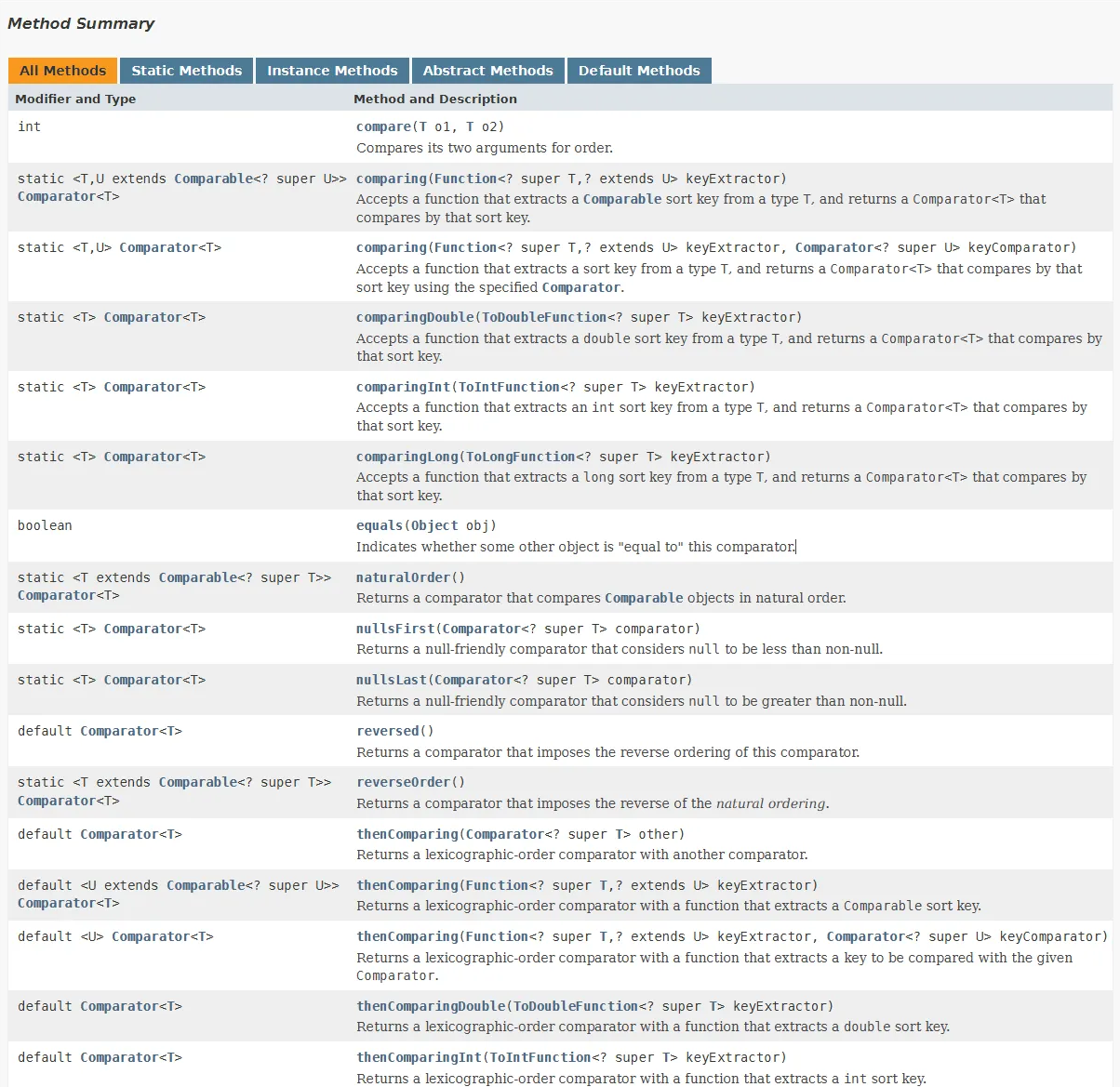
Comparator (Java Platform SE 8 )
- 공식 API 문서에 보면 여러 메서드들이 많이 존재하는데
compare(T o1,T o2)를 이용해서 객체를 비교해주면 된다 - 여기서
Comparable과 차이점이 생기게 되는데 ,Comparable은 자기 자신과 비교했다면Comparator는 파라미터로 들어온 두 객체를 비교하는 것이다
import java.util.Comparator; // import 해줘야 사용가능
public class ClassName implements Comparator<객체 타입> {
// 로직 작성
// 필수로 작성해야하는 부분
@Override
public int compare(Type o1, Type o2) {
// 비교 부분
}
}- 기본 구성은 위처럼 되어있다.
class Score implements Comparator<Score> {
int koreanScore; // 국어 점수
int englishScore; // 영어 점수
int mathScore; // 수학 점수
Score(int koreanScore, int englishScore, int mathScore) {
this.koreanScore = koreanScore;
this.englishScore = englishScore;
this.mathScore = mathScore;
}
@Override
public int compare(Score o1,Score o2) {
if (o1.koreanScore > o2.koreanScore) { // 자기 자신이 더 크다면 양수
return 1; //892374 로 적어도 문제없음
} else if (o1.koreanScore == o2.koreanScore) { // 자기 자신과 같다면 0
return 0;
} else { // 자기 자신보다 작다면 음수
return -1; // -203948 로 적어도 문제없음
}
}
}- 자기 자신과 비교를 진행했던
Comparable과 다르게 , 파라미터로 들어온 o1과 o2의 koreanScore를 비교해주는 것이다.- 이때, compare의 o1을 선행 원소 , o2는 후행 원소라고 한다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Score studentA = new Score(80, 90,100);
Score studentB = new Score(75, 85,95);
Score studentC = new Score(10, 100,70);
int test = studentC.compare(studentA,studentB);
if (test>0) {
System.out.println("studentA의 국어 점수가 더 높습니다");
} else if (test ==0) {
System.out.println("국어 점수가 서로 같습니다");
} else {
System.out.println("studentB의 국어 점수가 더 높습니다");
}
}
}
class Score implements Comparator<Score> {
int koreanScore; // 국어 점수
int englishScore; // 영어 점수
int mathScore; // 수학 점수
Score(int koreanScore, int englishScore, int mathScore) {
this.koreanScore = koreanScore;
this.englishScore = englishScore;
this.mathScore = mathScore;
}
@Override
public int compare(Score o1,Score o2) {
return o1.koreanScore - o2.koreanScore;
}
}
//결과 : studentA의 국어 점수가 더 높습니다studentC.compare(studentA,studentB);이런식으로 사용이 가능하다.- 코드를 보면 studentC 객체의 compare 메서드를 이용해서 비교를 하는데 , 내부에서는 두 매개변수인 studentA(o1), studentB(o2) 가 비교되는 것이기 때문에 studentC 와 관계 없이 두 객체를 비교한 값을 리턴하게 된다.