036 서비스 프로그래밍 (C++)
참고 링크 : 오로카 36강
1. 서비스(service)
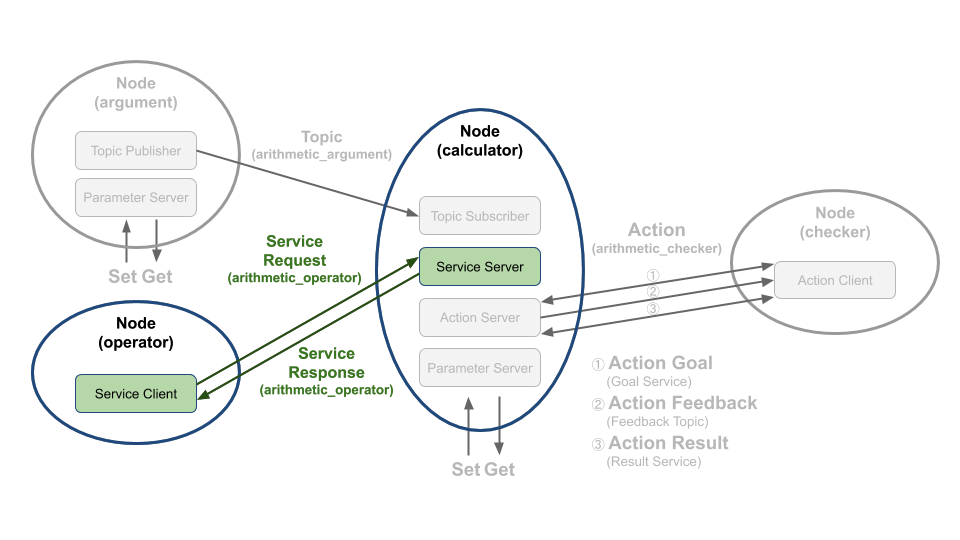
이번 포스트에서는 34강에서 실행했었던 topic_service_action_rclcpp_example의 service client와 server를 작성해보겠다. 서비스 요청 값으로는 연산자(더하기[ + ], 빼기 [ - ], 곱하기 [ * ], 나누기 [ / ])를 임의로 선택 한후에 보낼 것이다. 그리고 기존에 저장된 변수 a, b를 요청 값으로 받은 연산자로 계산하여 그 결괏값을 서비스 응답 값으로 보내는 프로그램을 짜볼 것이다.
2. 서비스 서버 코드
Calculator 노드는 토픽 서브스크라이버, 서비스 서버, 액션 서버를 모두 포함하고 있어서 매우 길기 때문에 전체 코드를 강좌 글에 담는 것은 생략하도록 하고 전체 소스 코드 중 서비스 서버와 관련한 코드만 살펴보도록 하겠다.
topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/include/calculator/calculator.hpp
topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/src/calculator/calculator.cpp
Calculator 클래스는 rclcpp::node 를 상속하고 있으며 생성자에서 'calculator' 라는 노드 이름으로 초기화되었다. arithmetic_argument_server 멤버변수는 rclcpp::Service 타입의 스마트포인터변수로 서비스명과 콜백함수를 인자로 받는 create_service 함수를 통해 실체화 된다. create_service 함수는 rclcpp::node클래스에 정의되어있다.
해당 코드에서는 그림과 같이 arithmetic_operator 서비스명을 사용했고, 콜백함수는 람다 표현식을 이용하여 get_arithmetic_operator를 지정하였다.
//calculator.cpp 중
auto get_arithmetic_operator =
[this](
const std::shared_ptr<ArithmeticOperator::Request> request,
std::shared_ptr<ArithmeticOperator::Response> response) -> void
{
argument_operator_ = request->arithmetic_operator;
argument_result_ =
this->calculate_given_formula(argument_a_, argument_b_, argument_operator_);
response->arithmetic_result = argument_result_;
std::ostringstream oss;// 아래 <<로 계속 연결되는 문장임
oss << std::to_string(argument_a_) << ' ' <<
operator_[argument_operator_ - 1] << ' ' <<
std::to_string(argument_b_) << " = " <<
argument_result_ << std::endl;
argument_formula_ = oss.str();
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "%s", argument_formula_.c_str());
};
//이 부분에서 service로 구현이 된다.
arithmetic_argument_server_ =
create_service<ArithmeticOperator>("arithmetic_operator", get_arithmetic_operator);해당 람다 표현식은 Request와 Response 인자를 가지고 있어서 함수 내부에서 이를 사용할 수 있다. 우선 argument_operator 멤버 변수에 에 요청받은 연산자를 저장한다. 그다음 argument_a, argument_b 와 함께 argument_operator 변수를 calculate_given_formula 함수에 넘겨주어 그 결괏값을 리턴받아 response 변수에 저장하여 서비스를 요청한 클라이언트가 이를 받아볼 수 있도록 한다.그리고 해당 연산식을 ostringstream 라이브러리를 이용해 string 변수에 저장하였다.
여기에서 몇가지 c++언어공부를 잠깐 하고 넘어가자.
- this?
해당 class를 의미하는 것으로, python의 self와 유사한 개념이라고 생각하면 된다. 계속해서 this->~와 같이 자기 자신을 참조하는 연산이 반복되는데, 이경우 함수 자체가 self의 함수를 이용한다고 생각하면 된다. 완전히 python의 self와 동일한 기능이다.- lambda 표현식
람다표현식은 일반적인 함수 정의식 int func(type argument){~~ return}과는 조금 다른 함수선언으로, 다음과 같은 형식을 지닌다.
[] 캡쳐 블록 (사용시 외부 변수를 캡쳐해 람다 몸통에서 사용 가능)
() 전달 인자
-> 반환 타입
{} 함수 몸통따라서 함수명이 없고, header 파일에도 선언을 따로하지 않는다.
위에서 사용된 request 구조체와 calculate_given_formular함수에 대한 내용은 다음과 같다.
-
Request 구조체 <ArithmeticOperator::Request>
msg_srv_action_interface_example/srv/ArithmeticOperator.srv
# Constants int8 PLUS = 1 int8 MINUS = 2 int8 MULTIPLY = 3 int8 DIVISION = 4 -
calculator::calculate_given_formular 함수
topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/src/calculator/calculator.cpp
float Calculator::calculate_given_formula(
const float & a,
const float & b,
const int8_t & operators)
{
float argument_result = 0.0;
ArithmeticOperator::Request arithmetic_operator;
if (operators == arithmetic_operator.PLUS) {
argument_result = a + b;
} else if (operators == arithmetic_operator.MINUS) {
argument_result = a - b;
} else if (operators == arithmetic_operator.MULTIPLY) {
argument_result = a * b;
} else if (operators == arithmetic_operator.DIVISION) {
argument_result = a / b;
if (b == 0.0) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "ZeroDivisionError!");
argument_result = 0.0;
return argument_result;
}
} else {
RCLCPP_ERROR(
this->get_logger(),
"Please make sure arithmetic operator(plus, minus, multiply, division).");
argument_result = 0.0;
}
return argument_result;
}3. 서비스 클라이언트 코드
서비스 서버 역할을 하는 operator 노드의 소스 코드 위치는 다음과같다.
topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/include/arithmetic/operator.hpp
topic_service_action_rclcpp_example/src/arithmetic/operator.cpp
- Operator 클래스(operator.hpp) 노드설정
class Operator : public rclcpp::Node
{
public:
using ArithmeticOperator = msg_srv_action_interface_example::srv::ArithmeticOperator;
explicit Operator(const rclcpp::NodeOptions & node_options = rclcpp::NodeOptions());
virtual ~Operator();
void send_request();
private:
rclcpp::Client<ArithmeticOperator>::SharedPtr arithmetic_service_client_;
};Operator 클래스는 rclcpp::Node 클래스를 상속받는 자식 클래스이고, 생성자에서 rclcpp::NodeOptions를 인자로 받는다. 그리고 서비스 요청을 위한 send_request 함수와 rclcpp::Client 스마트포인터타입의 멤버변수를 가지고 있다.
- Operator 클래스의 생성자 내부(operator.cpp) creat_clienct
Operator::Operator(const rclcpp::NodeOptions & node_options)
: Node("operator", node_options)
{
arithmetic_service_client_ = this->create_client<ArithmeticOperator>("arithmetic_operator");
while (!arithmetic_service_client_->wait_for_service(1s)) {
if (!rclcpp::ok()) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Interrupted while waiting for the service.");
return;
}
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Service not available, waiting again...");
}
}부모 클래스인 rclcpp::Node를 노드명과 node_options 인자로 먼저 초기화해 준다. 그리고 create_client 함수를 통해 서비스명을 인자로 받아 rclcpp::Client를 실체화 시켜준다. 서비스 통신도 DDS를 통해 동작하기에 QoS를 지원한다.
- 실제로 요청을 수행하는 send_request 함수 (operator.cpp) 요청함수
void Operator::send_request()
{
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
std::uniform_int_distribution<int> distribution(1, 4);
auto request = std::make_shared<ArithmeticOperator::Request>();
request->arithmetic_operator = distribution(gen);
using ServiceResponseFuture = rclcpp::Client<ArithmeticOperator>::SharedFuture;
auto response_received_callback = [this](ServiceResponseFuture future) {
auto response = future.get();
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Result %.2f", response->arithmetic_result);
return;
};
auto future_result =
arithmetic_service_client_->async_send_request(request, response_received_callback);
}랜덤한 연산자를 고르기 위해 1 ~ 4 사이의 랜덤한 숫자를 생성하여 request 변수에 저장하게 된다. 그리고 요청에 의한 응답이 왔을 때 불려질 response_received_callback 콜백함수를 람다 표현식을 이용하여 정의했다. 해당 람다 표현식은 인자로 future를 가지고 있는데, 이는 C++11의 비동기식 프로그래밍의 future, promise 개념과 동일하다. 콜백함수가 불려졌다면 future 변수를 통해 response 값을 저장할 수 있고, 이를 로그로 확인할 수 있다. 코드 마지막줄에서 정의된 request 변수와 람다 표현식을 가지고 async_send_request 함수를 통해 비동기식으로 서비스 요청을 보내는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
참고링크 : 동기식 비동기식, future?
4. 서비스 서버, 서비스 클라이언트 복습!
- 서비스 서버 (요청에 응답하는 프로그램)
1) Node 설정
2) create_server 설정
3) 콜백함수 설정
- 서비스 클라이언트 (요청하는 프로그램)
1) Node 설정
2) create_client 설정
3) 요청함수 설정
