Yolact - instance segmentation 공부
Task: instance segmentation
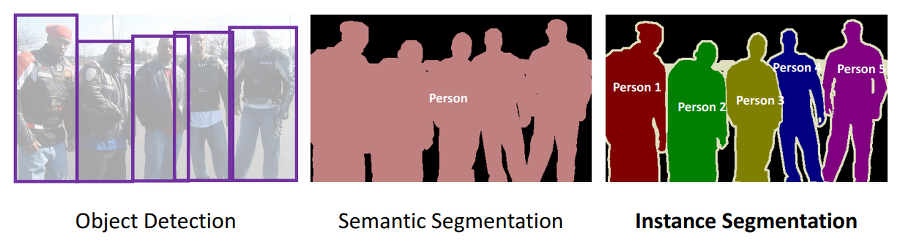
Image Segmentation은 이미지를 픽셀 단위의 다양한 segments로 분할하는 task이다. 쉽게 말하자면, 이미지의 모든 픽셀에 라벨을 할당하는 task이다. Segmentation에는 두 가지 세부문제가 있다. 동일한 클래스에 해당하는 픽셀을 같은 색으로 칠하는 Semantic Segmentation. 동일한 클래스여도 다른 사물의 픽셀이면 다른 색으로 칠하는 Instance Segmentation. 아래 그림을 보면 확연한 차이를 알 수 있다.
-
기존의 instance sementation
여태까지의 instance segmentation 모델은 잘 만들어진 object detection에 병렬적으로 모델을 추가하여 (e.g., mask R-CNN(Faster R-CNN), FCIS(R-FCN) 발전하였다. instance segmentation은 매우 어려운 task이여서, object detection의 SSD 그리고 YOLO 모델과 같이 one-stage로 모델을 짜기 힘들기 때문이다. 위의 two-stage 모델은 mask를 생성하기 위해 feature localization에 많은 신경을 썼다 (e.g., RoI align). 하지만 feature localization 후 mask를 예측하는 모델은 순차적으로 이루어질 수 밖에 없고, 스피드를 올릴 수(accelerate)가 없어진다. FCIS는 이를 병렬적으로 수행하였지만 과도한 post-processing 때문에 real-time 과는 거리가 있다.
-
YOLACT는 localization 단계를 생략한다.
대신에 두 가지 task를 병렬적으로 해결한다.
-
전체 이미지에 대한 prototype mask dictionary 생성
-
instance 마다의 linear combination coefficients 예측
각 instance 마다 예측된 coefficients를 이용하여 prototype mask를 linear하게 합친다. 그 후, 예측된 bounding box로 crop한다. 자세한 내용은 Method 부분에서 설명하겠다.
저자는 위 두 task를 이용하면, 네트워크 스스로 (시각적, 공간적, 의미적으로) 비슷한 instance를 다르게 나타내는 instance mask가 잘 localize 될 수 있도록 학습 되어진다고 하였다.
-
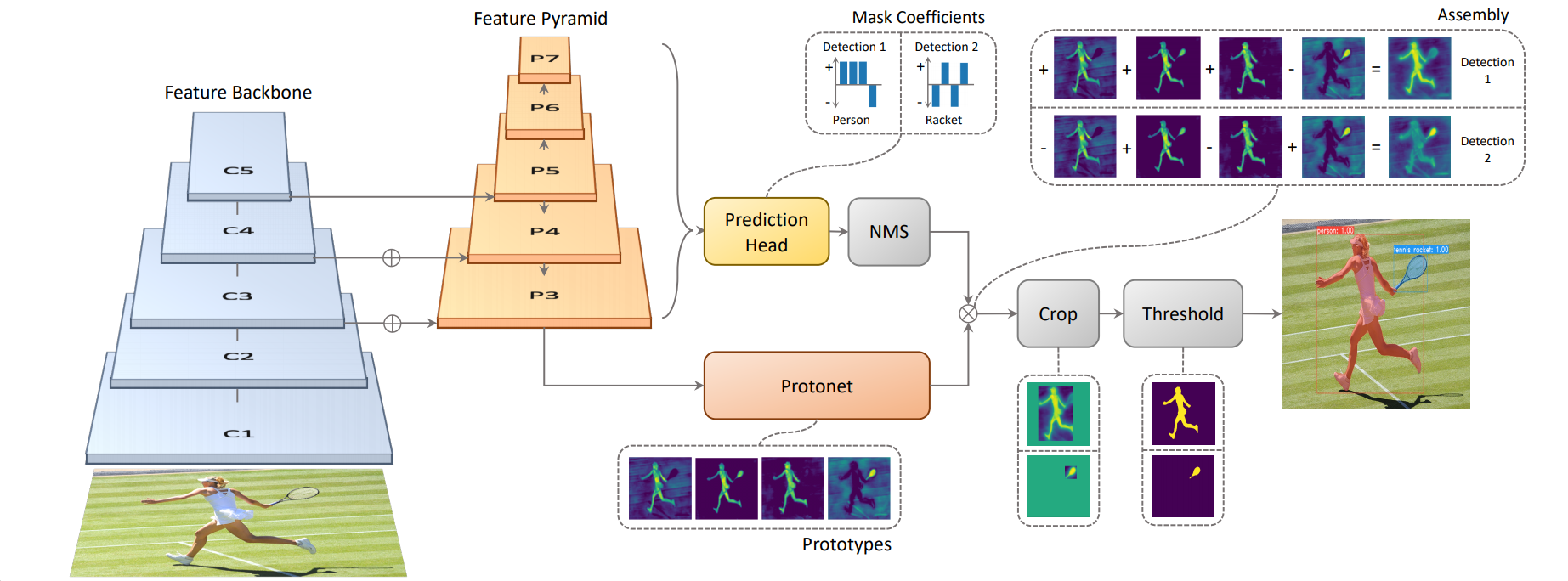
기본 모델은 one-stage object detection 모델인 RetinaNet을 수정하여 사용하였다. 이 one-stage 모델에 feature localization step 없이 mask branch를 추가하기 위해서 instance segmentation task를 두 가지의 간단한 task로 병렬 처리 한다. 위 그림을 보면 Protonet과 Prediction Head로 각각 병렬 처리 되는 것을 알 수 있다.
- FCN을 사용하여 instance에 의존하지 않은 image 크기의 prototype masks 생성하는 task
- prototype 공간에서 instance의 정보를 가진 mask coefficients를 예측하기 위한 object detection task
두 task의 결과물을 linear하게 합쳐서(combine), NMS를 통해 살아남은 instance의 mask를 생성한다.
저자는 masks는 공간적으로 일관성(spatially coherent)이 있기 때문에 위 방식을 선택했다고 한다. semantic한 결과를 얻을 수 있는 fc layer을 통해 mask coefficients를 예측하고, spatially coherent에 탁월한 conv layer을 통해 prototype masks를 생성하였다. 또한 두 결과물을 합칠때 생기는 계산량은 단순한 매트릭스 곱셈이기 때문에 빠르다.
- NMS에서나온 mask의 값과 밑에서 나온 prototype masks의 결과값을 합쳐서 mask값을 결정한다.
Prototype Generation
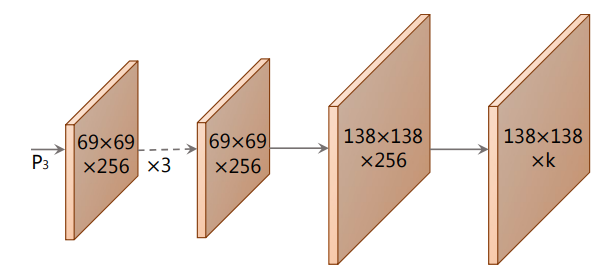
prototype masks를 생성하기 위해 FCN을 사용하였고, 최종 layer은 k 채널을 가지도록 하였다. 이로써 총 k개의 prototype masks를 생성한다.
P3인 경우 deep한 backbone의 featuremap이고, upsample을 하였기 때문에 조그마한 물체에도 좋은 성능을 내는 고 사양 masks를 얻을 수 있다. 마지막으로 ReLU activation function을 사용하여 background를 확실히 구분하였다.
-
YOLACT의 네트워크는 ResNet101 + FPN 을 이용하여 RetinaNet에 기반한 구조
ResNetBackbone( (layers): ModuleList( (0): Sequential( (0): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) (downsample): Sequential( (0): Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (1): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(256, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (2): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(256, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(64, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) ) (1): Sequential( (0): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(128, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) (downsample): Sequential( (0): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (1): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(512, 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d (128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(128, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (2): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(512, 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(128, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (3): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(512, 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(128, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) ) (2): Sequential( (0): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(512, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) (downsample): Sequential( (0): Conv2d(512, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (1): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (2): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (3): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (4): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (5): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (6): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (7): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (8): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (9): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (10): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (11): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (12): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (13): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (14): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (15): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (16): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (17): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (18): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (19): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (20): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (21): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (22): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(256, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) ) (3): Sequential( (0): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(1024, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(512, 2048, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(2048, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) (downsample): Sequential( (0): Conv2d(1024, 2048, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(2048, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (1): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(2048, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(512, 2048, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(2048, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) (2): Bottleneck( (conv1): Conv2d(2048, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv2): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn2): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (conv3): Conv2d(512, 2048, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (bn3): BatchNorm2d(2048, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) ) ) ) (conv1): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), padding=(3, 3), bias=False) (bn1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (relu): ReLU(inplace=True) (maxpool): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) )
-
Protonet Network
python Sequential( (0): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (1): ReLU(inplace=True) (2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (3): ReLU(inplace=True) (4): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (5): ReLU(inplace=True) (6): InterpolateModule() (7): ReLU(inplace=True) (8): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (9): ReLU(inplace=True) (10): Conv2d(256, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1)) ) output : torch.Size([4, 138, 138, 32])Mask Coefficients
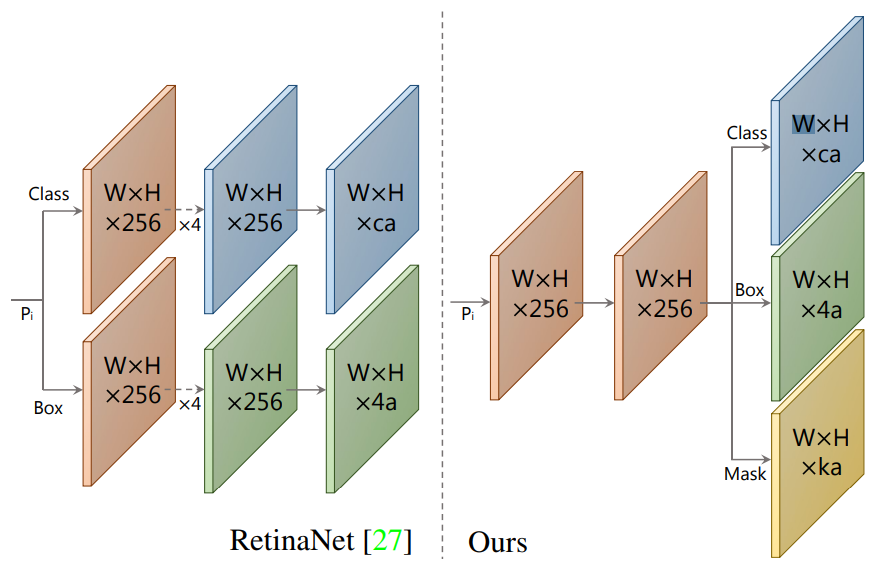
기존 anchor box를 이용하여 object detect하는 모델들은 두 가지를 예측하였다.
- c class confidences
- x, y, w, h의 4 bounding box regressors
이 논문에서는
- k mask coefficients
를 추가로 예측하여 각 prototype에 해당하는 정보를 가지고있다. 결국에는 한 anchor 당 4 + c + k 개의 값을 예측한다.
- 실제 코드상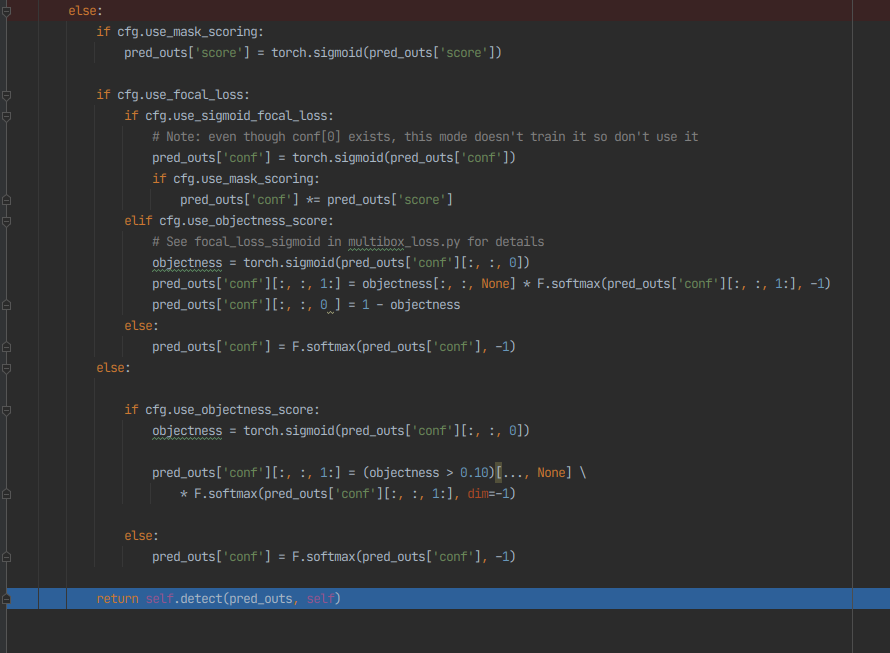
- detection 결과-
FPN make layer
def make_net(in_channels, conf, include_last_relu=True): """ A helper function to take a config setting and turn it into a network. Used by protonet and extrahead. Returns (network, out_channels) """ def make_layer(layer_cfg): nonlocal in_channels # Possible patterns: # ( 256, 3, {}) -> conv # ( 256,-2, {}) -> deconv # (None,-2, {}) -> bilinear interpolate # ('cat',[],{}) -> concat the subnetworks in the list # # You know it would have probably been simpler just to adopt a 'c' 'd' 'u' naming scheme. # Whatever, it's too late now. if isinstance(layer_cfg[0], str): layer_name = layer_cfg[0] if layer_name == 'cat': nets = [make_net(in_channels, x) for x in layer_cfg[1]] layer = Concat([net[0] for net in nets], layer_cfg[2]) num_channels = sum([net[1] for net in nets]) else: num_channels = layer_cfg[0] kernel_size = layer_cfg[1] if kernel_size > 0: layer = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, num_channels, kernel_size, **layer_cfg[2]) else: if num_channels is None: layer = InterpolateModule(scale_factor=-kernel_size, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False, **layer_cfg[2]) else: layer = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, num_channels, -kernel_size, **layer_cfg[2]) in_channels = num_channels if num_channels is not None else in_channels # Don't return a ReLU layer if we're doing an upsample. This probably doesn't affect anything # output-wise, but there's no need to go through a ReLU here. # Commented out for backwards compatibility with previous models # if num_channels is None: # return [layer] # else: return [layer, nn.ReLU(inplace=True)] -
ap 계산
def get_ap(self) -> float: """ Warning: result not cached. """ if self.num_gt_positives == 0: return 0 # Sort descending by score self.data_points.sort(key=lambda x: -x[0]) precisions = [] recalls = [] num_true = 0 num_false = 0 # Compute the precision-recall curve. The x axis is recalls and the y axis precisions. for datum in self.data_points: # datum[1] is whether the detection a true or false positive if datum[1]: num_true += 1 else: num_false += 1 precision = num_true / (num_true + num_false) recall = num_true / self.num_gt_positives precisions.append(precision) recalls.append(recall) # Smooth the curve by computing [max(precisions[i:]) for i in range(len(precisions))] # Basically, remove any temporary dips from the curve. # At least that's what I think, idk. COCOEval did it so I do too. for i in range(len(precisions)-1, 0, -1): if precisions[i] > precisions[i-1]: precisions[i-1] = precisions[i] # Compute the integral of precision(recall) d_recall from recall=0->1 using fixed-length riemann summation with 101 bars. y_range = [0] * 101 # idx 0 is recall == 0.0 and idx 100 is recall == 1.00 x_range = np.array([x / 100 for x in range(101)]) recalls = np.array(recalls) # I realize this is weird, but all it does is find the nearest precision(x) for a given x in x_range. # Basically, if the closest recall we have to 0.01 is 0.009 this sets precision(0.01) = precision(0.009). # I approximate the integral this way, because that's how COCOEval does it. indices = np.searchsorted(recalls, x_range, side='left') for bar_idx, precision_idx in enumerate(indices): if precision_idx < len(precisions): y_range[bar_idx] = precisions[precision_idx] # Finally compute the riemann sum to get our integral. # avg([precision(x) for x in 0:0.01:1]) return sum(y_range) / len(y_range) def calc_map(ap_data): print('Calculating mAP...') aps = [{'box': [], 'mask': []} for _ in iou_thresholds] for _class in range(len(cfg.dataset.class_names)): for iou_idx in range(len(iou_thresholds)): for iou_type in ('box', 'mask'): ap_obj = ap_data[iou_type][iou_idx][_class] if not ap_obj.is_empty(): aps[iou_idx][iou_type].append(ap_obj.get_ap()) all_maps = {'box': OrderedDict(), 'mask': OrderedDict()} # Looking back at it, this code is really hard to read :/ for iou_type in ('box', 'mask'): all_maps[iou_type]['all'] = 0 # Make this first in the ordereddict for i, threshold in enumerate(iou_thresholds): mAP = sum(aps[i][iou_type]) / len(aps[i][iou_type]) * 100 if len(aps[i][iou_type]) > 0 else 0 all_maps[iou_type][int(threshold*100)] = mAP all_maps[iou_type]['all'] = (sum(all_maps[iou_type].values()) / (len(all_maps[iou_type].values())-1)) print_maps(all_maps) # Put in a prettier format so we can serialize it to json during training all_maps = {k: {j: round(u, 2) for j, u in v.items()} for k, v in all_maps.items()} return all_maps
Loss
classification loss와 box regression loss는 SSD와 같은 방식으로 계산이 된다. 그리고 mask loss는 ground truth와 pixel-wise binary cross entropy(BCE)를 이용하여 계산이된다. 각각 loss에는 weight를 주었는데 classification loss, box regression loss, 그리고 mask loss 각각 1, 1.5, 그리고 6.125를 주었다. 즉 세 loss 중 mask loss에 많은 가중치를 주었다.
최종 mask에서, evaluation 할 때에는 예측한 bounding box를 이용하여 crop한다. 반면에 training 일 때는 작은 object를 잘 보존하기 위해 ground truth bounding box를 이용하여 crop한다. 그리고 mask loss에 ground truth bounding box를 나누어 계산한다.
SSD 방식
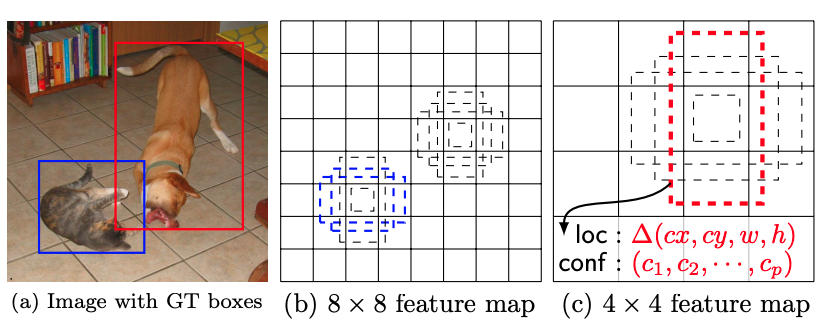
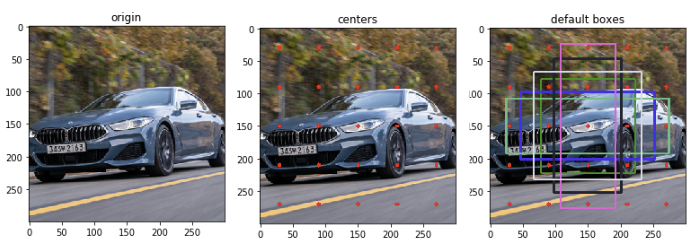
-
mask evaluation
for idx in range(batch_size): truths = targets[idx][:, :-1].data labels[idx] = targets[idx][:, -1].data.long() if cfg.use_class_existence_loss: # Construct a one-hot vector for each object and collapse it into an existence vector with max # Also it's fine to include the crowd annotations here class_existence_t[idx, :] = torch.eye(num_classes-1, device=conf_t.get_device())[labels[idx]].max(dim=0)[0] # Split the crowd annotations because they come bundled in cur_crowds = num_crowds[idx] if cur_crowds > 0: split = lambda x: (x[-cur_crowds:], x[:-cur_crowds]) crowd_boxes, truths = split(truths) # We don't use the crowd labels or masks _, labels[idx] = split(labels[idx]) _, masks[idx] = split(masks[idx]) else: crowd_boxes = None match(self.pos_threshold, self.neg_threshold, truths, priors.data, labels[idx], crowd_boxes, loc_t, conf_t, idx_t, idx, loc_data[idx]) gt_box_t[idx, :, :] = truths[idx_t[idx]] -
Yolact 설치과정
python
$ git clone https://github.com/dbolya/yolact$ cd yolactpython $ pip install torch==1.7.1+cu110 torchvision==0.8.2+cu110 torchaudio==0.7.2 -f [https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html](https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html) - 반드시 torch 1.7.1!! 1.8.1의 경우 에러가 발생함 $ pip install cython $ pip install opencv-python pillow pycocotools matplotlib - YOLACT++ ``` $ cd external/DCNv2 $ python setup.py build develop # 직접 해보지 않았으므로 확인 필요 ``` - Train {Yolact}/scripts/config.py ``` coco2017_dataset = dataset_base.copy({ 'name': 'COCO 2017', 'train_info': '/mnt/data/COCO/coco2017/annotations/instances_train2017.json', 'valid_info': '/mnt/data/COCO/coco2017/annotations/instances_val2017.json', 'label_map': COCO_LABEL_MAP }) # path만 수정해주면 됨 ``` - eval $ python [eval.py](http://eval.py/) --trained_model=weights/yolac t_base_54_800000.pth --score_threshold=0.15 --top_k=15 --video_multiframe=4 --video=my_video.mp4 위에 해당하는 파라미터를 넣어주면 됨
