오늘은 Core Data Relationship과 비슷하지만? 다른 Fetched Property에 대해서 알아보겠습니다.
외국의 글을 보면 두 방법의 차이점은 양방향 또는 단방향 연결성입니다. Relationship 같은 경우에는 두 Entity를 연결해 관계를 설정하는 방법이지만 Fetched Property는 우리가 아는 Computed Property(계산 속성)처럼 특정 조건을 만족하는 Entity의 데이터를 사용하는 방법입니다.
Fetched Property를 사용하는 방법은 Relationship과 큰 차이는 없지만 한 가지 강조하는 사항이 있습니다. 바로 새로고침입니다. 이 부분에 대해서는 코드를 보며 다루도록 하겠습니다.
Fetched Property
제일 먼저 Fetched Property를 추가해야 합니다.
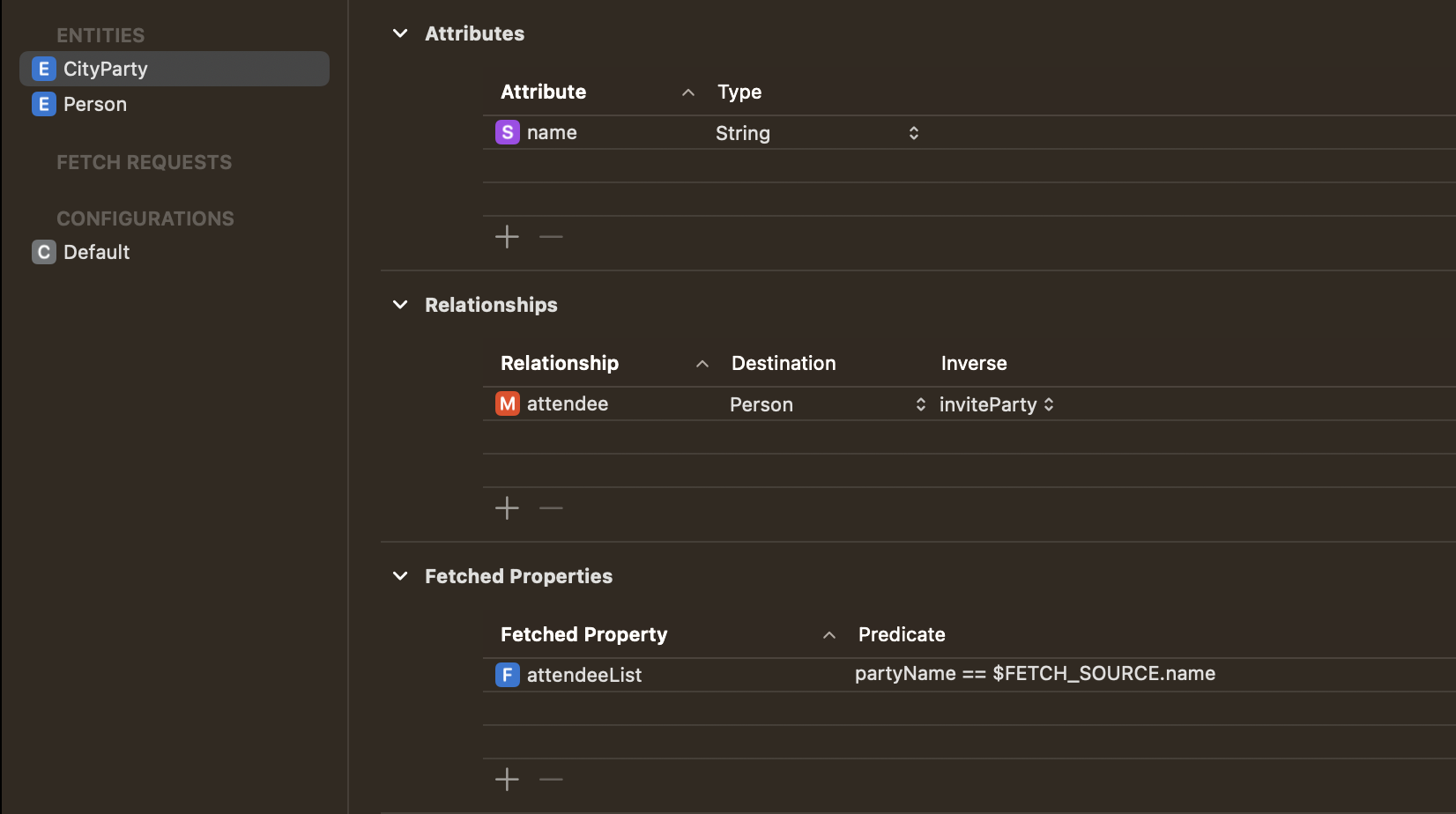
Property에 이름을 설정하고 조건을 추가합니다. 저 같은 경우에는 Person의 partyName과 CityParty의 name이 같다는 조건을 추가했습니다.
Apple Devleoper를 보면 간단한 설명을 확인할 수 있습니다. $FETCH_SOURCE와 $FETCHED_PROPERTY를 이용해 조건을 만들어 사용합니다.
그럼 이제 코드를 확인해 보겠습니다. 그전에 먼저 attendeeList Property를 CityParty에 추가하도록 하겠습니다.
extension CityParty : Identifiable {
var attendeeList: [Person]? {
return value(forKey: "attendeeList") as? [Person]
}
}앱에서 참석자 리스트를 확인하기 위해 사용하는 데이터 타입은 Person Array 타입입니다. value(forKey:) 함수를 이용해 저희가 위에서 설정한 Fetched Property를 만족하는 데이터를 가져와야 합니다.
Person을 생성하는 코드는 Relationship과 큰 차이는 없습니다. 다만 Relationship에서 add 함수를 이용해 CityParty에 attendee를 추가하는 게 아니라 그냥 Person을 생성해 추가하면 됩니다.
// Relationship 추가 방법
let appDelegate = UIApplication.shared.delegate as! AppDelegate
let context = appDelegate.container.viewContext
let request = NSFetchRequest<CityParty>(entityName: "CityParty")
request.predicate = NSPredicate(format: "name = %@", selectedParty as CVarArg)
let partyObject = try! context.fetch(request)[0]
let personObject = NSEntityDescription.insertNewObject(forEntityName: "Person", into: context) as! Person
personObject.setValue(selectedParty, forKey: "partyName")
personObject.setValue(self.textField.text, forKey: "name")
partyObject.addToAttendee(personObject)
do {
try context.save()
} catch {
context.rollback()
}
// Fetched Property
let appDelegate = UIApplication.shared.delegate as! AppDelegate
let context = appDelegate.container.viewContext
let cityParty = NSEntityDescription.insertNewObject(forEntityName: "CityParty", into: context) as! CityParty
let person = Person(context: context)
person.partyName = self.selectedParty
person.name = self.textField.text
do {
try context.save()
} catch {
context.rollback()
}
context.refresh(cityParty, mergeChanges: true) 여기서 처음 보는 refresh 함수를 볼 수 있습니다. 공식 문서를 보면 Fetched Property는 Relationship과 다르게 context가 저장될 때 자동으로 업데이트하지 않기 때문에 refresh를 통해 새로고침을 해주어야 합니다.
마지막으로 Person을 사용하는 쪽에서는 우리가 제일 처음 만들었던 attendeeList를 이용해 파티에 참석하는 사람들의 명단을 확인할 수 있습니다.
var attendee = [String]()
let attendeeList = cityParty.attendeeList
attendeeList?.forEach { person in
attendee.append(person.name!)
}이렇게 오늘은 Core Data의 Fetched Property에 대해서 알아봤습니다. Relationship과 유사하다는 느낌을 많이 받지만 목적에 따라 각각 활용할 수 있는 방법이 다를 것 같습니다.
혹시라도 내용이 부족하거나 활용하신 경험이 있다면 댓글 달아주시면 감사합니다.
