순열 (Permutation)
서로 다른 n개 중 r개를 중복 없이 골라 순서대로 나열하는 것(정렬이 되어 있음)
✔️ 모든 경우의 수를 계산하는 완전 탐색에서 사용하는 알고리즘
예시
{1,2,3} 에서 3개를 뽑는 경우의 수
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 1 3
2 3 1
3 1 2
3 2 1{1,2,3} 에서 2개를 뽑는 경우의 수
1 2
1 3
2 1
2 3
3 1
3 2순열 구현 방식
- Swap을 이용한 순열
- Visited 배열을 이용한 순열
1. Swap을 이용한 순열
✔️ swap 함수를 만들어서 배열들의 값을 직접 바꾸는 방법
✔️ 배열의 첫 값부터 순서대로 하나씩 바꾸며 모든 값을 한번씩 swap

과정
- 0번째 인덱스 원소를 0번째 부터 n-1번째까지 위치를 바꾼다. (ABC, BAC, CBA)
- 1번 과정을 진행해서 나온 경우들을, 1번째 인덱스 원소를 1번째부터 n-1번째까지 위치를 바꾼다.
- 이러한 과정을 n-1번 반복한다.
주의할 점
순열들의 순서가 보장되지 않는다.
ex) C,A,B가 먼저 나오는게 아니라 C,B,A가 먼저 나옴
구현
public void permutation(int[] arr, int n, int r, int depth) {
if(depth == r){
doSomething(); // 마지막 요소까지 도달하였으므로 종료
return;
}
for(int i=depth; i<n; i++){
swap(arr, depth, i); // 현재 인덱스와 depth에 해당하는 요소를 swap
permutation(arr, n, r, depth+1); // depth를 한칸 이동시키고 swap
swap(arr, depth, i); // 원래대로 돌림
}
}
public void swap(int[] arr, int depth, int i){
int temp = arr[depth];
arr[depth] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}2. Visited 배열을 이용한 순열
✔️ visited 배열을 이용
✔️ 사전식으로 순열 구현 가능
✔️ DFS로 구현
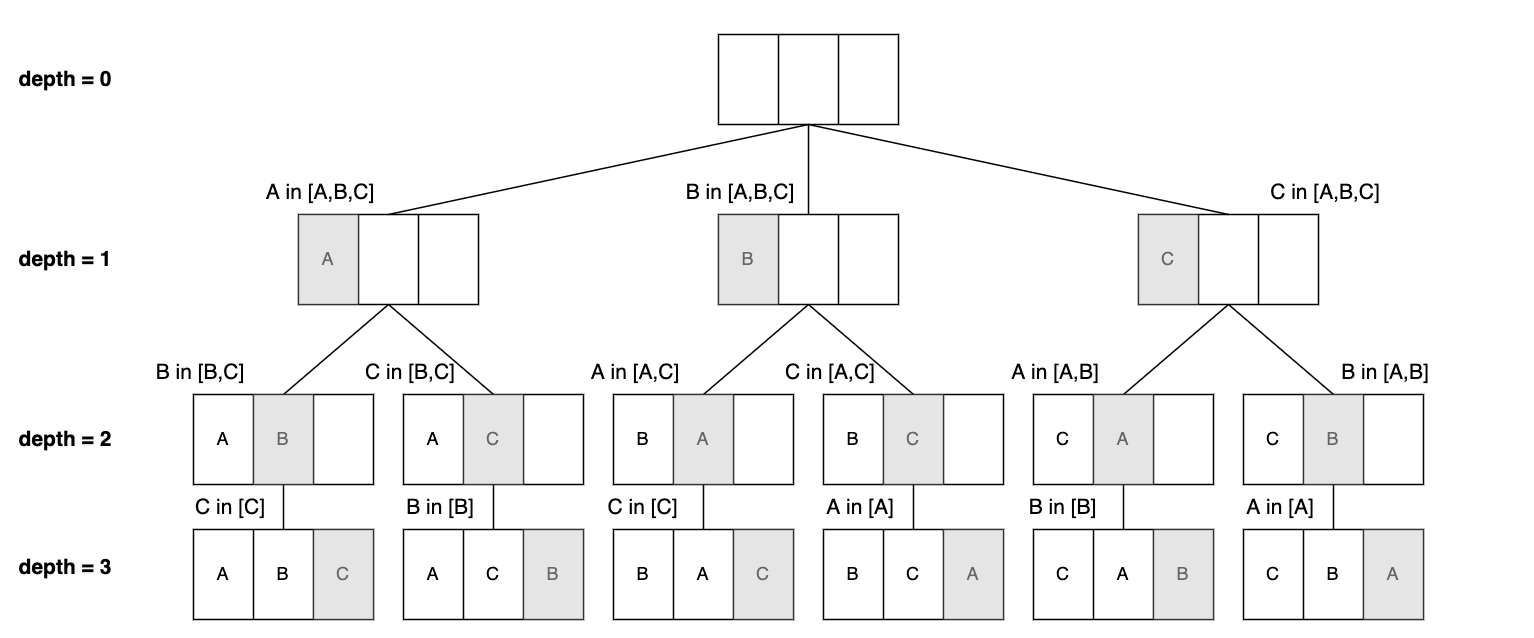
과정
- DFS를 돌면서 모든 인덱스에 방문해 output 배열에 값을 넣는다
- 이미 들어간 값은 visited를 true로 변경해서 중복해서 값이 들어가지 않도록 한다
- 이러한 과정을 depth가 r 값과 같아질 때까지 반복한다
구현
static void perm(int[] arr, int[] output, boolean[] visited, int depth, int n, int r) {
if (depth == r) { // depth가 r이 되면 종료
print(output, r);
return;
}
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
if (visited[i] != true) {
visited[i] = true; // 방문처리
output[depth] = arr[i];
perm(arr, output, visited, depth + 1, n, r);
visited[i] = false; // 방문해제
}
}
}시간 복잡도
✔️ 이기 때문
