9-1. Array
1) array
- 여러 데이터 타입의 값을 순차적으로 나열한 자료 구조
- 배열 리터럴을 통한 생성
- 배열이 가지고 있는 값을 요소라고 부르며 자바스크립트의 "모든 값"은 배열의 요소가 될 수 있음
const arr = ['바나나', '복숭아', '키위']; - 배열 생성자 함수
const arr2 = new Array();- 전달 된 인수가 1개이고, 숫자인 경우 length 프로퍼티 값이 인수인 배열 생성
const arr3 = new Array(10); //[ <10 empty items> ] console.log(arr3);- 전달 된 인수가 2개 이상이거나 숫자가 아닌 경우 인수를 요소로 갖는 배열 생성
const arr4 = new Array(1,2,3); console.log(arr4); const arr5 = new Array('코코아'); console.log(arr5); - Array.of 메소드
- 전달 된 인수를 요소로 갖는 배열 생성
console.log(Array.of(10));- 배열의 요소는 자신의 위치를 나타내는 인덱스를 가지며 배열의 요소에 접근할 때 사용한다
console.log(arr[0]); console.log(arr[1]); console.log(arr[2]);- 배열은 요소의 개수, 즉 배열의 길이를 나타내는 length 프로퍼티를 갖는다
- 배열은 별도의 타입이 존재하지 않으며 객체타입이다.
console.log(typeof arr); //Object
2) diffrences from regular array
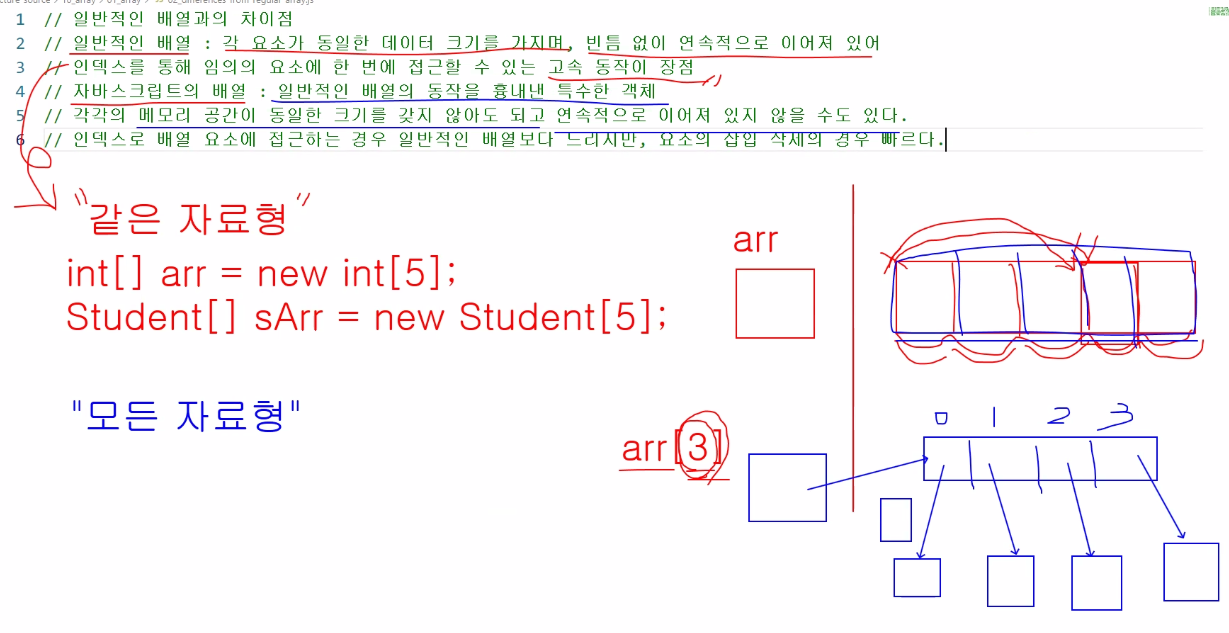
- 일반적인 배열
- 각 요소가 동일한 데이터 크기를 가지며, 빈틈 없이 연속으로 이어져 있어 인덱스를 통해 임이의 요소에 한 번에 접근할 수 있는 고속 동작이 장점
- 자바스크립트의 배열
- 일반적인 배열의 동작을 흉내낸 특수한 객체
- 각각의 메모리 공간이 동일한 크기를 갖지 않아도 되고 연속적으로 이어져 있지 않을 수도 있다.
- 인덱스로 배열 요소에 접근하는 경우 일반적인 배열보다 느리지만, 요소 삽입 삭제의 경우 빠르다.
- 인덱스가 아니라 하나의 프로퍼티 키 값으로 생각
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors([1,2,3]));- 자바스크립트의 모든 값이 객체의 프로퍼티 값이 될 수 있으므로 모든 값이 배열의 요소가 될 수 있다.(객체도 가능)
const arr = [ '홍길동', 20, true, null, undefined, NaN, Infinity, [], {}, function(){} ];
3) length property
- 요소의 개수를 나타내는 0 이상의 정수 값을 갖는다
- length property 값은 배열에 요소를 추가하거나 삭제하면 자동으로 갱신된다.
arr.push(6);
console.log(arr);
console.log(arr.length);
arr.pop();
console.log(arr);
console.log(arr.length);- length property에 임의의 숫자 값을 명시적으로 할당 할 수 있다.
arr.length = 3;
console.log(arr);
console.log(arr.length);- 현재 length보다 작은 숫자 값을 할당하면 배열의 길이가 줄어든다
- 현재 length보다 큰 숫자를 할당하면 length 프로퍼티 값은 변경되지만 배열의 길이가 늘어나지는 않는다.
arr.length = 10;
console.log(arr);
console.log(arr.length);
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(arr));- 자바스크립트는 배열의 요소가 연속적으로 위치하지 않고 일부가 비어있는 희소 배열을 문법적으로 허용한다.
const sparse = [ , 2, 4];
console.log(sparse);
console.log(sparse.length);
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(sparse));9-2. Array Method
1) array method
const arr = [];
// 배열의 생성자 함수는 Array
console.log(arr.constructor === Array); // true
// 배열의 프로토타입 객체는 Array.prototype
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(arr) === Array.prototype); // true
// => Array.prototype은 배열을 위한 빌트인 메서드를 제공한다.- Array.prototype.indexOf
- 배열에서 요소가 위차한 인덱스를 리턴
- lastIndexOf
- 배열의 요소가 위치한 마지막 인덱스를 리턴
- 맨 끝의 인덱스에서부터 찾는 요소가 있는 인덱스를 리턴
- includes
- 배열에 해당 요소 포함 여부 리턴
const foodList = ['물회', '삼계탕', '냉면', '수박', '물회'];
console.log(`foodList.indexOf('물회') : ${foodList.indexOf('물회')}`); // 0
// 1번 인덱스에서부터 물회가 위치한 인덱스 찾기(0번 인덱스는 무시)
console.log(`foodList.indexOf('물회', 1) : ${foodList.indexOf('물회', 1)}`); // 4
console.log(`foodList.indexOf('삼겹살') : ${foodList.indexOf('삼겹살')}`); // -1
console.log(`foodList.lastIndexOf('물회') : ${foodList.lastIndexOf('물회')}`); // 4
console.log(`foodList.lastIndexOf('물회', 1) : ${foodList.lastIndexOf('물회', 1)}`); // 0
console.log(`foodList.lastIndexOf('삼겹살') : ${foodList.lastIndexOf('삼겹살')}`); // 요소가 없으면 -1
console.log(`foodList.includes('물회') : ${foodList.includes('물회')}`); // true
console.log(`foodList.includes('삼겹살') : ${foodList.includes('삼겹살')}`); // false- Array.prototype.push
- 배열의 맨 뒤에 요소 추가
- Array.prototype.pop
- 배열의 맨 뒤에 요소 제거
const chineseFood= ['짜장면', '짬뽕', '우동'];
console.log(`push 전 chineseFood : ${chineseFood}`); // 짜장면,짬뽕,우동
chineseFood.push('탕수육');
chineseFood.push('양장피');
// chineseFood.push('탕수육', '양장피');
console.log(`push 후 arr : ${chineseFood}`); // 짜장면,짬뽕,우동,탕수육,양장피
console.log(`chineseFood.pop() : ${chineseFood.pop()}`); // 양장피
console.log(`chineseFood.pop() : ${chineseFood.pop()}`); // 탕수육
console.log(`chineseFood.pop() : ${chineseFood.pop()}`); // 우동
console.log(`pop 후 chineseFood : ${chineseFood}`); // 짜장면,짬뽕- Arrays.prototype.unshift
- 배열의 맨 앞에 요소 추가
- 맨 윗줄에 추가한다(머저 입력한 요소가 아래에서부터 위로 추가)
- 한번에 앞에 추가하면 하나의 덩어리로 취급해서 들어간다
- Arrays.prototype.shift
- 배열의 맨 앞 요소 제거 후 반환
const chickenList = ['양념치킨', '후라이드', '파닭'];
console.log(`unshift 전 chickenList : ${chickenList}`); // 양념치킨,후라이드,파닭
// 맨 윗줄에 추가한다(먼저 입력한 요소가 아래에서부터 위로 추가)
chickenList.unshift('간장치킨');
chickenList.unshift('마늘치킨');
// 한번에 앞에 추가하면 하나의 덩어리로 취급해서 들어간다.
// chickenList.unshift('간장치킨', '마늘치킨');
console.log(`unshift 후 chickenList : ${chickenList}`); // 마늘치킨,간장치킨,양념치킨,후라이드,파닭
console.log(`chickenList.shift() : ${chickenList.shift()}`); // 마늘치킨
console.log(`chickenList.shift() : ${chickenList.shift()}`); // 간장치킨
console.log(`chickenList.shift() : ${chickenList.shift()}`); // 양념치킨
console.log(`shift 후 chickenList : ${chickenList}`); // 후라이드,파닭- Array.prototype.concat
- 두 개 이상의 배열을 결합
const idol1 = ['아이브', '오마이걸'];
const idol2 = ['트와이스', '에스파'];
const idol3 = ['블랙핑크', '레드벨벳'];
// 배열명.concat(배열명1, 배열명2, ...)
const mix = idol1.concat(idol2);
const mix2 = idol3.concat(idol1, idol2);
console.log(`idol1 기준으로 idol2 배열을 concat : ${mix}`); // 아이브,오마이걸,트와이스,에스파
console.log(`idol3 기준으로 idol1, idol2 배열을 concat : ${mix2}`); // 블랙핑크,레드벨벳,아이브,오마이걸,트와이스,에스파- Arrays.prototype.slice
- 배열의 요소 선택 잘라내기
- slice(시작인덱스, 종료인덱스)
- 원본 배열 변경 X
- Array.prototype.splice
- 배열의 index 위치의 요소 제거 및 추가
- splice(index, 제거수, 추가값1, 추가값2...)
- 원본 배열 변경 O
// slice(시작인덱스, 종료인덱스)
// 원본 배열 변경 X
console.log(`front.slice(1, 3) : ${front.slice(1, 3)}`); // CSS,JavaScript
console.log(`front : ${front}`); // HTML,CSS,JavaScript,jQuery
// splice(index, 제거수, 추가값1, 추가값2, ...)
// 원본 배열 변경 O
console.log(`front.splice(3, 1, "React") : ${front.splice(3, 1, "React")}`); // jQuery
console.log(`front : ${front}`); // HTML,CSS,JavaScript,React- Array.prototype.join
- 배열을 구분자로 결합하여 문자열로 반환
- 구분자를 쓰지 않으면 ',' 기준으로 결합
const snackList = ['사탕', '초콜렛', '껌', '과자'];
console.log(`snackList.join() : ${snackList.join()}`); // 사탕,초콜렛,껌,과자
console.log(`snackList.join('/') : ${snackList.join('/')}`); // 사탕/초콜렛/껌/과자- Array.prototype.reverse
- 배열의 순서를 뒤집음
- 원본 배열 변경 O
console.log(`[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].reverse() : ${[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].reverse()}`); // 5,4,3,2,12) array higher order function
-
배열 고차 함수
- 고차 함수 : 함수를 인수로 전달 받거나 함수를 반환하는 함수
-
Array.prototype.sort
- 배열을 정렬 기준으로 정렬
let numbers = []; for(let i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++){ numbers[i] = Math.floor(Math.random()*100) + 1; } console.log(`정렬 전 numbers : ${numbers}`);- 오름차순 정렬이 기본 정렬이며 정렬 후 정렬 순서를 유지함
- 배열은 기본적으로 문자열 정렬이 되므로 한자리수, 세자리수가 올바르지 않게 정렬되는 모습을 보임 -> 다른 정렬 기준을 사용하려면 compare 함수를 인수로 전달
numbers.sort(); console.log(`정렬 후 numbers : ${numbers}`); // 숫자 오름차순 정렬 function compare(a,b){ if(a > b) return 1; if(a == b) return 0; if(a < b) return -1; } numbers.sort(compare); console.log(`매개변수로 compare 함수 전달하여 숫자 오름차순 정렬`); console.log(numbers);- 숫자 내림차순 정렬
numbers.sort(function(a,b){return b - a;}); numbers.sort((a,b) => b - a); console.log(`숫자 내림차순 정렬`); console.log(numbers); -
Arrays.prototype.forEach
- for를 대체할 수 있는 함수
- 배열.forEach(function(item, index, array){
// 배열 요소에 각각 실행할 기능 작성
});
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; numbers.forEach(function(item, index, array){ console.log(`itme : ${item}`); console.log(`index : ${index}`); console.log(`array : ${array}`); }); // 각 요소 별로 * 10 한 값을 콘솔에 출력 numbers.forEach(item => console.log(item*10)); -
Array.prototype.map
- 배열 요소 전체를 대상으로 콜백 함수 호출 후 반환 값들로 구성 된 새로운 배열 반환
- 배열.map(function(item, index, array){
//배열 요소 각각에 반환할 새로운 값
});
// true, 1, 'text'로 구성된 배열 types를 item의 자료형 타입으로 변경 const types = [true, 1, 'text'].map(item => typeof item); //boolean, number, String console.log(types); const length = ['apple', 'banana', 'cat', 'dog', 'egg'].map(function(item){return item.length}); console.log(length); -
Arrays.prototype.filter
- 배열 요소 전체를 대상으로 콜백 함수 호출 후 반환 값이 true인 요소로만 구성된 새로운 배열 반환
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; const odds = numbers.filter(item => item % 2); -
Array.prototype.reduce
- 배열을 순회하며 각 요소에 대하여 이전의 콜백 함수 실행 반환값을 전달하여 콜백함수를 실행하고 그 결과를 반환
- previousValue : 이전 콜백의 반환값
- currentValue : 배열 요소의 값
- currentIndex : 인덱스
- array : 호출한 배열
numbers.reduce(function(previousValue, currentValue, currentIndex, array){ console.log(`previousValue : ${previousValue}`); console.log(`currentValue : ${currentValue}`); console.log(`curruentIndex : ${currentIndex}`); console.log(`array : ${array}`); }); // 합산 const sum = numbers.reduce(function(previousValue, curruentValue){ return previousValue + curruentValue; }); /* previousValue = 1, currentValue = 2 return 3 previousValue = 3, currentValue = 3 return 6 previousValue = 6, currentValue = 4 return 10 previousValue = 10, currentValue = 5 return 15 */ console.log(`sum : ${sum}`); // 최대값 취득 const max = numbers.reduce(function(pre, cur){ return pre > cur ? pre : cur; }); console.log(`max : ${max}`); -
Arrays.prototype.some
- 배열 내 일부 요소가 콜백 함수의 테스트를 통과하는지 확인하여 그 결과를 boolean으로 반환
- 콜백 함수 테스트의 true 값이 1개 이상이라도 존재하면 true 반환
// 배열 내 요소 중 10보다 큰 값이 1개 이상 존재하는지 확인 let result = [1, 5, 3, 2, 4].some(item => item > 10); console.log(`result : ${result}`); // 배열 내 요소 중 3보다 큰 값이 1개 이상 존재하는지 확인 result = [1, 5, 3, 2, 4].some(item => item > 3); console.log(`result : ${result}`); -
Arrays.prototype.every
- 배열 내 모든 요소가 콜백 함수의 테스트를 통과하는지 확인하여 그 결과를 boolean으로 반환
// 배열 내 요소의 모든 값이 3보다 큰지 확인 result = [1, 5, 3, 2, 4].every(item => item > 3); console.log(`result : ${result}`); // 배열 내 요소의 모든 값이 0보다 큰지 확인 result = [1, 5, 3, 2, 4].every(item => item > 0); console.log(`result : ${result}`); -
Arrays.prototype.find
- 배열을 순회하며 각 요소에 대하여 인자로 주어진 콜백 함수를 실행하여 그 결과가 참인 첫번째 요소를 반환
- 참인 요소가 존재하지 않는다면 undefined 반환
- 무조건 하나의 값만 반환
-
Arrays.prototype.findIndex
- 배열을 순회하며 각 요소에 대하여 인자로 주어진 콜백 함수를 실행하여 그 결과가 참인 첫번째 요소의 인덱스를 반환.
- 참인 요소가 존재하지 않는다면 -1 반환
const student = [
{name : '유관순', score : 90},
{name : '홍길동', score : 80},
{name : '장보고', score : 70}
];
result = student.find(item => item.name === '유관순');
console.log(result);
result = student.findIndex(item => item.name === '유관순');
console.log(result);
result = student.find(item => item.name === '신사임당');
console.log(result);
result = student.findIndex(item => item.name === '신사임당');
console.log(result);- find, findIndex는 일치하는 요소를 찾으면 더 이상 차색하지 않고 하나의 요소, 인덱스만 반환
- 만약 60점 이상인 학생들을 찾고 싶다면? filter 사용
result = student.find(item => item.score >= 60);
console.log(result);