이 글은 Newlecture의 자바 컬렉션과 제네릭 강의를 보며 정리한 글입니다.
🤍 JAVA 컬렉션과 제네릭 🤍

🤍 컬렉션이란 🤍
컬렉션은 '가변길이' 배열이 필요할 때 사용하는 객체
데이터를 수집하고 관리해주는 객체

↓
컬렉션을 사용하는 이유
① 데이터 관리를 직접할 필요가 없다.
② 공간을 필요에 따라서 유동적으로 바꿀 수 있기 때문이다. (배열을 사용할 경우 공간의 크기를 직접 정하고, 그 공간을 필요에 따라서 바꿀 수가 없었다.)
🤍 정수형 컬렉션 구현하기 🤍
데이터를 수집하고 관리해주는 객체
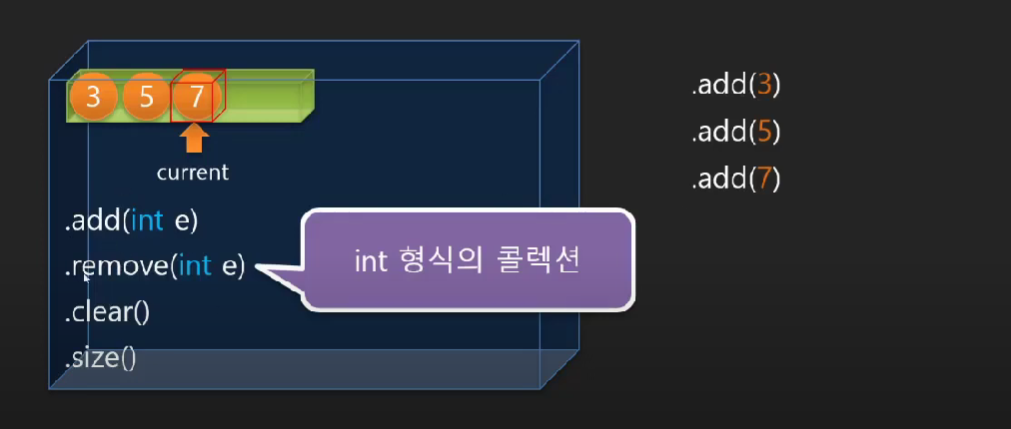
CollectionPrj 생성 → com.newlecture.app.util package 생성 → IntList.java
IntList.java
package com.newlecture.app.util;
public class IntList {
private int[] nums;
private int current;
// 생성자 추가
public IntList() {
nums = new int[3];
current = 0;
}
public void add (int num) {
nums[current] = num;
current++;
}
public void clear() {
/* for (int i=0; i<current; i++)
nums[i] = 0; */
//nums = new int[3];
current = 0;
}
public int size() {
return current;
}
public int get(int index) {
if(current <= index)
// 입력값에 대한 오류 = 예외처리
throw new IndexOfBoundsException();
return nums[index];
}
}Program.java
package com.newlecture.app.util;
public class Program {
public static void main (String[] args) {
IntList list = new IntList();
list.add(3);
list.add(5);
int size = list.size();
System.out.printlf("size : %d\n", size);
list.clear();
size = list.size();
System.out.printlf("size : %d\n", size);
list.add(7);
int num = list.get(0);
System.out.printlf("num : %d\n", num);
num = list.get(1);
}
}🤍 Object 형식 🤍
모든 데이터를 목록으로 관리할 수 있는 자료형식이 있나요?
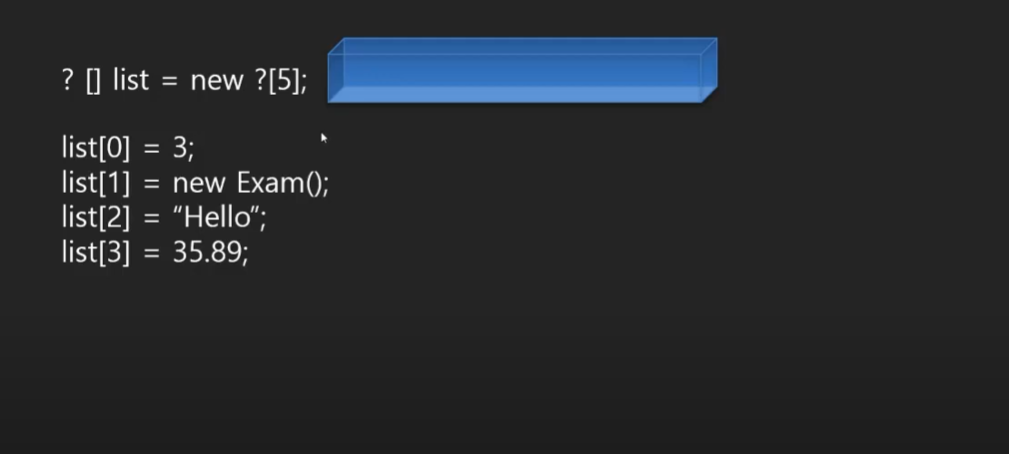
최상위 추상 클래스 - 모든 클래스는 Object이다. 그러면 primitive 형식과의 관계는?

↓
Object가 있어야 하는 이유 : 모든 객체를 섭렵할 수 있는 범용 자료형이기 때문이다.
모든 객체를 묶을 수 있는 범용 자료형식
Object 형식으로 참조 할 수 없는 객체는 없다.
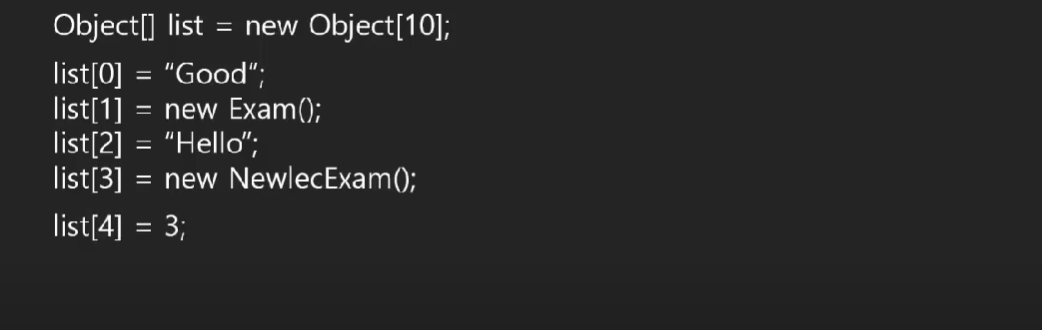
↓
참조변수는 공간이 없기에 추가된 list[4] = 3; 즉, 값을 참조할 수 없다.
🤍 Wrapper 클래스와 Auto Boxing / UnBoxing 🤍

Boxing에 사용되는 Wrapper 클래스
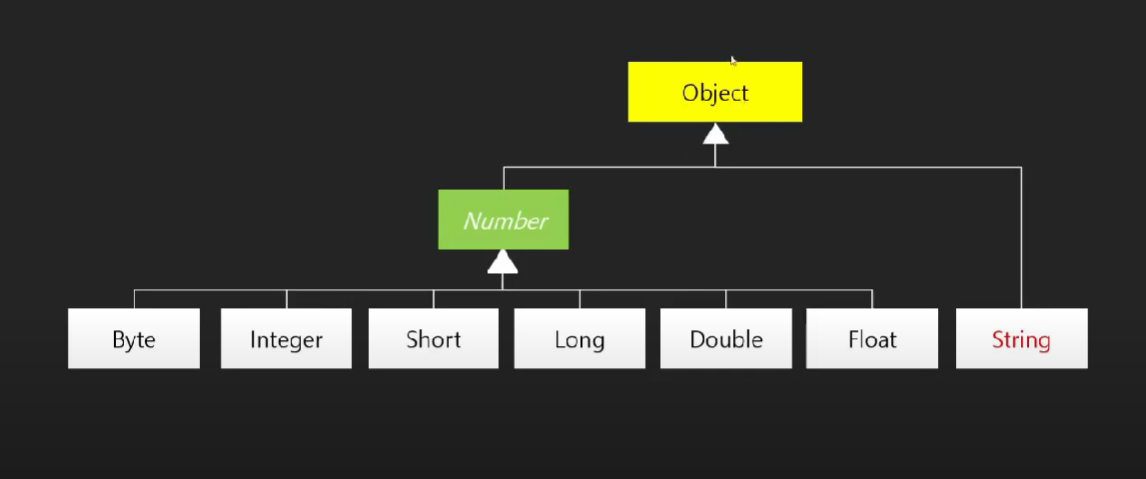
값 형식과 참조형식
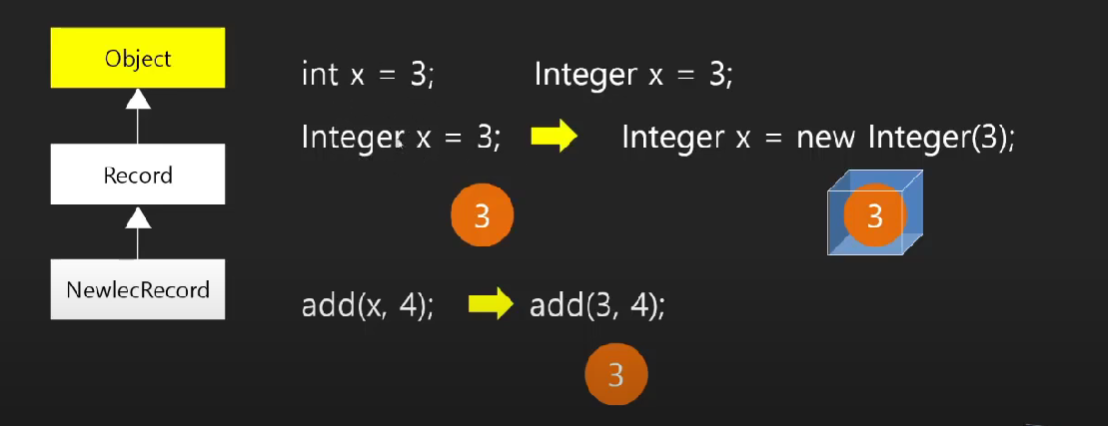
Integer가 아닌 Object형식으로 진행하여도 Boxing과 UnBoxing 이 일어난다.
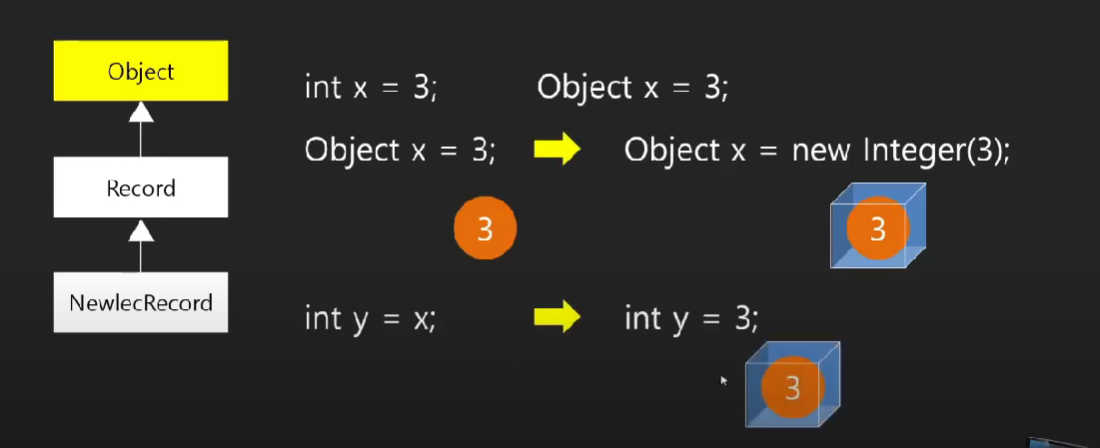
모든 데이터를 단잏라게 일괄 관리하기 위한 방법이 필요하다.

↓
일괄적으로 관리할 때, Object 배열을 만들어서 모든 데이터 형식을 다 담아두어도 문제되지 않는다.
🤍 Object 컬렉션으로 변경하기 🤍
범용 컬렉션의 필요성
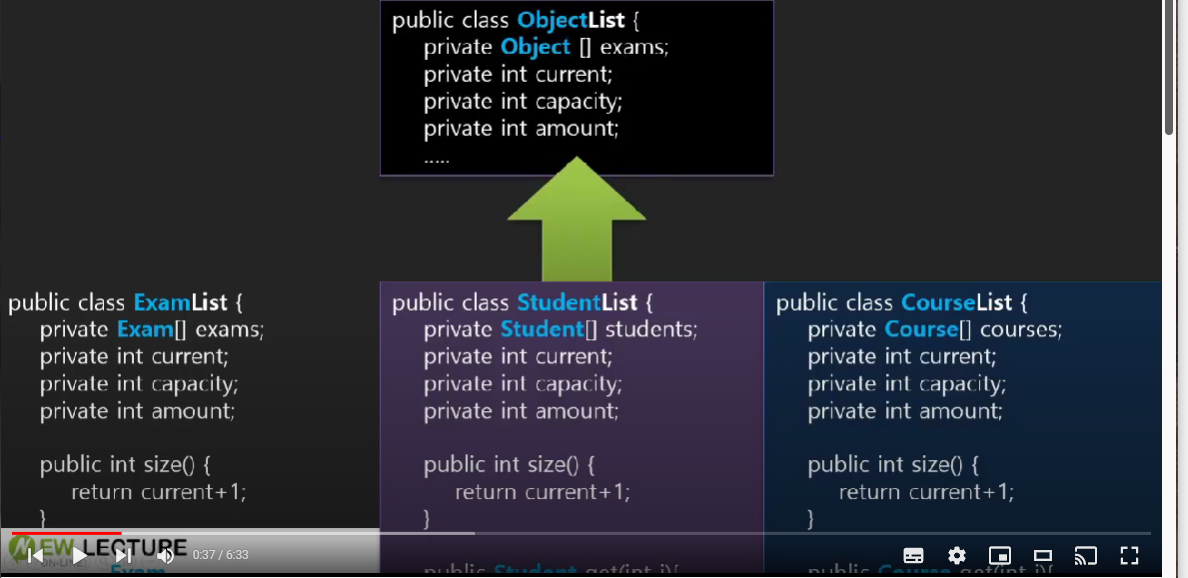
Program.java
package com.newlecture.app.util;
public class Program {
public static void main (String[] args) {
ObjectList list = new ObjectList();
list.add(3);
list.add(5);
int size = list.size();
System.out.printlf("size : %d\n", size);
list.clear();
size = list.size();
System.out.printlf("size : %d\n", size);
list.add(7);
// 참조형식 바꾸기
int num = (Integer)list.get(0); // Object → Integer
System.out.printlf("num : %d\n", num);
//num = (Integer)list.get(1);
}
}Object.java
package com.newlecture.app.util;
public class ObjectList {
private Object[] nums;
private int current;
public ObjectList() {
nums = new Object[3];
current = 0;
}
public void add (Object num) {
nums[current] = num;
current++;
}
public void clear() {
/* for (int i=0; i<current; i++)
nums[i] = 0; */
//nums = new int[3];
current = 0;
}
public int size() {
return current;
}
public Object get(int index) {
if(current <= index)
// 입력값에 대한 오류 = 예외처리
throw new IndexOfBoundsException();
return nums[index];
}
}🤍 Generic 이란 🤍
범용 컬렉션의 장점과 특화된 클래스의 장점을 모두 겸비한 Template
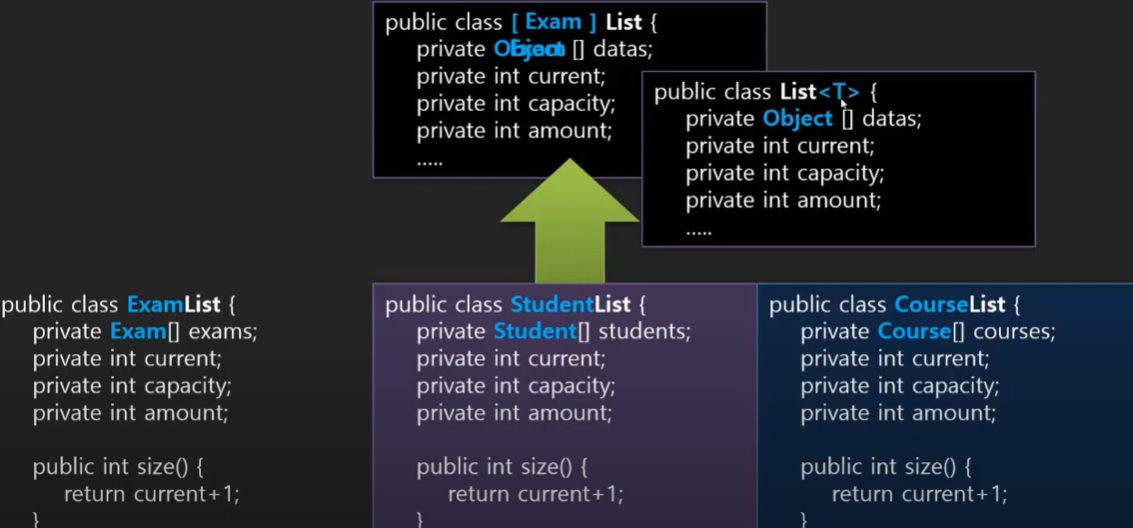
GList.java 생성
package com.newlecture.app.util;
public class GList<T> { // T = Type 의 T
private Object[] nums;
private int current;
public ObjectList() {
nums = new Object[3];
current = 0;
}
public void add (T num) {
nums[current] = num;
current++;
}
public void clear() {
/* for (int i=0; i<current; i++)
nums[i] = 0; */
//nums = new int[3];
current = 0;
}
public int size() {
return current;
}
public T get(int index) {
if(current <= index)
// 입력값에 대한 오류 = 예외처리
throw new IndexOfBoundsException();
return (T)nums[index];
}
}Program.java
package com.newlecture.app.util;
public class Program {
public static void main (String[] args) {
GList<Integer> list = new GList<>();
list.add(3);
list.add(5);
int size = list.size();
System.out.printlf("size : %d\n", size);
list.clear();
size = list.size();
System.out.printlf("size : %d\n", size);
list.add(7);
// 참조형식 바꾸기
int num = list.get(0); // Object → Integer
System.out.printlf("num : %d\n", num);
//num = (Integer)list.get(1);
}
}🤍 연습문제 🤍
가변크기 컬렉션으로 변경하기
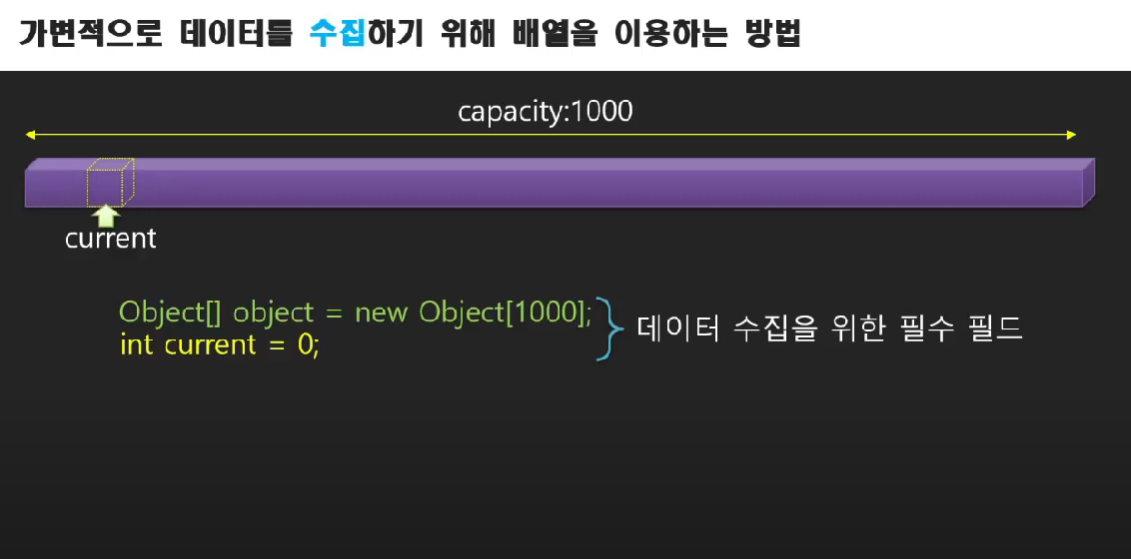
정적인 크기의 배열을 동적인 크기로 만들기
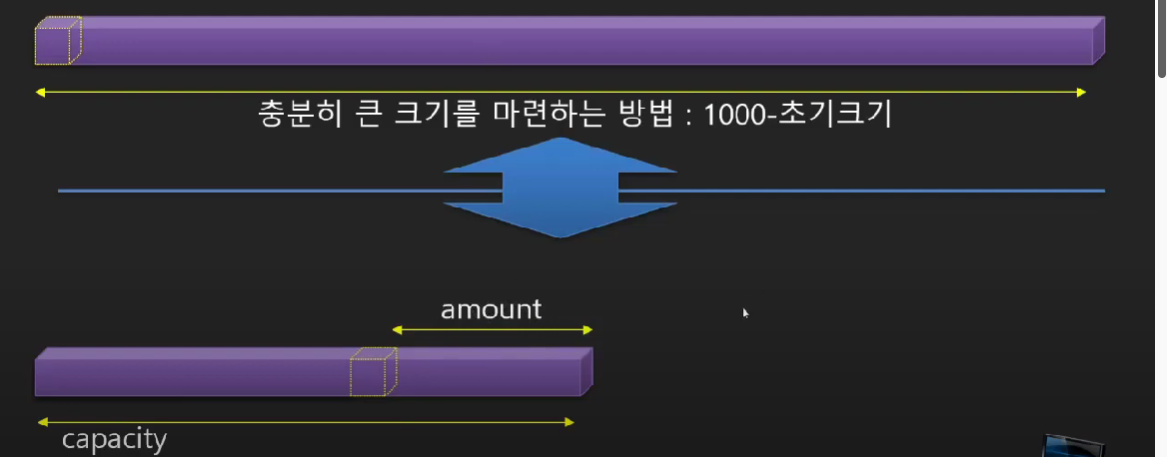
동적인 공간을 관리하기 위해 필요한 capacity 변수
용량(capacity)이 변하기 때문에 새로운 변수가 필요하다.

GList 클래스를 동적으로 공간을 늘릴 수 있도록 수정

연습문제 : 공간을 점진적으로 늘리는 위치와 방법
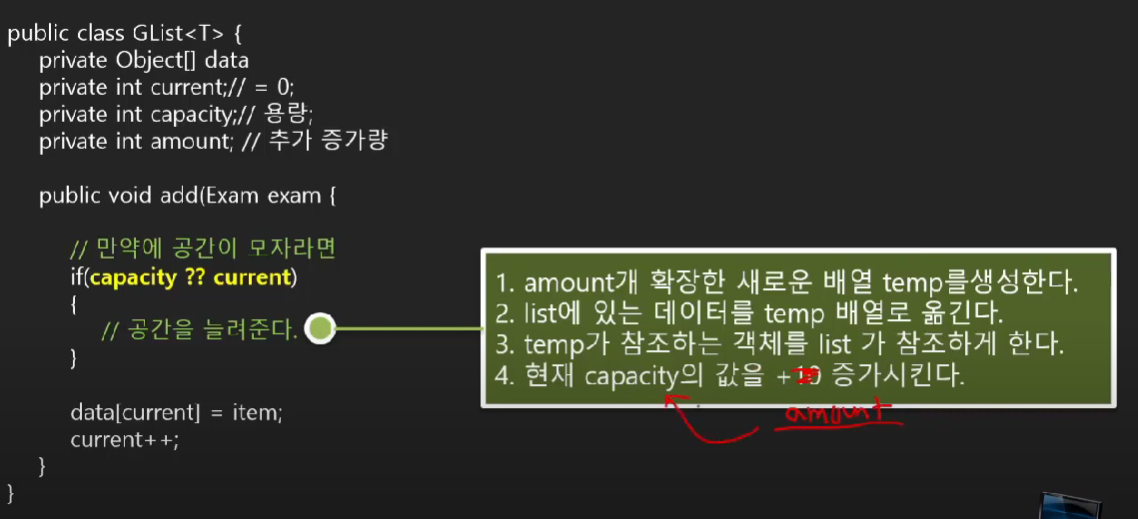
🤍 가변크기 컬렉션으로 변경 - 풀이 🤍
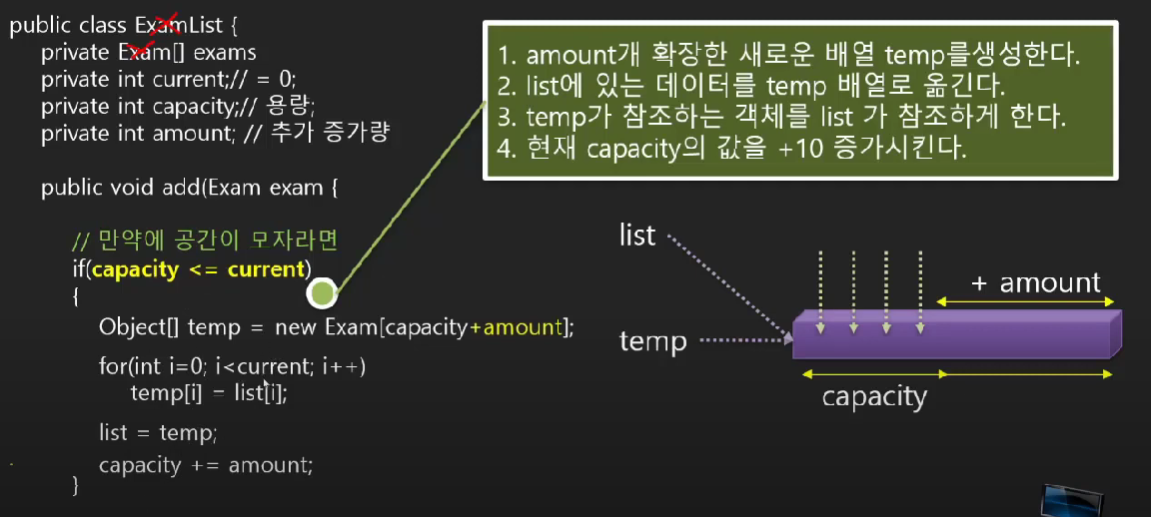
GList.java
package com.newlecture.app.util;
public class GList<T> {
private Object[] nums;
private int current;
public ObjectList() {
nums = new Object[3];
current = 0;
}
public void add (T num) {
//공간이 부족할 때만 실행되는 코드
❕if(capacity <= current) {
Object[] temp = new Object[capacity+amount];
for(int i=0; i<current; i++)
temp[i] = nums[i];
nums = temp;
capacity += amount;
}❕
nums[current] = num;
current++;
}
public void clear() {
/* for (int i=0; i<current; i++)
nums[i] = 0; */
//nums = new int[3];
current = 0;
}
public int size() {
return current;
}
public T get(int index) {
if(current <= index)
// 입력값에 대한 오류 = 예외처리
throw new IndexOfBoundsException();
return (T)nums[index];
}
}Program.java
package com.newlecture.app.util;
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GList<Integer> list = new GList<>();
list.add(3);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
list.add(3);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
list.add(3);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
}
}🤍 Java Collection FrameWork 🤍
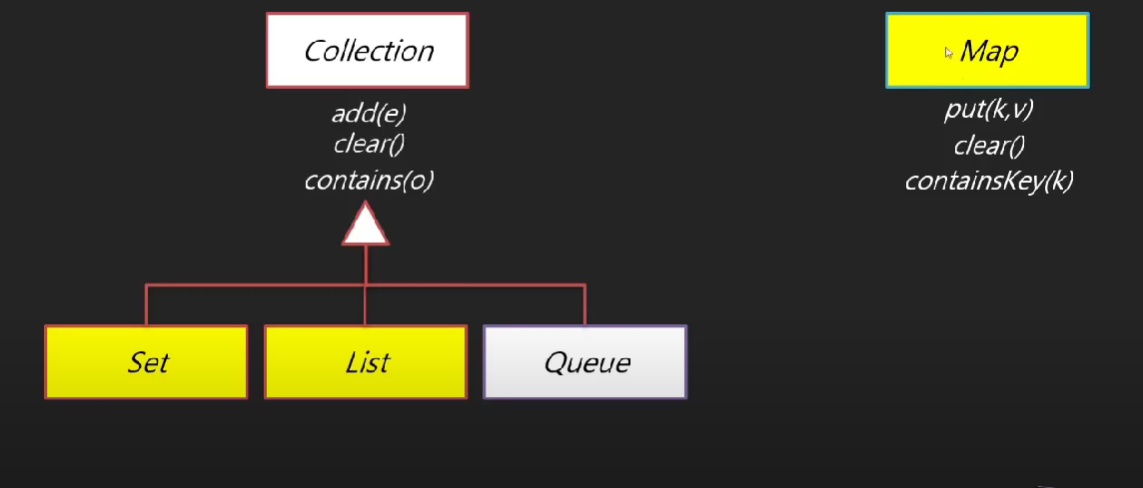
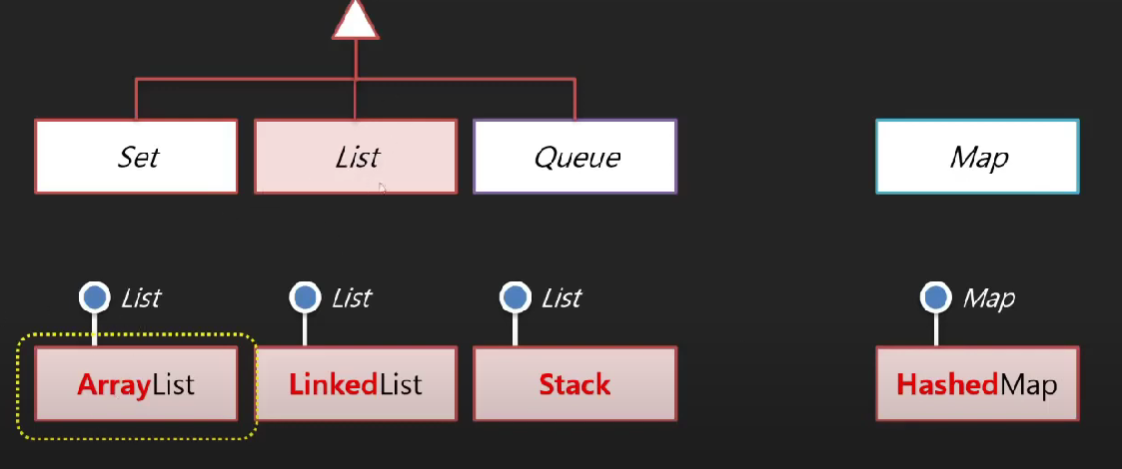
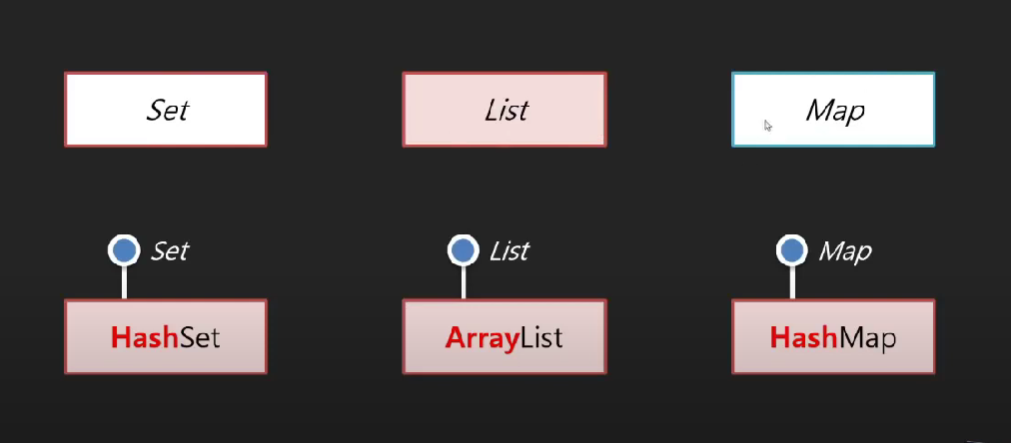
자바 컬렉션의 3대 계보
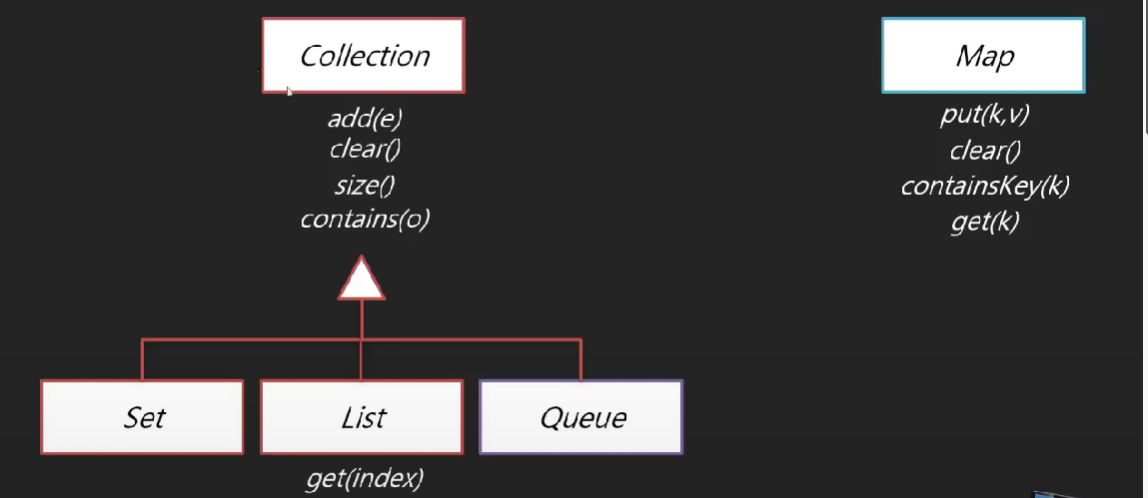
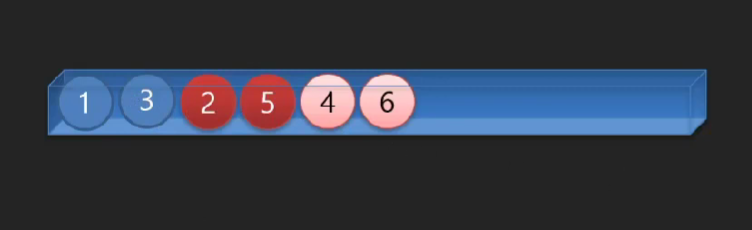
배열에 값을 저장하는 일반적인 방법 - 선형 데이터구조
배열에 값을 저장하는 다른 방법 - 비션형 데이터구조 (Tree 모양)
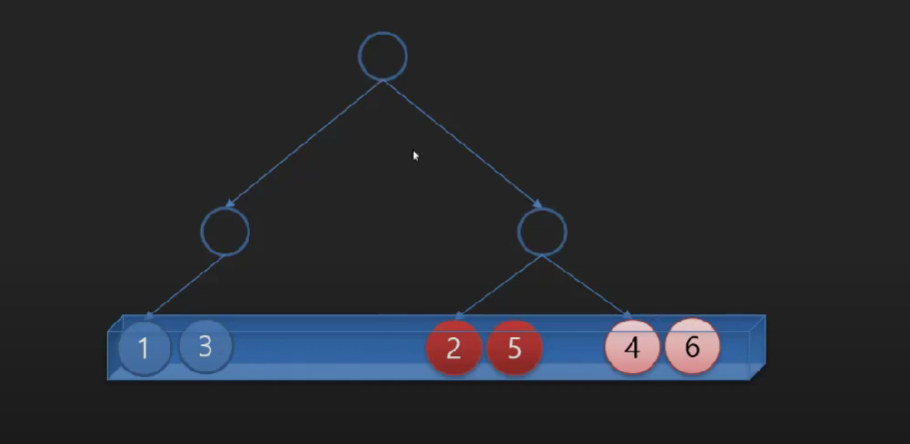
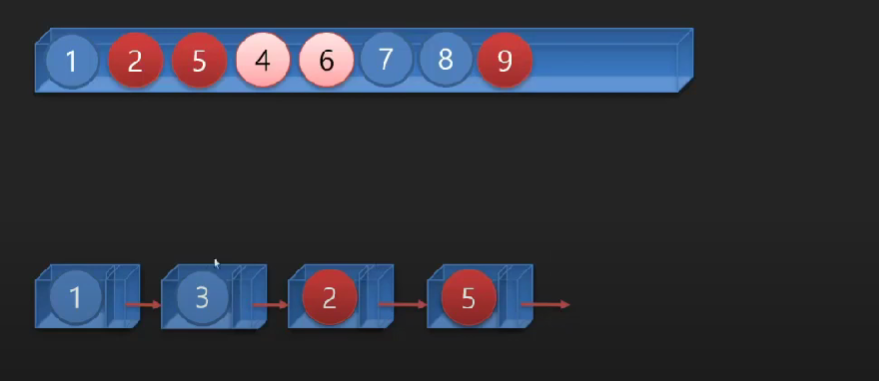
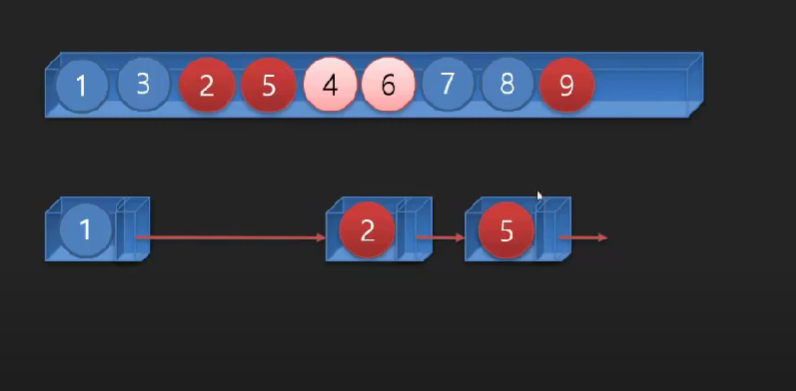
배열에 값을 저장하는 다른 방법 - 선형 데이터 구조 (링크(참조,포인터등)로 연결된 데이터
자바 컬렉션 상속과 구현관계
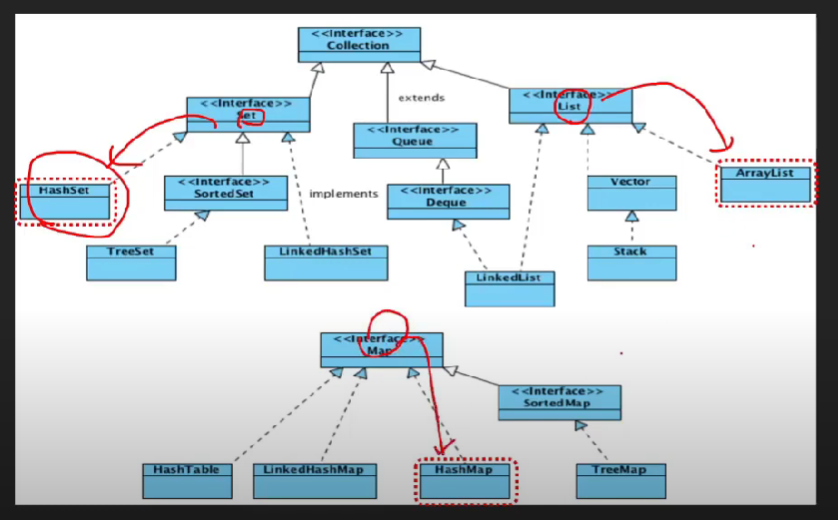
🤍 Set/List/Map 컬렉션 🤍
자바 컬렉션의 3대 계보
Program.java
package com.newlecture.app.util;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//GList<Integer> list = new GList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(3);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
list.add(7);
list.add(7);
System.out.println(list.get(5));
System.out.println(list.size());
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(3);
set.add(5);
set.add(6);
set.add(7);
set.add(7);
set.add(7);
//System.out.println(7);
System.out.println(set.size());
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id", 3);
map.put("title", "Hello");
map.put("hit", 12);
System.out.println(map.get("title"));
list.add(3);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
}
}출처 : 링크텍스트
