URL 패턴
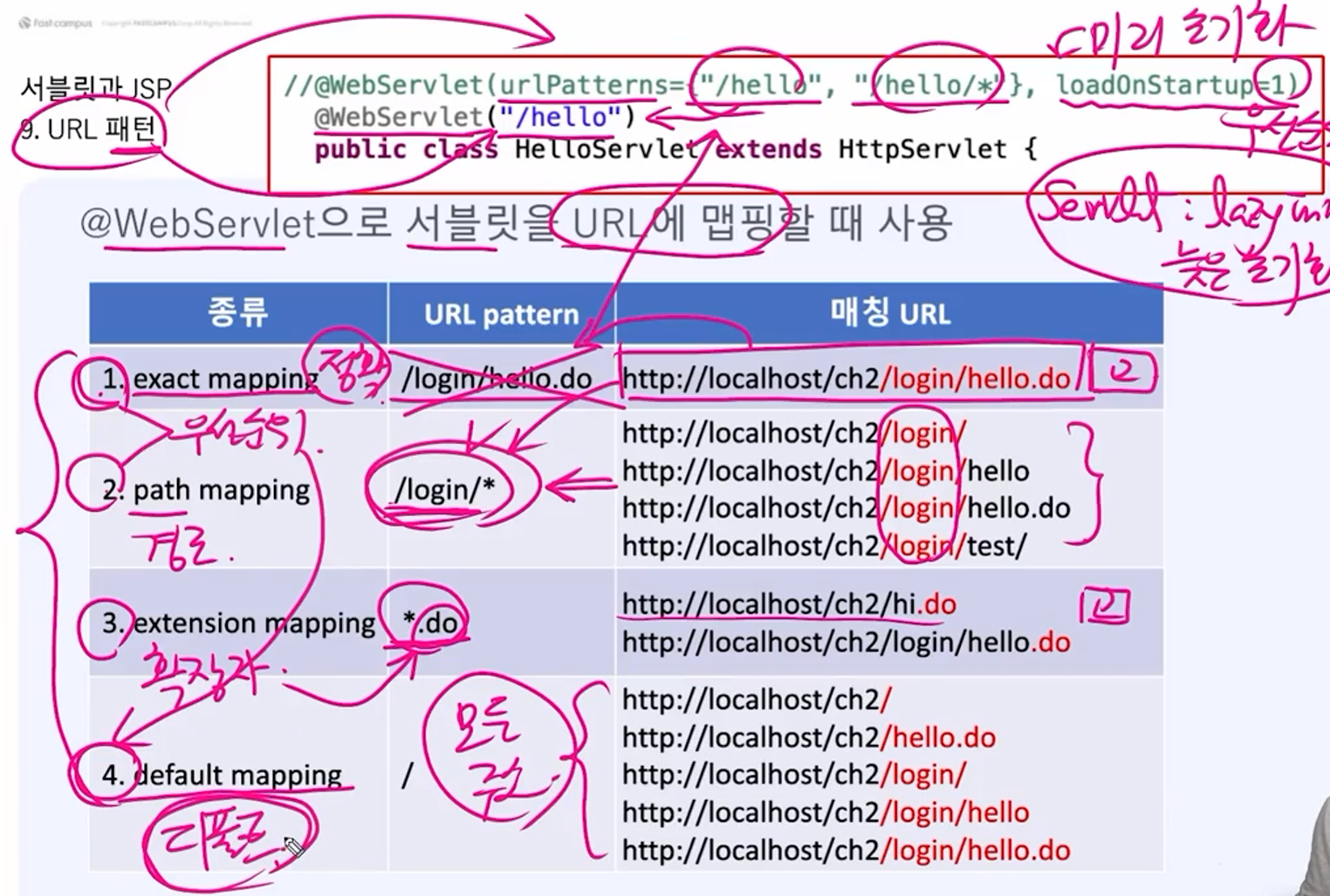
@WebServlet으로 서블릿의 URL에 맵핑할 때 사용.
//배열로 여러개의 URL패턴을 등록 가능
//loadOnStartup=1 : 미리 초기화(early init)
//@WebSerblet(urlPatterns={"/hello", "/hello/*"}, loadOnStartup=1)
@WebServlet("/hello")
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {}URL패턴 종류와 우선순위
1. exact mapping(정확)
- URL pattern : /login/hello.do
- 매칭 URL : http://localhost/ch2/login/hello.do
2. path mapping(경로 맵핑)
- URL pattern : /login/*
- 매칭 URL : http://localhost/ch2/login/...
3. extension mapping(확장자 맵핑)
- URL pattern : *.do
- 매칭 URL : http://localhost/ch2/.../*.do
4. default mapping(디폴트 맵핑, 모든 주소)
- URL pattern : /
- 매칭 URL : http://localhost/ch2/...Servlet Context
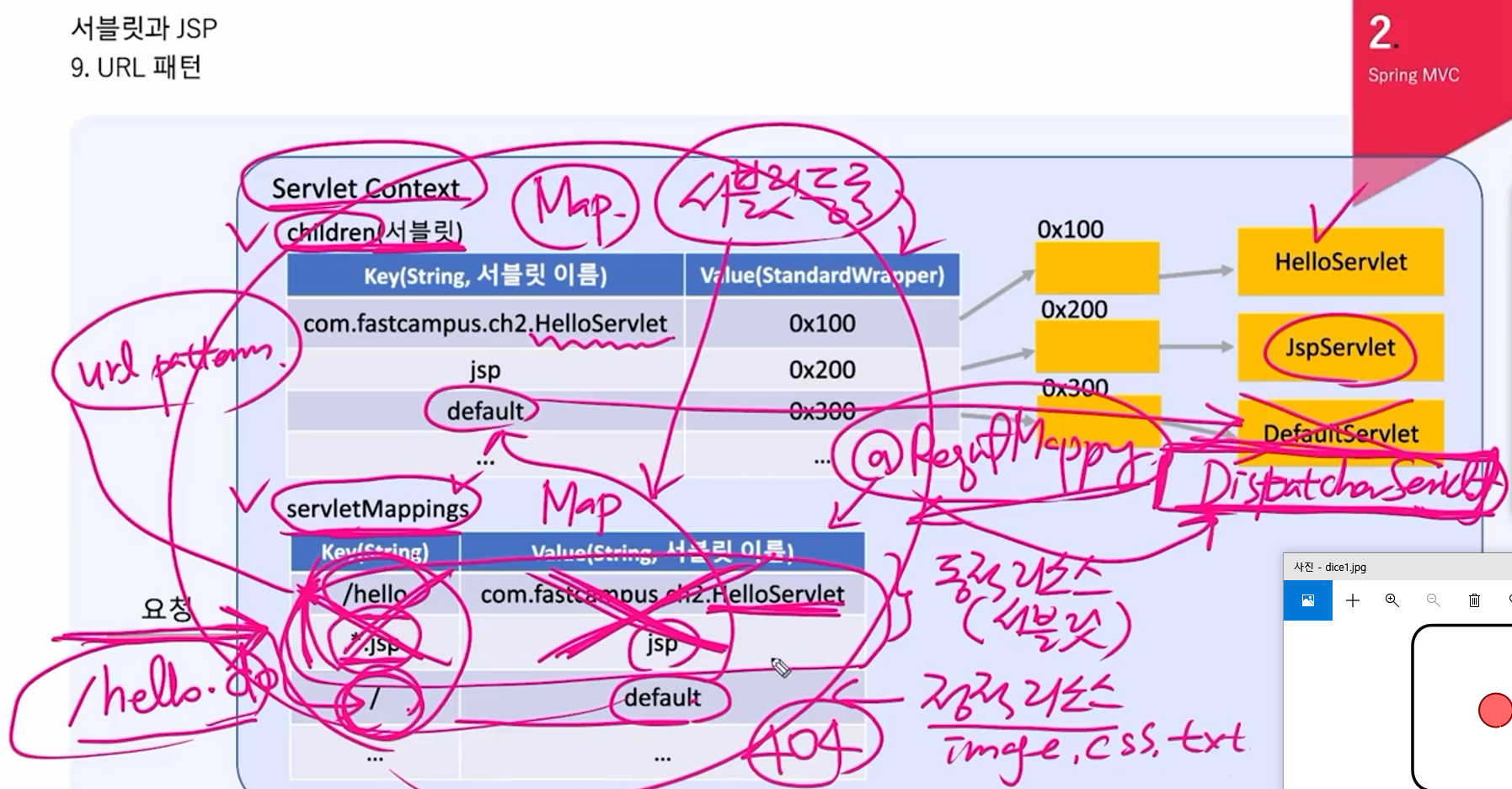
2개의 Map(저장소) children(서블릿), servletMappings가 존재.
요청 --> servletMappings --> children --> Servlet
ServletMapping의 default는
정적 리소스(image, css, txt) 또는 404에러.
나머지는 동적 리소스(서블릿).
But Spring에서는 모든 요청을
default로 연결된 DispatcherServlet이 받아서
RequestMapping으로 등록된 패턴을
DispatcherServlet 내부에서 처리.
web.xml(톰캣 공통 설정)
default Servlet의 내용
<!-- The mapping for the default servlet -->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>web.xml(프로젝트 개별 설정)
DispatcherServlet의 내용
(톰캣 공통 설정의 default Servlet내용을 덮어씀.
--> 즉 모든 요청을 DispatcherServlet이 받게 함)
<!-- Processes application requests -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/appServlet/servlet-context.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>el.jsp
EL(Expression Language)
<%= 값 %> --> ${값}(간단하고 편리하게 해줌)
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=utf-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="fmt" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" %>
<%@ page import="com.fastcampus.ch2.*" %>
<%
Person person = new Person(); //person은 lv. EL은 lv 사용 불가. 저장소에 저장해야 사용 가능.
request.setAttribute("person", person); //setAttribute()로 저장소에 저장해야 EL에서 사용 가능.
request.setAttribute("name", "남궁성");
request.setAttribute("list", new java.util.ArrayList());
%>
<html>
<head>
<title>EL</title>
</head>
<body>
person.getCar().getColor()=<%=person.getCar().getColor()%> <br>
person.getCar().getColor()=${person.getCar().getColor()} <br>
<!-- 아래 EL에서 person(key값 "person").car(getter사용: getCar()).color(getter사용: getColor) -->
person.getCar().getColor()=${person.car.color} <br>
name=<%=request.getAttribute("name")%> <br>
<!-- requestScope은 request의 저장소 이름. -->
<!-- requestScope라는 저장소인 Map에 저장된 key값 "name" -->
name=${requestScope.name} <br>
<!-- requestScope가 없어도 scope이 좁은범위에서 넓은 범위로 찾음. -->
<!-- pageContext, request, session, application 순으로 찾음. -->
<!-- requestScope에 key값"name"이 있으므로 EL사용 가능. -->
name=${name} <br>
id=<%=request.getParameter("id")%> <br>
<!-- request객체의 메서드를 EL로 사용하고 싶을때 -->
<!-- request는 lv이므로 EL에서 바로 request.getParameter()사용 불가. -->
<!-- pageContext를 앞에 붙여야 함. -->
<!-- 이게 pageContext가 필요한 이유. -->
id=${pageContext.request.getParameter("id")} <br>
<!-- 위의 첫번째 id는 null을 출력.But EL은 null을 출력하지 않음. -->
<!-- param객체는 EL의 내장객체. 파라미터값을 얻어올 수 있다. -->
id=${param.id} <br>
<!-- 문자열(숫자) + 숫자(문자열) => 숫자 + 숫자 -->
"1"+1 = ${"1"+1} <br>
<!-- 숫자(문자열) += 숫자(문자열) => 문자열 -->
"1"+="1" = ${"1"+="1"} <br>
"2">1 = ${"2">1} <br>
null = ${null}<br>
<!-- 계산 할 때는 null이 0으로 바뀜. -->
null+1 = ${null+1} <br>
null+null = ${null+null} <br>
<!-- 빈문자열은 계한 할 때 0으로 바뀜. -->
"" + null = ${""+null} <br>
""-1 = ${""-1} <br>
<!-- empty는 null이거나 빈 컬렉션 배열일 때 true -->
empty null=${empty null} <br>
empty list=${empty list} <br>
<!-- null은 비교연산 할 때는 0이 아님. -->
null==0 = ${null==0} <br>
<!-- eq는 equal -->
null eq 0 = ${null eq 0} <br>
<!-- 문자열은 ==, !=, eq, ne(not equal), equals()로 비교 가능 -->
name == "남궁성"=${name=="남궁성"} <br>
name != "남궁성"=${name!="남궁성"} <br>
name eq "남궁성"=${name eq "남궁성"} <br>
name ne "남궁성"=${name ne "남궁성"} <br>
name.equals("남궁성")=${name.equals("남궁성")} <br>
</body>
</html>