1. Conditional Processing
- Conditional Processing
- Boolean and Comparison Instructions
- Conditional Jumps
- Conditional Loop Instructions
- Conditional Structures
- Application: Finite-State Machines
- Conditional Control Flow Directives
Boolean and Comparison Instructions
- CPU Status Flags
- The Zero flag is set when the result of an operation equals zero. : 결과가 0
- The Carry flag is set when an instruction generates a result that is too large (or too small) for the destination operand.
- The Sign flag is set if the destination operand is negative, and it is clear if the destination operand is positive.
- The Overflow flag is set when an instruction generates an invalid signed result.
- The Parity flag is set when an instruction generates an even number of 1 bits in the low byte of the destination operand.
- The Auxiliary Carry flag is set when an operation produces a carry out from bit 3 to bit 4
AND Instruction
- Performs a Boolean AND operation between each pair of matching bits in two operands
- Syntax: AND destination, source (the same operand types as MOV)
- Example
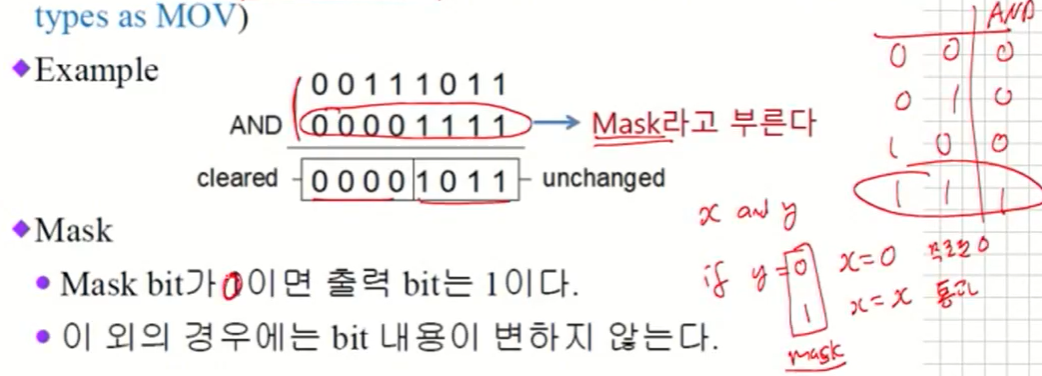
- Mask
- Mask bit가 0이면 출력 bit는 0이다.
- 이 외의 경우에는 bit 내용이 변하지 않는다.
OR Instruction
- Syntax: OR destination, source(아무나 maskㄱ 될 수 있다)
- Example
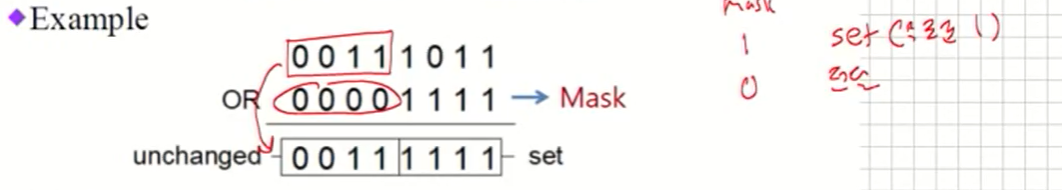
- Mask
- Mask bit가 1이면 출력 bit는 1이다.
- 이 외의 경우에는 bit 내용이 변하지 않는다.
NOT Instruction
- Syntax: NOT destination

XOR Instruction
-
Syntax: XOR destination, source

-
XOR mask
- 1이면 데이터 bit가 invert 된다.
- 0이면 데이터 bit 변함 없음.
-
같은 mask로 XOR 연산을 두 번 연속하면 데이터가 복구된다 (보안 분야에서 중요하게 사용).
-
Example
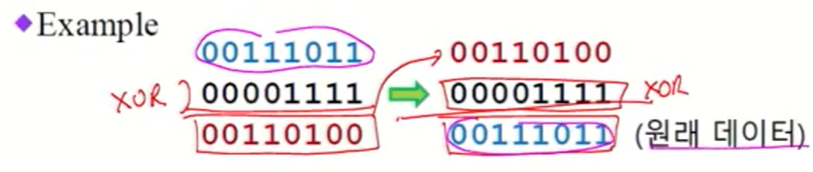
-
Application 1 : 소문자를 대문자로 바꾸기
- Task: Convert the character in AL to upper case.
- Solution: Use the AND instruction to clear bit 5.

- and 아닌 다른 instruction을 사용한다면?

-
Application 2 : binary를 10진수로 바꾸기
- Task: Convert a binary decimal byte into its equivalent ASCII decimal digit.
- Solution: Use the OR instruction to set bits 4 and 5.

-
Application 3
- Task: Jump to a label if an integer is even.
- Solution: AND the lowest bit with a 1. If the result is zero, the number was even.

- ax 값은 훼손된다.
-
Application 4
- Task: Jump to a label if the value in AL is not zero. : al이 0이 아니면 jump하라
- Solution: OR the byte with itself, then use the JNZ (jump if not zero) instruction. : or al, al 해서 al은 그대로 flag은 set

- 같은 값을 OR하면 본래 값에는 변함이 없지만, 그 값에 따른 flag 변화는 있다.
- 이와 유사한 연산으로는 add al, 0 가 있다(그러나 2 bytes instruction).

TEST Instruction
TEST 명령어는 주로 해당 값의 참, 거짓을 판별할때 사용한다. dest와 src 를 and 연산을 하여서 그 결과가 0이라면 ZF = 1 이고 아니라면 ZF = 0으로 set 한다.
- Performs a nondestructive AND operation between each pair of matching bits in two operands. : AND와 동일 그러나 flag만 set
- Syntax

- No operands are modified, but the Zero flag is affected. : 결과값은 바뀌지 않는데 flag가 바뀐다. and연산과 유사하다.
- Example: jump to a label if either bit 0 or bit 1 in AL is set.
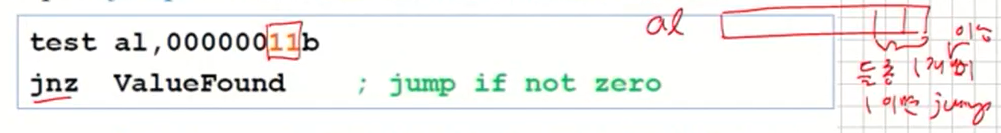
- Example: jump to a label if neither bit 0 nor bit 1 in AL is set.

CMP Instruction
dest - src 의 결과값을 보고 flag를 설정한다.
-
Compares the destination operand to the source operand.
-
Nondestructive subtraction of source from destination (destination operand is not changed) : SUB 처럼 뺄셈인데 flag만 set한다. operand는 불변한다.
-
Syntax:

-
Example: destination == source
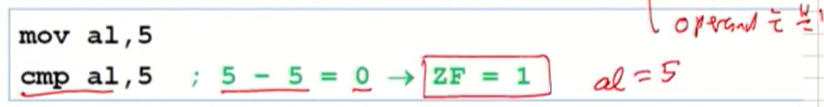
-
Example: destination < source
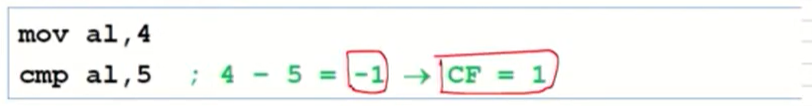
-
Example: destination > source
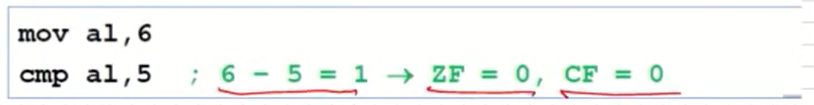
-
Example: destination > source (signed)
- 결과는 항상 양수 -> SF = 0
- 큰 값에서 작은 값을 빼므로 no overflow -> OF = 0

-
Example: destination < source (signed)
- Overflow가 아니면 -> SF = 1, OF = 0.

- Overflow이면 -> SF = 0, OF = 1.

- Overflow가 아니면 -> SF = 1, OF = 0.
-
Setting and Clearing Individual CPU Flags
-
각종 flag 들을 미리 설정할 필요가 있을 수 있다.
-
Zero Flag

-
Sign Flag (아래 두 방법 모두 AL 값이 바뀐다)
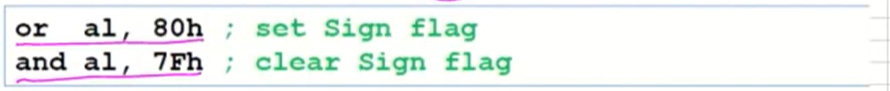
-
Carry Flag (전용 instruction이 있다)
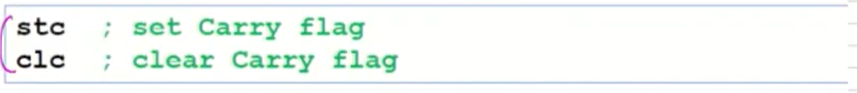
-
Overflow Flag

-
Boolean Instructions in 64-Bit Mode
- For the most part, 64-bit instructions work exactly the same in 64-Bit mode as they do in 32-bit mode.
- However, when the source operand is a 32-bit constant or register, only the lower 32 bits of the destination operand are affected.
- Example

source operand가 바뀔때는 하위 8byte만 바뀐다는 것만 알면된다.
2. Conditional Jumps
Conditional Jumps
연산을(cmp, test) 하면 flag set된다. 이 flag를 가지고 jump가 가능해진다. 이런것을 conditional jump라고 부른다.
-
A conditional jump instruction branches to a label when specific register or flag conditions are met.
-
Syntax: jcond destination ; cond = e, z, ne,등
-
Examples:
- JB, JC jump to a label if the Carry flag is set.
(jump if below -> unsigned 인 경우 less / jump if carry - JE, JZ jump to a label if the Zero flag is set.
(jump if equal / jump if zero) - JS jumps to a label if the Sign flag is set.
- JNE, JNZ jump to a label if the Zero flag is clear.
(jump if not equal) - JECXZ jumps to a label if ECX equals 0.
- JB, JC jump to a label if the Carry flag is set.
-
Conditional Jump Range
- Prior to the 386:
- Jump must be within –128 to +127 bytes from the current location counter. (relative jump, operand가 8bit two's complement)
- x86 processors:
- 32-bit offset permits jump anywhere in the memory : 메모리의 어디에나 점프가 가능하다.
- Prior to the 386:
-
Jumps Based on Specific Flags
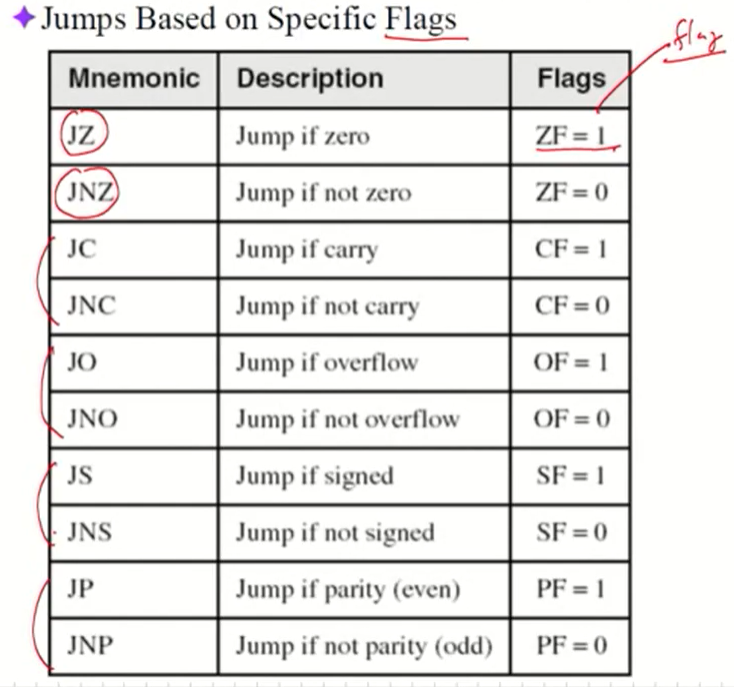
-Jumps Based on Equality
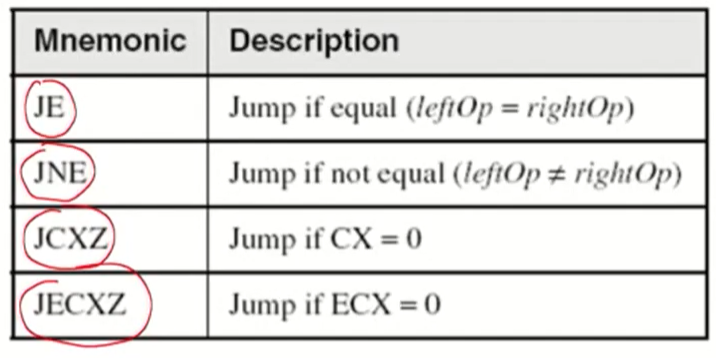
-
Jumps Based on Unsigned Comparisons

-
Jumps Based on Signed Comparisons
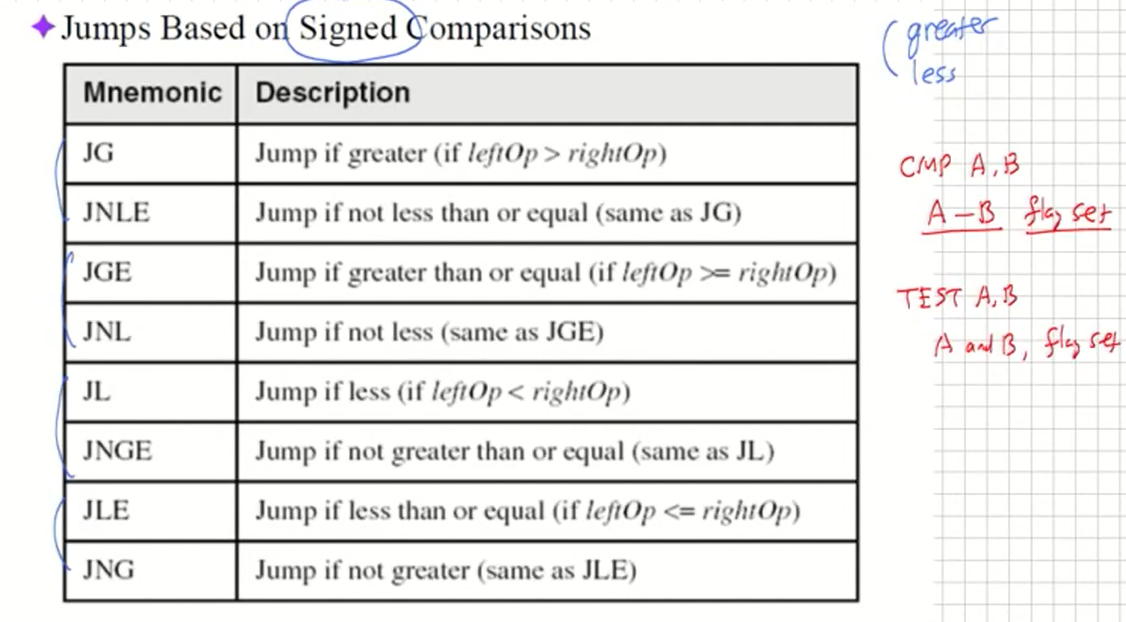

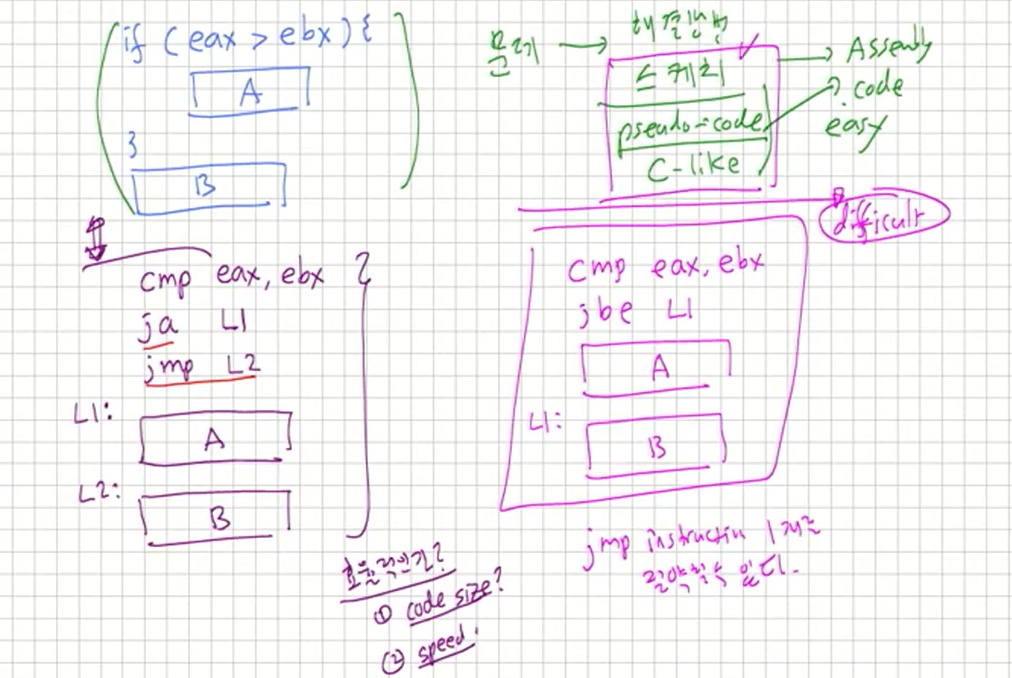
앞으로 어셈블리코드를 짤때는 우선 C나 수도코드를 먼저 작성한다음 어셈블리 코드로 바꾸자
Applications
-
Jump to a label if unsigned EAX is greater than EBX.

-
Jump to a label if signed EAX is greater than EBX.

-
Jump to label L1 if unsigned EAX is less than or equal to Val1.

-
Jump to label L1 if signed EAX is less than or equal to Val1.

-
Compare unsigned AX to BX, and copy the larger of the two into a variable named Large.

-
Compare signed AX to BX, and copy the smaller of the two into a variable named Small.

-
Jump to L1 if the memory word pointed to by ESI equals Zero.

-
Jump to label L2 if the doubleword in memory pointed to by EDI is even.
- LSB가 1이면 홀수, 0이면 짝수.

- LSB가 1이면 홀수, 0이면 짝수.
-
Jump to label L1 if bits 0, 1, and 3 in AL are all set.
- Clear all bits except bits 0, 1,and 3.
- Then compare the result with 00001011 binary.

-
Jump to label L1 if one or more of bits 0, 1, and 3 in AL are set.
- Clear all bits except bits 0, 1,and 3.
- Then jump if the result is not zero.

- AL의 내용을 보전하고 싶다면?
- Stack에 잠시 보관

- TEST instruction 사용 (better)

- Stack에 잠시 보관
Programming Tips
-
EAX 값을 0으로 초기화 하려면?

그냥 mov eax,0 이라고 하면 instuction size에서 opcode(1 byte) + operand(4 byte) 이다.
-
EAX 값이 0인지 check하려면? 즉, EAX 값에 따른 zero flag을 설정하려면?

-
Smallest of Three Integers
- Compare the unsigned 16-bit values in the variables V1. V2, and V3 and move the smallest of the three to AX.

- Compare the unsigned 16-bit values in the variables V1. V2, and V3 and move the smallest of the three to AX.
-
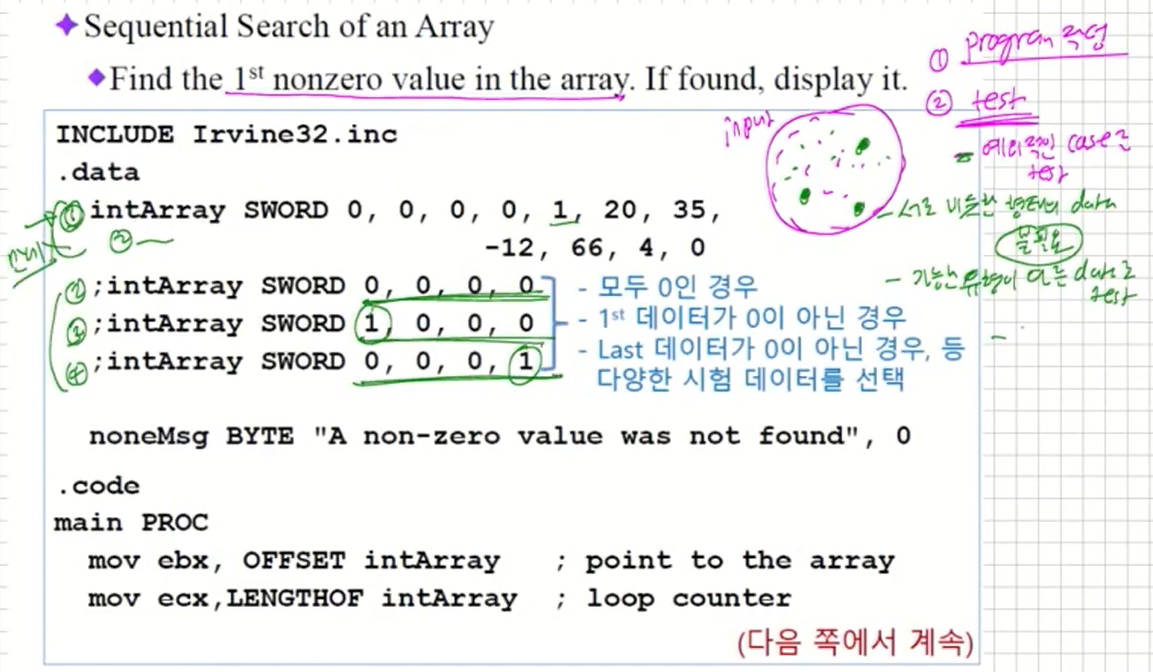
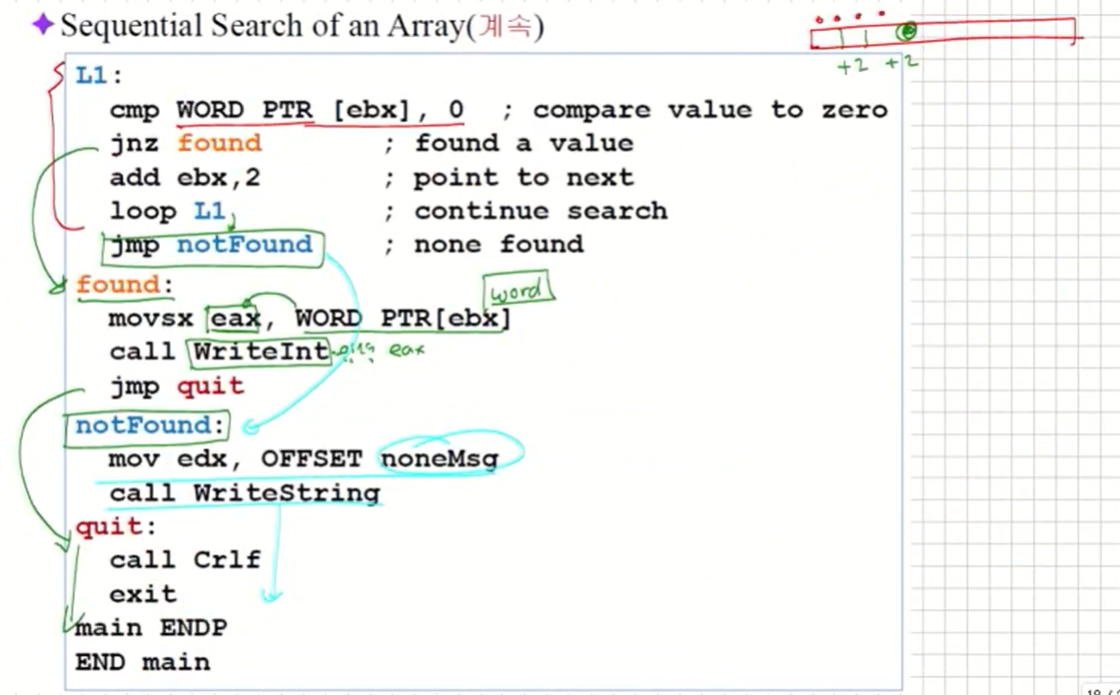
Sequential Search of an Array
- Find the 1st nonzero value in the array. If found, display it.
이제 만약 프로그램을 짠다음 다음의 단계를 거치게 될 것이다.
- Find the 1st nonzero value in the array. If found, display it.
- program 작업
- test 작업
- 이때 test하는 것은 예외적인 case를 test해본다.
- test 하기 위해 input data가 굉장히 많을 것이다. 이중에서 test하려면 골라야 한다. 서로 비슷한 형태의 data는 불필요하다. 그리고 가능한 유형이 다른 data로 test 해보아야 한다. 특히나 극단적인 경우들
Encrypting a String
-
The following loop uses the XOR instruction to transform every character in a string into a new value.
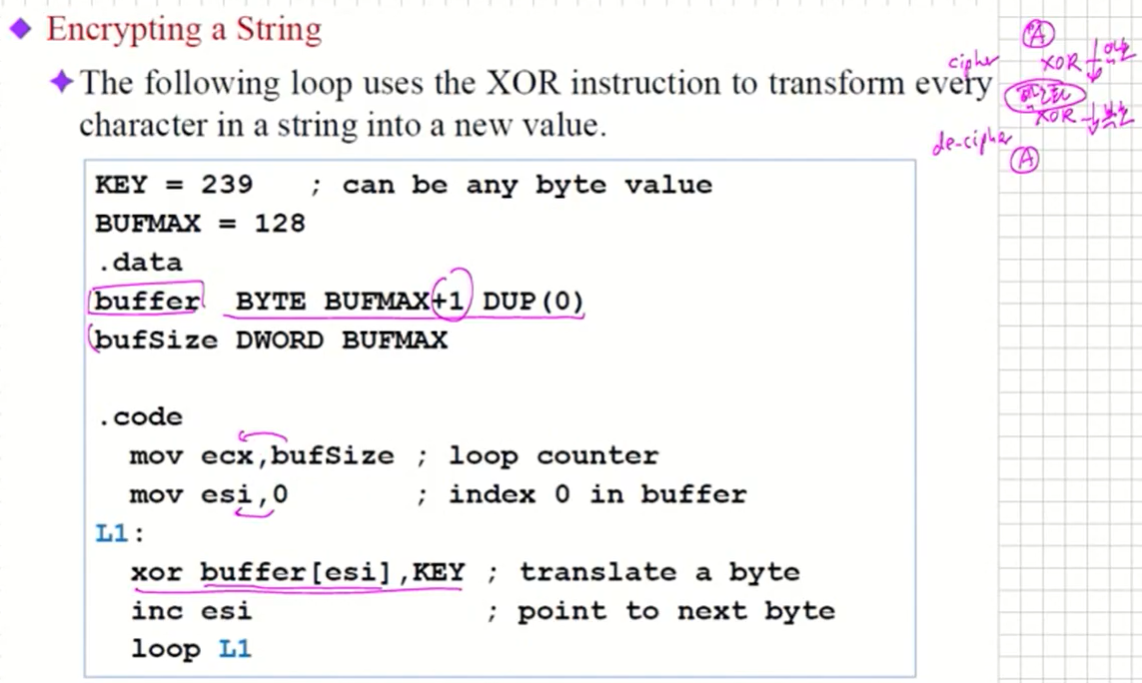
-
String Encryption Program
- Input a message (string) from the user
- Encrypt the message
- Display the encrypted message
- Decrypt the message
- Display the decrypted message
-
Sample Output:

-
A Sample Program(1/5)
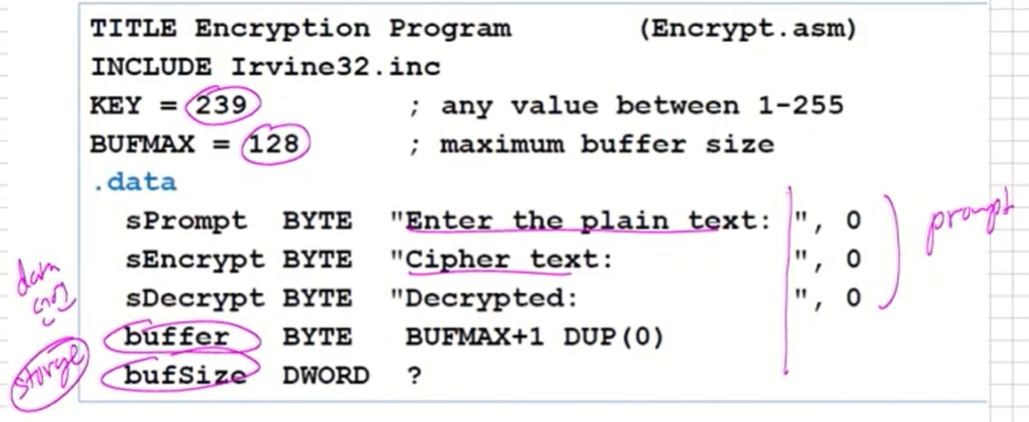
-
A Sample Program(2/5)
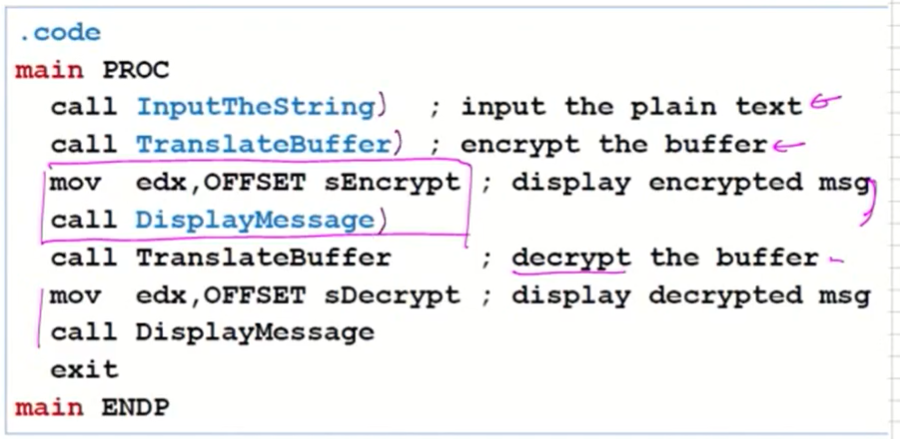
-
A Sample Program(3/5)

-
A Sample Program(4/5)

-
A Sample Program(5/5)
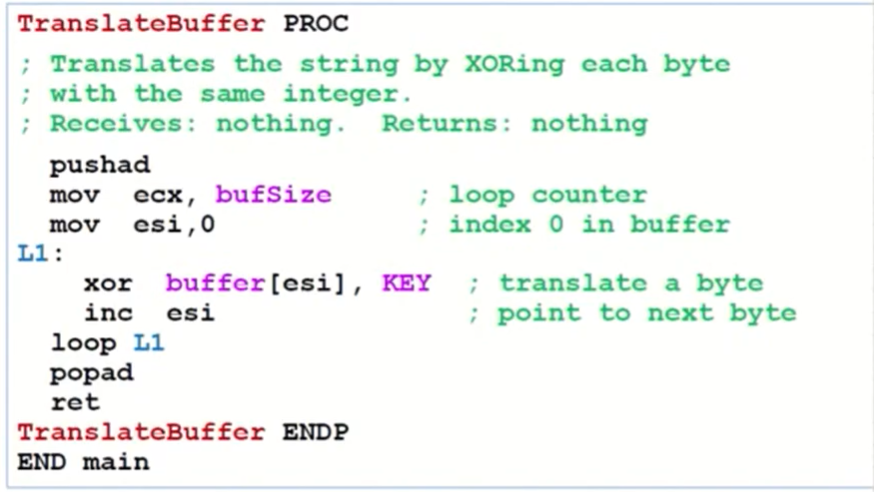
- 평가: 위에 보인 것과 같이 bufSize, buffer, KEY 등 현재 프로그램에 특정된 변수 이름을 사용하는 것은 reusability 관점에서 좋지 않다.
-
함수 TranslateBuffer 수정
- 다음과 같이 레지스터를 통하여 입력을 받도록 수정한다.

- Main 함수에서의 호출

- 다음과 같이 레지스터를 통하여 입력을 받도록 수정한다.
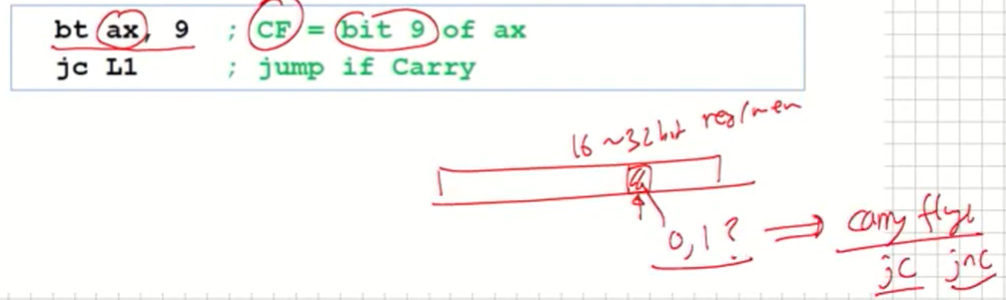
BT (Bit Test) Instruction
비트를 체크하는 instruction이다.
- Copies bit n from an operand into the Carry flag
- Syntax: BT bitBase, n
- bitBase may be r/m16 or r/m32 (Note: it can not be 8 bits)
- n may be r16, r32, or imm8 (Note: n can not be 8 bit register)
- Example: jump to label L1 if bit 9 is set in the AX register: 아래의 예시를 보면 9번째 bit를 체크해서 CF에 9번째 bit가 0인지 1인지에 대한 결과를 넣는다.
3. Conditional Loop Instructions
Conditional Loop Instructions
-
LOOPZ and LOOPE
- Syntax: LOOPE dest LOOPZ dest
- Logic:

- Useful when scanning an array for the first element that does not match a given value. : match 되지 않는 첫번째 element를 찾을때 사용한다.
- 즉, ecx > 0이고, 결과가 zero 또는 같으면 loop 반복. 두가지 조건을 모두 만족해야만 L1으로 간다. => 마지막으로 zero flag에 영향을 주는 instruction의 결과에 따라 계속할지 중지할지가 결정을 하게 된다.
-
LOOPNZ and LOOPNE
- Syntax: LOOPNZ dest LOOPNE dest
- Logic:

- Useful when scanning an array for the first element that matches a given value.
- 즉, ecx > 0이고 결과가 nonzero 또는 다르면 loop 반복.
-
LOOPNZ Example: find the first positive value in an array. : 첫번째 양수를 찾으라

-
Loopnz를 사용하지 않을 경우 프로그램은?
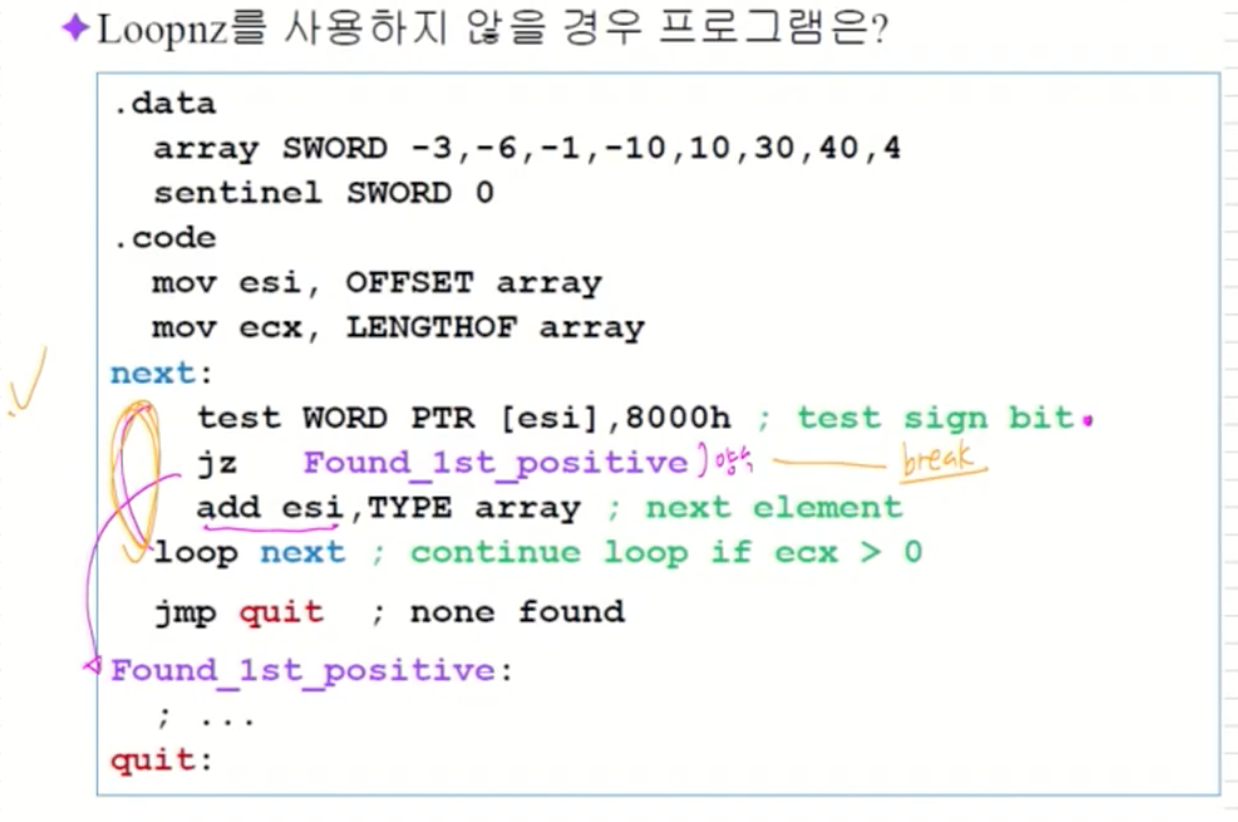
loopnz를 안쓰는게 보다 간단할 수도 있다. -
Locate the first nonzero value in the array. If found, let ESI point to the sentinel value:

-
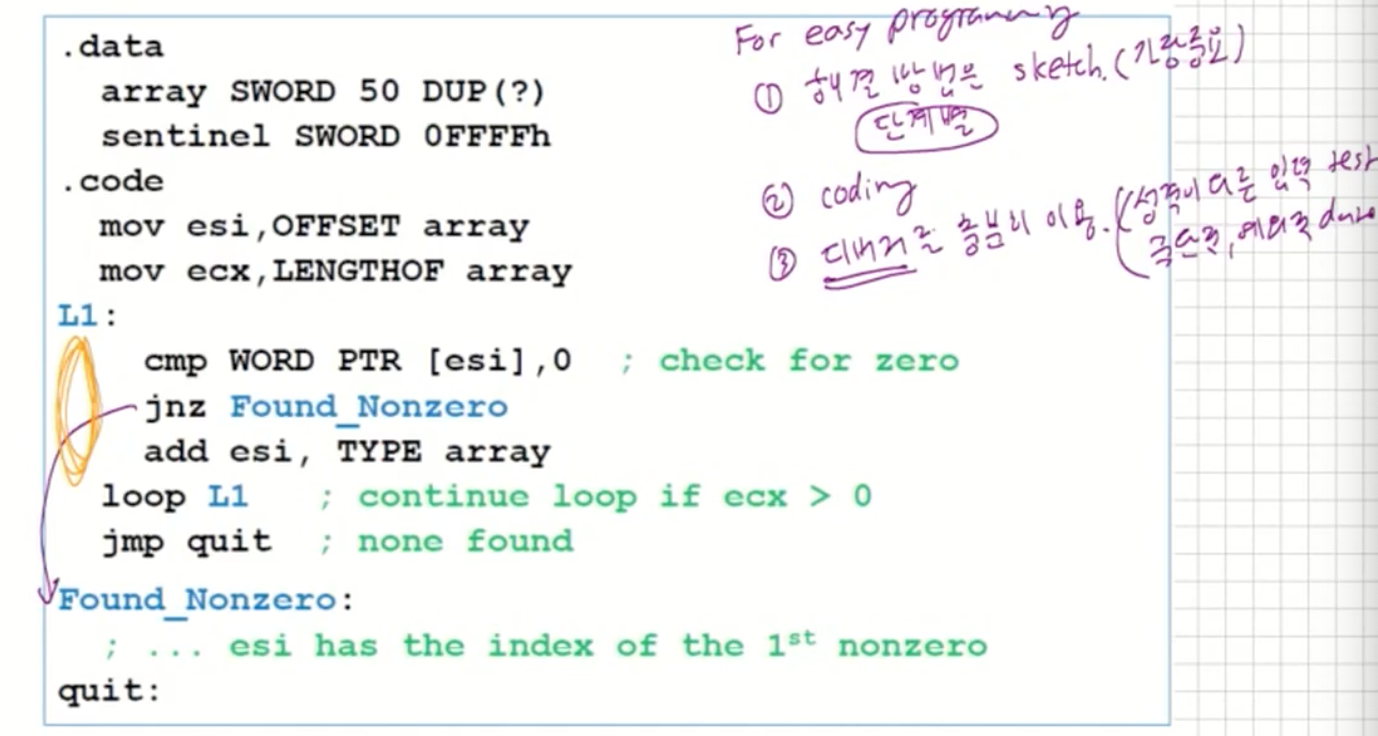
Loop instruction을 사용한다면? (find 1st nonzero)
Conditional Structures
코딩하는데 도움이 될 수 있는 Conditional Structure을 해보자
-
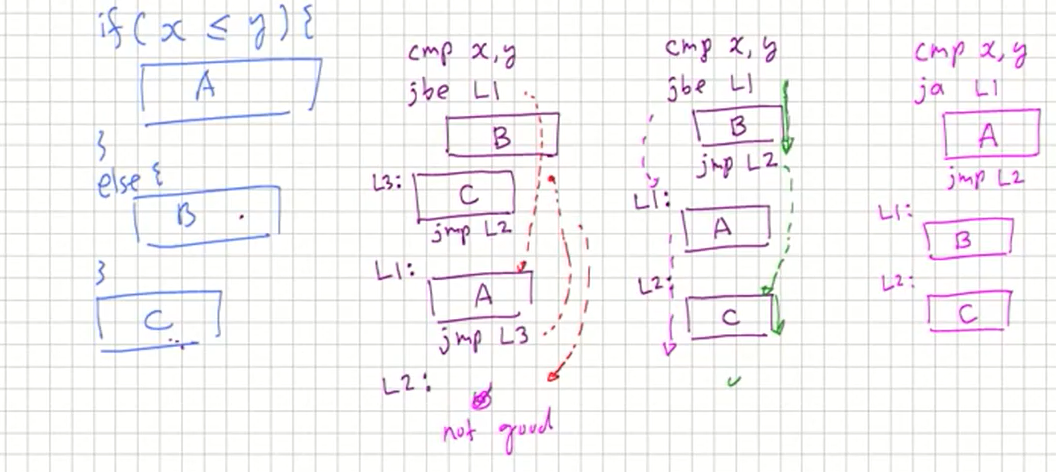
Block-Structured IF Statements
-
Assembly language programmers can easily translate logical statements written in C++/Java into assembly language.
-
Example:

-
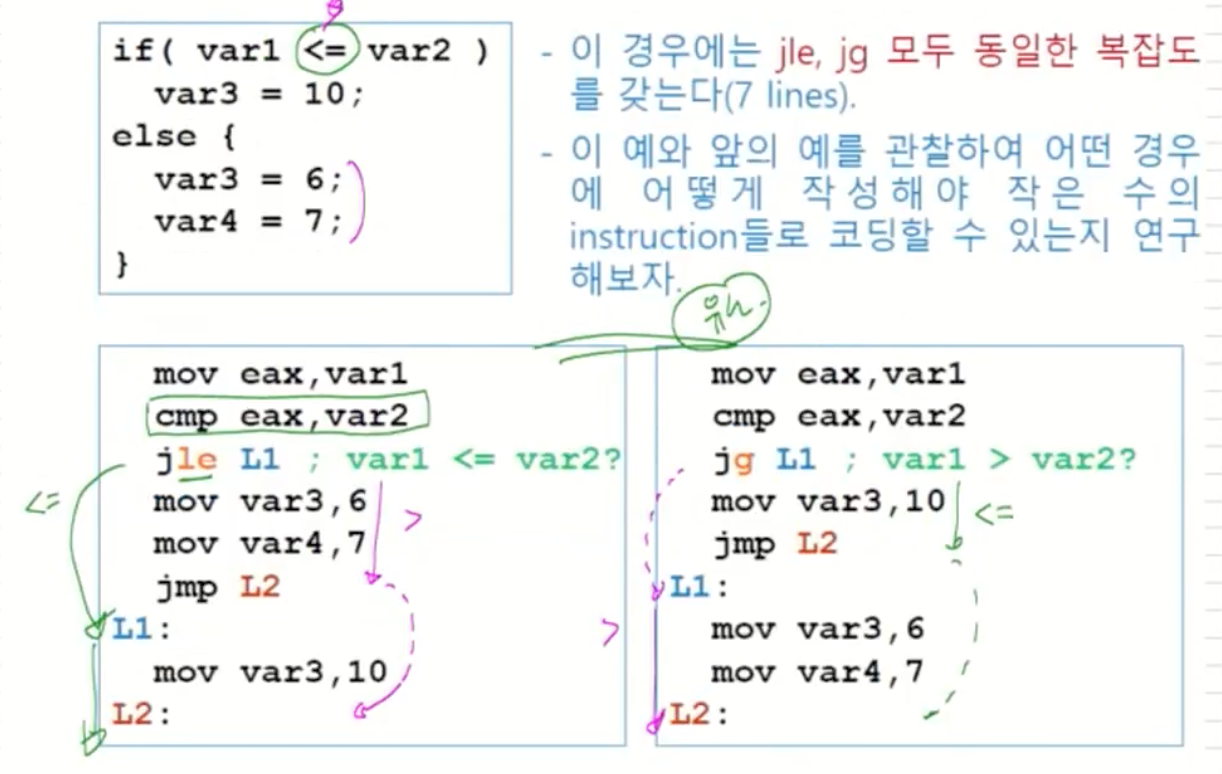
Example (Signed)
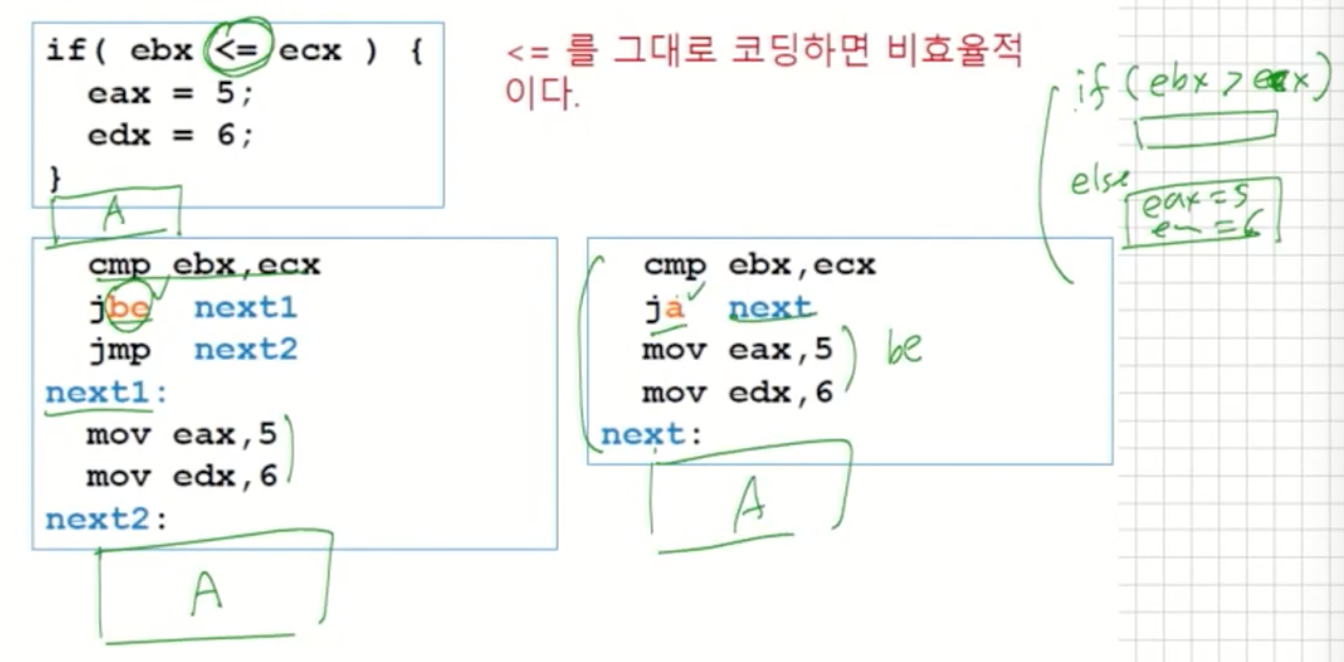
-
이 경우에는 jle, jg 모두 동일한 복잡도를 갖는다(7 lines).
-
이 예와 앞의 예를 관찰하여 어떤 경우에 어떻게 작성해야 작 은 수 의 instruction들로 코딩할 수 있는지 연구해보자.
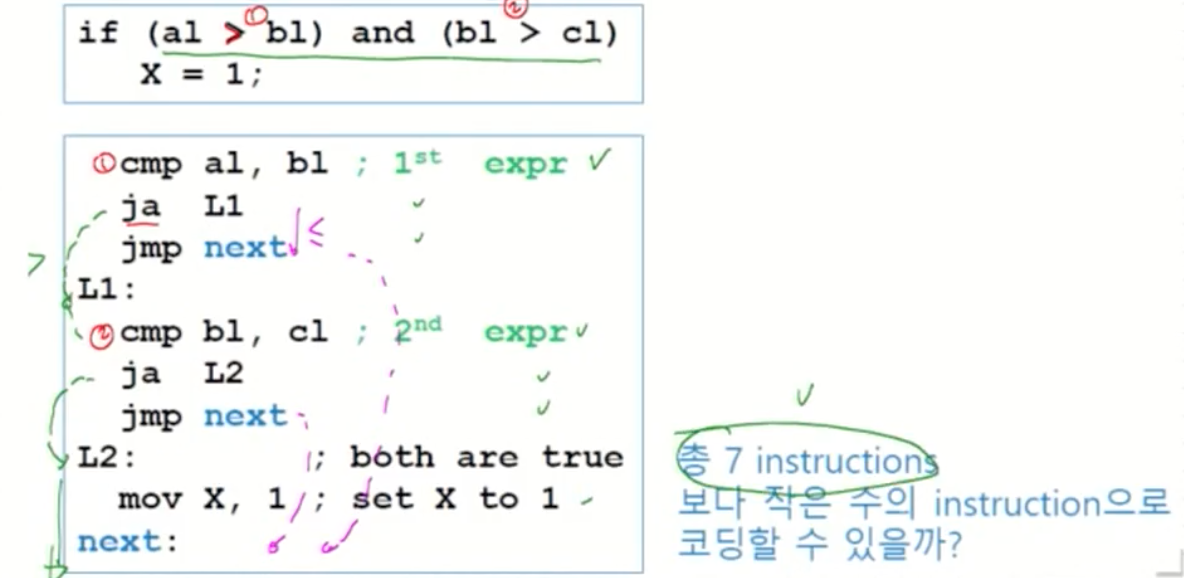
Compound Expression with AND
-
When implementing the logical AND operator, consider that HLLs use short-circuit evaluation
-
In the example shown below, if the first expression is false, the second expression is skipped.
보다 작은 수의 instruction으로 코딩할 수 있을까? -
Simplification

- 위 코드를 아래와 같이 구조를 바꿔보자.

- 논리적으로 not(A and B)는 not(A) or not(B)와 동등하다.(드모르간의 법칙)
- 따라서 위 코드는 아래와 같이 변경할 수 있다.

- 위 코드를 아래와 같이 구조를 바꿔보자.
-
Simplification(계속)
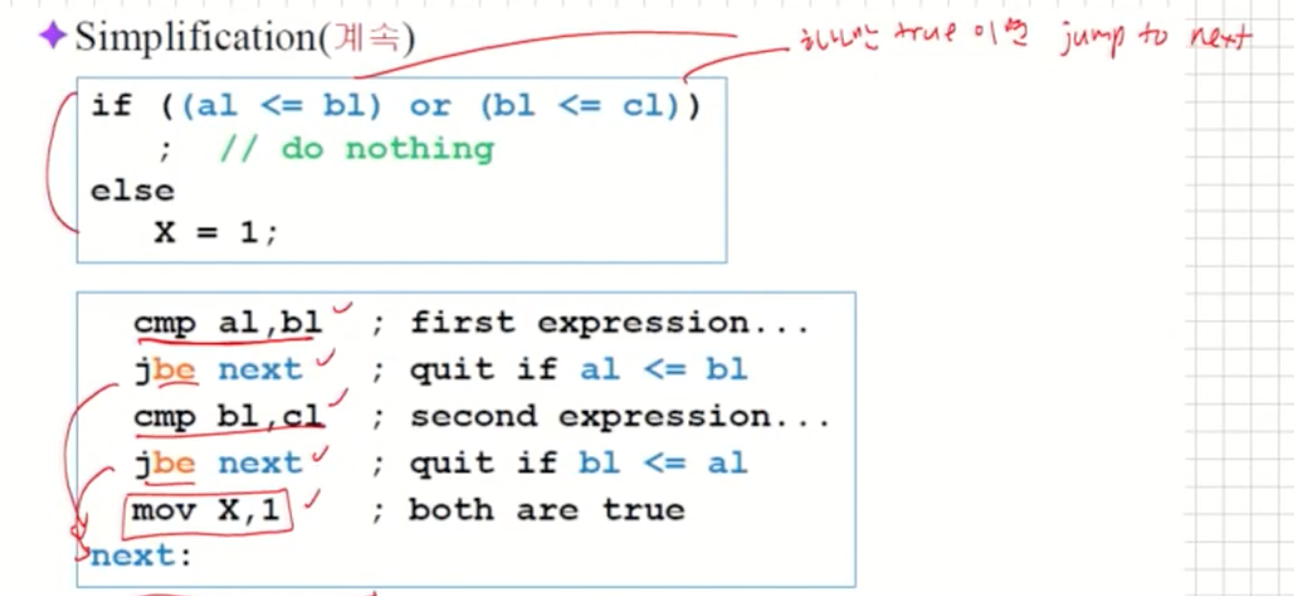
- 총 5 instruction으로 가능(이전 코드는 7 instruction 사용).
- 이렇게 instruction 수를 줄일 수 있게 하는 기본 idea는 가능성이 없으면 속히 quit label로 가게 하는 것이다.
-
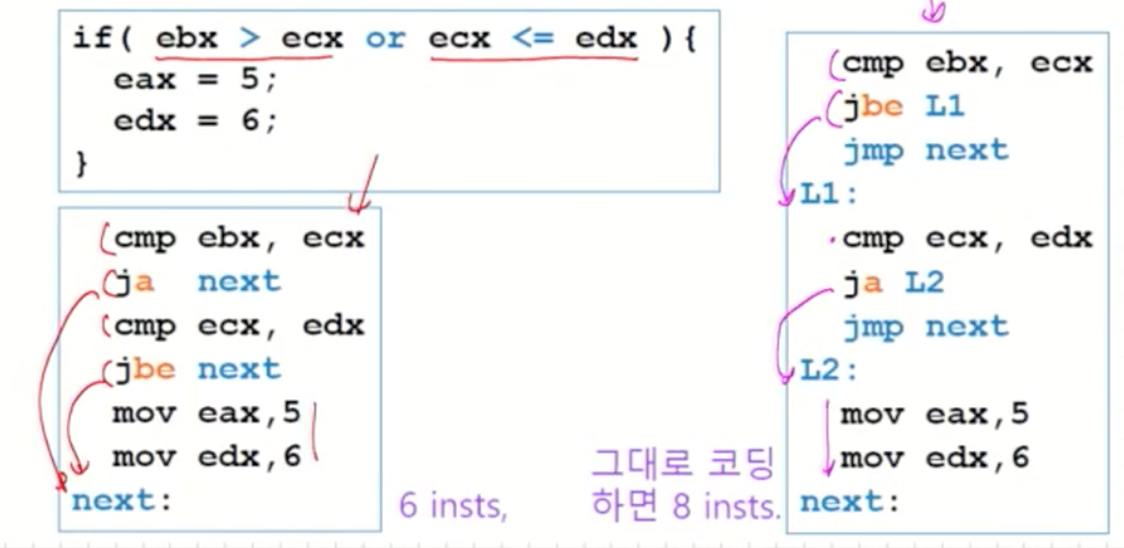
Another Example(unsigned)

이 역시, 가망 없으면 먼저 skip하도록 코드를 수정한다.
Compound Expression with OR
- When implementing the logical OR operator, consider that HLLs use short-circuit evaluation
- In the following example, if the first expression is true, the second expression is skipped:

마지막으로 체크하는 조건에 대해서는 아예 다른 라인으로 가는 조건을 생각해보자 위와 비슷한 형태로
WHILE Loops
-
A WHILE is an if statement (i) followed by the body of the loop, (ii) followed by an unconditional jump to the top of the loop.
-
Consider the following example(eax, ebx have unsigned values)
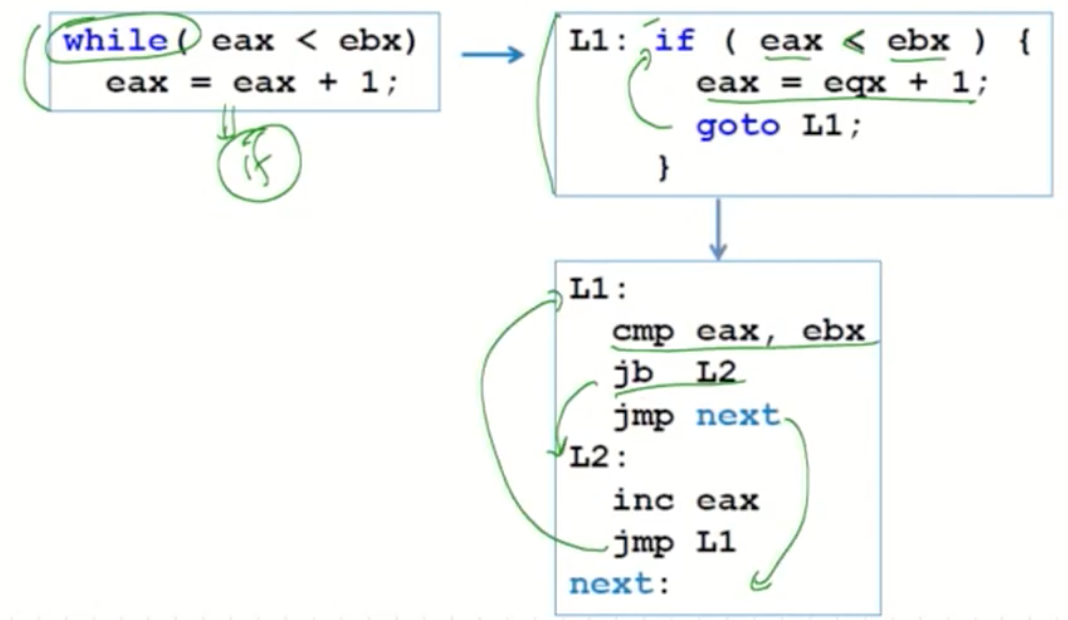
-
Better Implementation
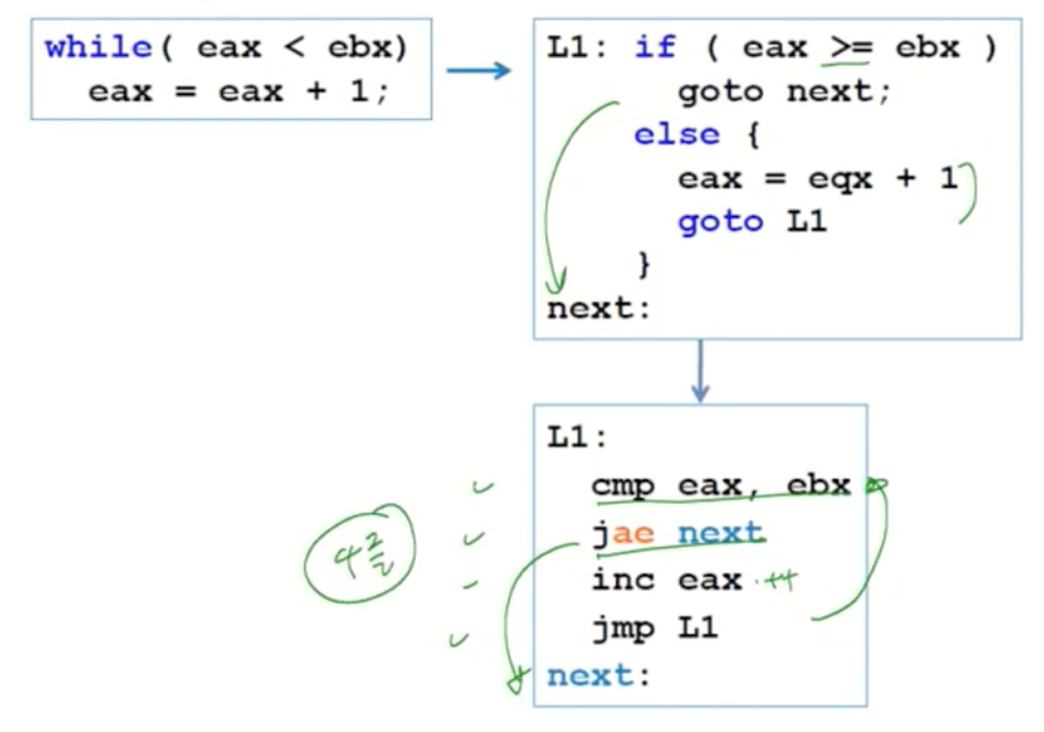
-
Example (signed)
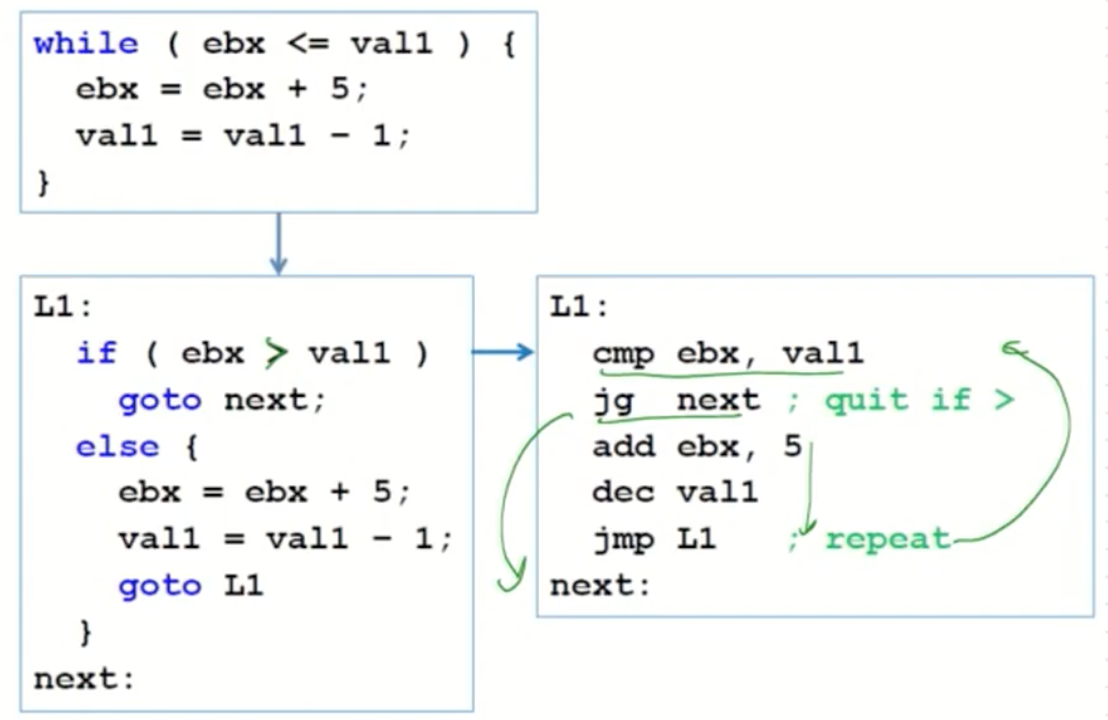
4. Table-Driven Selection
Table-Driven Selection
이번에하는 주제는 switch-case 문이다.
-
Table-driven selection uses a table lookup to replace a multiway selection structure.
-
Create a table containing lookup values and the offsets of labels or procedures.
-
Use a loop to search the table.
-
Suited to a large number of comparisons.
-
Similar to switch in C

-
Creating a table containing lookup values and procedure offsets
- Example(1)
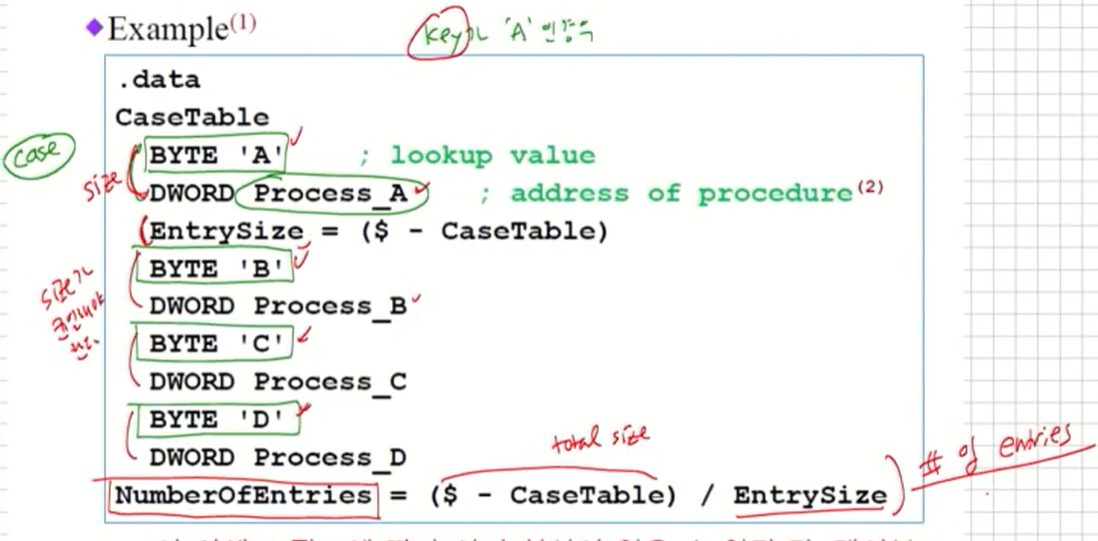
(1) 이 외에도 필요에 따라 여러 형식이 있을 수 있다(단, 테이블
entry는 동일 크기에 규칙적이어야 한다).
(2) 이 table로 다시 돌아오지 않을 경우, jmp address일 수도 있다.
- Example(1)
-
Use a loop to search the table.
-
When a match is found, call the procedure offset in the table.
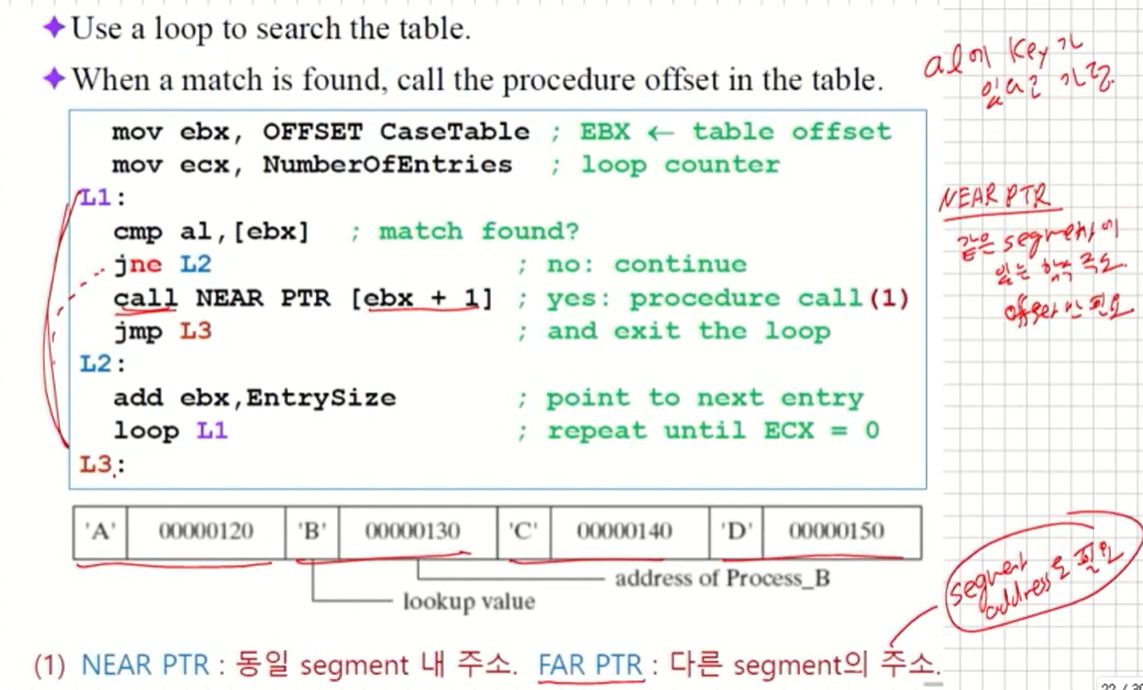
(1) NEAR PTR : 동일 segment 내 주소. FAR PTR : 다른 segment의 주소.(FAR PTR은 flat memo addr을 쓰기 때문에 잘 사용안한다.)
5. Runtime Expressions
Runtime Expressions
어셈블리에 high level언어와 비슷하게 runtime expression을 제공한다.
악영향을 미칠 수 있기 때문에 문제풀이에는 사용금지, 단 알고는 있기 그래야 시험문제를 풀 수 있기 때문
-
.IF, .ELSE, .ELSEIF, and .ENDIF can be used to evaluate runtime expressions and create block-structured IF statements.
-
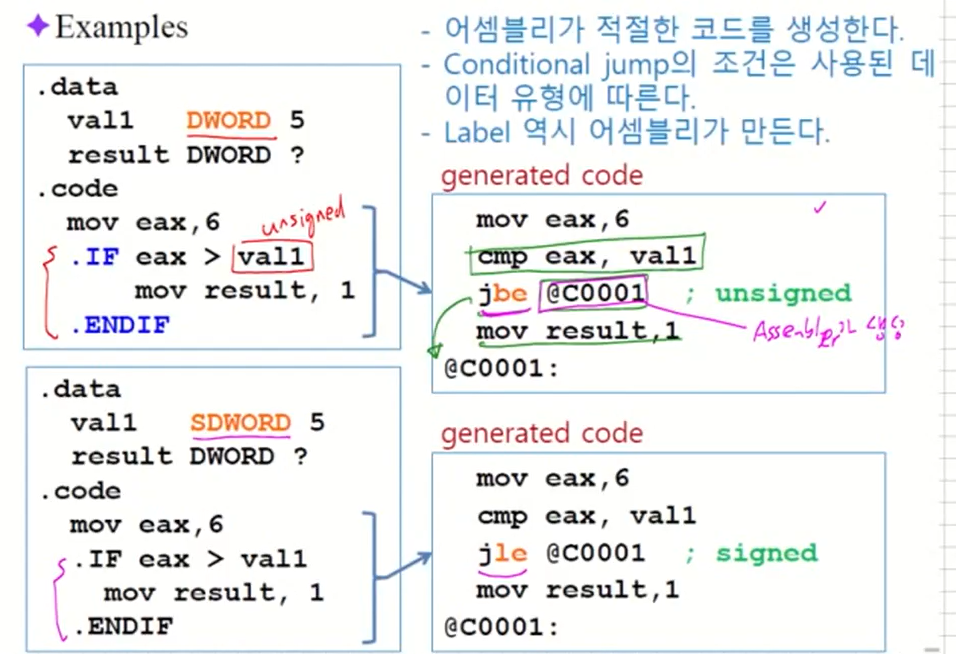
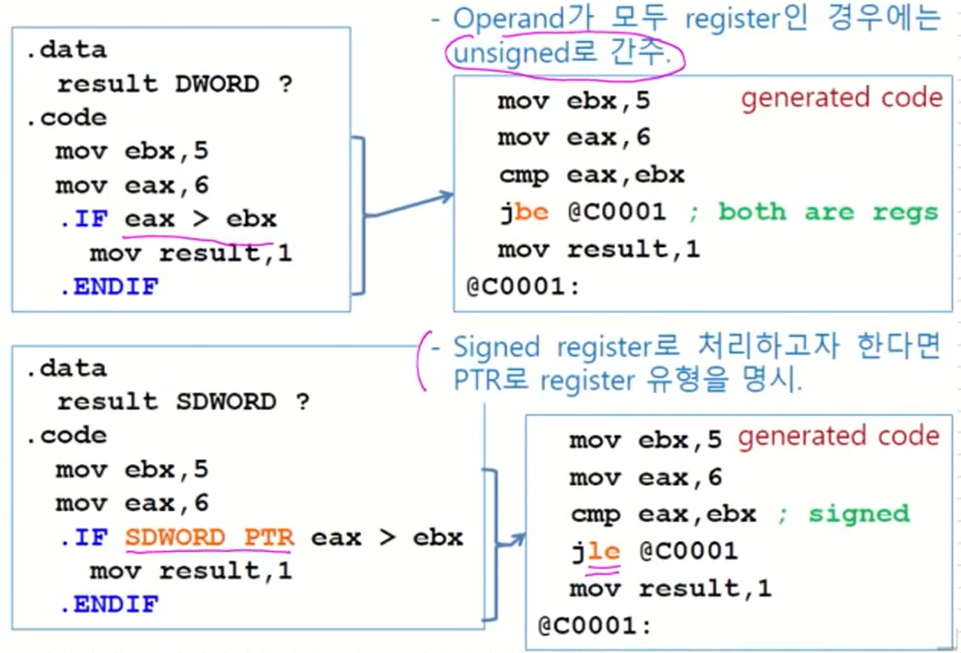
Examples

위와 같이 작성하면 assembler가 code를 만들어준다. -
MASM generates "hidden" code for you, consisting of code labels, CMP and conditional jump instructions.
-
주의
- 어셈블리를 배우는 입장에서 runtime expression은 어셈블리 프로그래밍 능력 향상에 장애가 될 수 있다.
- 따라서, 프로그램 숙제, 실기 시험 등에서는 사용을 불허한다.
- 필기 시험에서 문제로 출제할 가능성은 있다.
-
Assembly Generated Code 보기
- Runtime expression을 사용했을 때, 어셈블러가 생성한 코드를 보고 싶다면, 다음 두 가지 방법으로 볼 수 있다.
- 리스트 파일에 옵션 추가
- 우 클릭 프로젝트 -> 속성 -> Microsoft Macro Assembler -> Listing File -> Enable Assembly Generated Code Listing
- 예(/Sg) 선택
- 리스트 파일에 어셈블러가 생성한 코드가 보인다.
- 디버그 모드에서 보는 방법
- 코드에 적당히 break point를 설정하고 F5를 눌러 디버그모드로 진입한다.
- 디버그 모드에서 디버그 -> 창 -> 디스어셈블리를 클릭하면 편집 창에 디스어셈블리 창이 나타난다.
Relational and Logical Operators
MASM-Generated Code
-
Examples
-
Examples
.REPEAT Directive
- Executes the loop body before testing the loop condition associated with the .UNTIL directive.
- Example

.WHILE Directive
Tests the loop condition before executing the loop body
The .ENDW directive marks the end of the loop.
Examples

