해시 기본 개념
해시(hash)
- 자료를 입력할 때부터 검색하기 쉬운 위치에 입력하는 방법이다. 따라서 해시는 검색을 빠르게 하는 방법이라기보다는 빠른 검색을 위한 자료관리 기법이라고 할 수 있다.
- 대표적으로 주소록을 예로 들어보면, 가 나 다 라 순으로 페이지를 분류하고, 이름을 첫 글자 자음을 기준으로 이름을 저장하는 방식이다. 이와 같이 이름 저장 시 성별로 구분하여 저장하면 나중에 이름을 찾을 때 매우 쉽게 찾을 수 있다.
구조
- 해시테이블: 해싱방식의 데이터를 저장하는 저장소이며, 여러 개의 버킷으로 나누어진다. 주소록의 ㄱ, ㄴ, ㄷ, ㄹ 과 같은 페이지가 각 버킷이 된다.
- 슬롯: 버킷 내부에 저장되는 실제 데이터를 슬롯이라고 하는데, 주소록에서 각 이름에 해당된다.
기본 동작
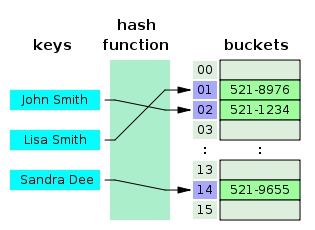
- 해시 알고리즘(함수): 새 데이터가 새로 입력되면, 가장 먼저 어떤 버킷에 넣을 것인지 결정해야 하는데 이 연산을 하는 기능이다.
- 특정 데이터를 검색시에도 해시알고리즘 기능을 사용하면 어떤 버킷에서 찾을 것인지 결정되기 때문에 빠르게 검색할 수 있다.
Question 1
- 0보다 큰 정수값을 사용자로부터 입력 받아서 해시테이블에 저장한다.
- 해시테이블 생성 시 버킷 수는 10개 슬롯 수는 1개로 지정한다.
- 해시테이블에서 값이 0이면 빈 데이터 공간을 의미한다.
- 5개의 각 정수를 입력 시 각각의 입력값은 입력할 버킷을 찾는 해시 함수에 의해 버킷을 찾아 해시테이블에 저장한다.
- 5개의 정수 입력이 끝났으면, 검색할 키를 입력 받아 검색 결과를 출력한다.
- 검색 시에도 해시함수를 이용하여 해시테이블을 검색한다.
- 각 기능은 함수로 모듈화 하여 구현한다.
- 해시함수 이름은 Hash, 값 입력 함수 이름은
InsertValue, 값 검색 함수 이름은FindValue로 정한다. - 입력 입력할 키값을 프로그램 콘솔 키보드로부터 입력 받는다. 입력 키값은 양의 정수로만 입력 받는다.
- 사용자가 입력한 키값이 검색되었을 경우 : “검색되었습니다.”
- 사용자가 입력한 키값이 검색되지 않았을 경우 : “검색되지 않았습니다.”
e.g) 키를 5개 입력하세요.
11 22 54 396 87
검색할 키를 입력하세요.
22
검색되었습니다.
코드 기본 형태
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int hashtable[10][1];
//키 값에 따른 위치값 출력 함수
int Hash(int nKey) {
return nKey % 10;
}
void main()
{
int key = 22;
memset(hashtable, 0, sizeof(hashtable));
int bucket = Hash(key);
hashtable[bucket][0] = key;
}기초 해시 테이블 구현 (충돌 처리 없는 정적 해시)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define BK 10
#define SL 1
int hashtable[BK][SL]; // 해시 테이블을 저장할 배열, 크기는 10으로 설정
// 키 값에 따른 위치값을 계산하여 반환하는 해시 함수
int Hash(int nKey) {
return nKey % 10; // 키 값에 10을 나눈 나머지를 반환하여 해시값 생성
}
// 해시 테이블에 값을 삽입하는 함수
void InsertValue(int nKey) {
int bucket = Hash(nKey); // 키 값을 해시 함수로 계산하여 버킷(위치) 찾기
if (hashtable[bucket][0] == 0) { // 해당 위치가 비어 있으면 값을 삽입
hashtable[bucket][0] = nKey;
}
}
// 해시 테이블에서 값을 찾는 함수
int FindValue(int nKey) {
int bucket = Hash(nKey); // 키 값을 해시 함수로 계산하여 버킷(위치) 찾기
return (hashtable[bucket][0] == nKey); // 해당 위치에 값이 일치하면 1을 반환, 아니면 0을 반환
}
int main() {
int key = 0; // 검색할 키 값
memset(hashtable, 0, sizeof(hashtable)); // 해시 테이블 초기화 (0으로 채움)
// 사용자로부터 5개의 키 값을 입력받아 해시 테이블에 삽입
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d번째 값을 입력하세요 : ", i + 1);
scanf("%d", &key);
InsertValue(key); // 입력된 값을 해시 테이블에 삽입
}
// 검색할 키 값을 입력받고 검색 결과 출력
printf("검색할 키를 입력하세요 : ");
scanf("%d", &key);
if (FindValue(key)) { // 키가 테이블에 있으면
printf("검색되었습니다.\n");
} else { // 키가 테이블에 없으면
printf("검색되지 않았습니다.\n");
}
return 0;
}
- 해시 테이블
- 데이터를 저장할 배열. 여기선
hashtable[10][1]사용. - 배열의 인덱스를 계산해 데이터를 빠르게 저장하고 찾음.
- 데이터를 저장할 배열. 여기선
- 해시 함수 (
Hash)- 키를 테이블 인덱스로 바꿔주는 함수.
Hash(nKey) = nKey % 10→ 0~9 사이의 인덱스를 만듦.
- 삽입 함수 (
InsertValue)- 키 값을 해시 함수로 계산해서 빈 칸이면 저장함.
- 충돌(같은 인덱스)에 대한 처리는 없음 (단순한 구조).
- 검색 함수 (
FindValue)- 입력된 키가 해시 테이블에 있는지 확인함.
- 인덱스를 계산해서 값이 같으면 "있다", 다르면 "없다".
- 초기화 (
memset)- 해시 테이블을 0으로 초기화해서 비어있는 상태로 만듦.
🟨 JavaScript Code
const readline = require('readline');
const rl = readline.createInterface({
input: process.stdin,
output: process.stdout,
});
const BK = 10;
const SL = 1;
// 해시 테이블 생성
let hashtable = Array.from({ length: BK }, () => []);
// 해시 함수
function Hash(nKey) {
return nKey % 10;
}
// 값 삽입 함수
function InsertValue(nKey) {
const bucket = Hash(nKey);
if (!hashtable[bucket].includes(nKey)) {
hashtable[bucket].push(nKey);
}
}
// 값 찾기 함수
function FindValue(nKey) {
const bucket = Hash(nKey);
return hashtable[bucket].includes(nKey);
}
// 사용자 입력 받기
let inputCount = 0;
let keys = [];
function askQuestion() {
if(inputCount < 5) {
rl.question(`${inputCount + 1}번째 값을 입력하세요: `, (key) => {
InsertValue(parseInt(key, 10));
inputCount++;
askQuestion();
});
} else {
rl.question('검색할 키를 입력하세요: ', (key) => {
if (FindValue(parseInt(key, 10))) {
console.log("검색되었습니다.")
} else {
console.log('검색되지 않았습니다.')
}
rl.close();
});
}
}
askQuestion();자바스크립트 배열 함수
Array.from()
- 배열 또는 유사 배열 객체로부터 새 배열을 만듭니다. 두 번째 인자에 콜백을 넘겨 초기값 지정 가능.
let hashtable = Array.from({ length: BK }, () => []);Array.prototype.includes()
- 배열 안에 특정 값이 존재하는지 여부를 확인 (불리언 반환).
if (!hashtable[bucket].includes(nKey)) { ... }Array.prototype.push()
- 배열 끝에 요소를 추가합니다.
hashtable[bucket].push(nKey);Step. 2 버킷 충돌 해결 (슬롯 확장)
슬롯을 배열로 만들기
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define BUCKET_SIZE 10
#define SLOT_SIZE 10
int hashtable[BUCKET_SIZE][SLOT_SIZE]; // 각 해시 버킷마다 SLOT_SIZE 크기의 배열
int count[BUCKET_SIZE]; // 각 버킷에 들어간 값의 개수 (삽입 위치 추적)
int Hash(int nKey) {
return nKey % 10;
}
void InsertValue(int nKey) {
int bucket = Hash(nKey);
for (int i = 0; i < count[bucket]; i++) {
if(hashtable[bucket][i] == nKey) return;
}
if (count[bucket] < SLOT_SIZE) {
hashtable[bucket][count[bucket]] = nKey;
count[bucket]++;
}
}
int FindValue(int nKey)
{
int bucket = Hash(nKey);
for (int i = 0; i < count[bucket]; i++) {
if (hashtable[bucket][i] == nKey) {
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
int key;
memset(hashtable, 0, sizeof(hashtable));
memset(count, 0, sizeof(count));
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d번째 값을 입력하세요 : ", i + 1);
scanf("%d", &key);
InsertValue(key);
}
printf("검색할 키를 입력하세요 : ");
scanf("%d", &key);
if (FindValue(key)) {
printf("검색되었습니다.\n");
} else {
printf("검색되지 않았습니다.\n");
}
return 0;
}Step. 3 버킷 충돌 해결 (동적 배열)
버킷마다 여러 개의 값을 저장할 수 있도록, 각 버킷에 정수 배열(리스트처럼)을 연결하는 구조로 만들기.
삽입 함수 (InsertValue)
void InsertValue(int nKey) {
int bucket = Hash(nKey);
// 버킷이 아직 할당되지 않았다면, 처음 할당
if (hashtable[bucket] == NULL) {
hashtable[bucket] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
hashtable[bucket][0] = nKey;
count[bucket] = 1;
return;
}
// 중복 검사
for (int i = 0; i < count[bucket]; i++) {
if (hashtable[bucket][i] == nKey) return;
}
// 공간 확장
hashtable[bucket] = (int*)realloc(hashtable[bucket], sizeof(int) * (count[bucket] + 1));
hashtable[bucket][count[bucket]] = nKey;
count[bucket]++;
}
검색 함수 (FindValue)
int FindValue(int nKey) {
int bucket = Hash(nKey);
for (int i = 0; i < count[bucket]; i++) {
if (hashtable[bucket][i] == nKey) return 1;
}
return 0;
}메모리 해제 (종료 시)
for (int i = 0; i < BUCKET_SIZE; i++) {
if (hashtable[i] != NULL) {
free(hashtable[i]);
}
}전체코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define BUCKET_SIZE 10
int* hashtable[BUCKET_SIZE]; // 각 버킷이 가리키는 int 배열 (동적 할당)
int count[BUCKET_SIZE]; // 각 버킷에 저장된 값 개수
// 해시 함수: 키를 버킷 인덱스로 변환
int Hash(int nKey) {
return nKey % BUCKET_SIZE;
}
// 해시 테이블에 값 삽입
void InsertValue(int nKey) {
int bucket = Hash(nKey);
// 버킷이 비어 있다면 새 배열 할당
if (hashtable[bucket] == NULL) {
hashtable[bucket] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
hashtable[bucket][0] = nKey;
count[bucket] = 1;
return;
}
// 중복 검사
for (int i = 0; i < count[bucket]; i++) {
if (hashtable[bucket][i] == nKey) return; // 중복이면 삽입 안 함
}
// 배열 크기 확장 후 삽입
hashtable[bucket] = (int*)realloc(hashtable[bucket], sizeof(int) * (count[bucket] + 1));
hashtable[bucket][count[bucket]] = nKey;
count[bucket]++;
}
// 해시 테이블에서 값 검색
int FindValue(int nKey) {
int bucket = Hash(nKey);
for (int i = 0; i < count[bucket]; i++) {
if (hashtable[bucket][i] == nKey) return 1; // 찾음
}
return 0; // 없음
}
// 전체 해시 테이블 출력 (디버깅용)
void PrintHashTable() {
for (int i = 0; i < BUCKET_SIZE; i++) {
printf("[%d]: ", i);
for (int j = 0; j < count[i]; j++) {
printf("%d ", hashtable[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main() {
int key;
// 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < BUCKET_SIZE; i++) {
hashtable[i] = NULL;
count[i] = 0;
}
// 값 삽입
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d번째 값을 입력하세요: ", i + 1);
scanf("%d", &key);
InsertValue(key);
}
// 해시 테이블 출력
printf("\n=== 해시 테이블 상태 ===\n");
PrintHashTable();
// 검색
printf("\n검색할 키를 입력하세요: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
if (FindValue(key)) {
printf("검색되었습니다.\n");
} else {
printf("검색되지 않았습니다.\n");
}
// 메모리 해제
for (int i = 0; i < BUCKET_SIZE; i++) {
if (hashtable[i] != NULL) {
free(hashtable[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}
