DFS
백준 2606번을 DFS 를 이용해 Java 로 풀어봤다. 인접리스트(Adjancey List)를 Java 를 이용해 어떻게 구현해야하는지 다 잊어먹어서 이것부터 다시 찾아봤다.
그래프를 구현하는 두 가지 방식 인접행렬과 인접리스트 중 인접 리스트를 사용하는 것이 더 적절한 방식 같아서 인접리스트를 사용했다.
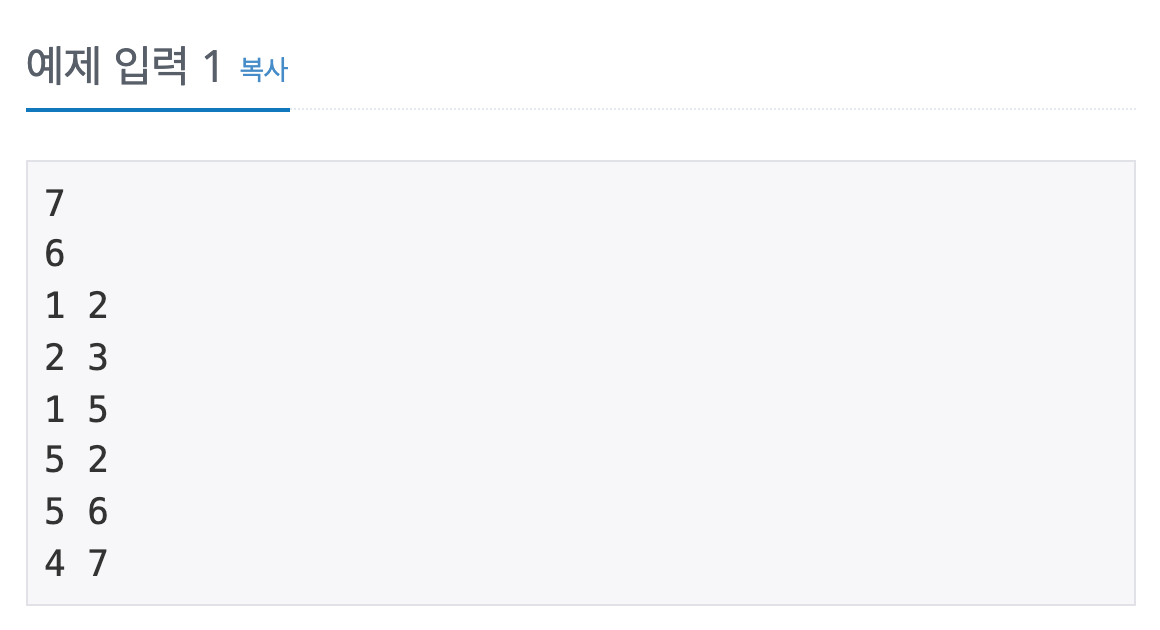
위와 같은 예시를 인접 리스트로 구현하기 위해서는 1 2 를 입력 받아서 1번 정점에 2를 추가해주고, 2번 정점에도 1을 추가해주는 방식이다.
for(int i=0; i<M; i++){
stk = new StringTokenizer(bfr.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(stk.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(stk.nextToken());
graph.get(a).add(b); // a 정점에 b를 추가해주고
graph.get(b).add(a); // b 정점에도 a를 추가해주자
}이와 같은 방식으로 인접리스트 를 완성한다.
탐색할 정점을 dfs 메소드에 넘겨주면 해당 정점이 갖고 있는 인접 정점들을 돌며 아직 방문하지 않은 정점들에 대해 dfs 를 수행해주며 count 값을 1씩 더해준다.
이렇게 dfs 메소드가 탐색을 마치면 감염된 컴퓨터의 수를 얻게 된다.
static void dfs(int start){
visited[start] = true;
count += 1;
int size = graph.get(start).size();
for(int i=0; i<size; i++){
int vertex = graph.get(start).get(i);
if(visited[vertex])
continue;
dfs(vertex);
}
}아래는 제출한 코드다.
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class boj2606 {
static int N,M,count;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph;
static boolean[] visited;
static void dfs(int start){
visited[start] = true;
count += 1;
int size = graph.get(start).size();
for(int i=0; i<size; i++){
int vertex = graph.get(start).get(i);
if(visited[vertex])
continue;
dfs(vertex);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bfr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bfw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
StringTokenizer stk;
N = Integer.parseInt(bfr.readLine());
M = Integer.parseInt(bfr.readLine());
graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
visited = new boolean[N+1];
for(int i=0; i<N+1; i++)
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
for(int i=0; i<M; i++){
stk = new StringTokenizer(bfr.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(stk.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(stk.nextToken());
graph.get(a).add(b);
graph.get(b).add(a);
}
dfs(1);
bfw.write(String.valueOf(count-1));
bfw.close();
}
}
오늘 배운 것
- 자바로
인접리스트( Adjancey List )구현하는 방법인접리스트( Adjancey List )에서 DFS 탐색하는 방법

