
구현 ( BFS )
프로그래머스 2020 KAKAO BLIND RECRUITMENT Level 3 문제 블록 이동하기를 Java를 이용해 풀어보았다. 결국 못 풀고 다른 사람 풀이를 참고해 간신히 제출했다.
존나 더럽고... 개빡치는 문제였다...
문제 링크 첨부한다.
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/60063
두 칸짜리 이동하기 ( BFS )
결론적으로는 BFS 문제인데 한 좌표만을 이동시키는 것이 아니라 동시에 두 좌표를 한 몸처럼 이동시키는 문제였고 회전까지 들어가서 돌아버리는 줄 알았다.
두 칸짜리를 회전까지 시키니까 가로로 있는지 세로로 있는지의 여부도 함께 추적해야한다. 이를 위해 Info 클래스를 정의했다.
class Info{
int r1; int c1;
int r2; int c2;
int type;
int cnt;
Info(int r1, int c1, int r2, int c2, int type, int cnt){
this.r1 = r1; this.c1 = c1;
this.r2 = r2; this.c2 = c2;
this.type = type;
this.cnt = cnt; // 여기까지 몇 초 걸렸는지
}
}큐에 가장 첫 시작점인 (0,0)과 (0,1)과 가로 type 값인 0을 넣어주고 시작한다.
그리고 큐에서 하나씩 빼면서 그 상태 그대로 상하좌우 방향으로 움직여서 이동 가능한 좌표들은 큐에 넣어준다.
이때 네 가지 각 방향을 상,하 + 좌,우로 나누자.
1. 가로일 경우에는 상,하 방향으로 회전시킨 좌표 중 이동 가능한 좌표들을 큐에 넣어준다.
2. 세로일 경우에는 좌,우 방향으로 회전시킨 좌표 중 이동 가능한 좌표들을 큐에 넣어준다.
이게 무슨 말이냐 하면... 0~3의 방향값, 즉 상하좌우로 방향 좌표를 미리 정해두면 상하로 움직일 때는 우측과 같이 (nr1,nc1) 과 (r1,c1)을 큐에 넣어주고 또 (nr2,nc2)과 (r2,c2)를 큐에 넣어주면 되는 것이다.
좌우에 대해서도 동일하게 진행하면 된다.
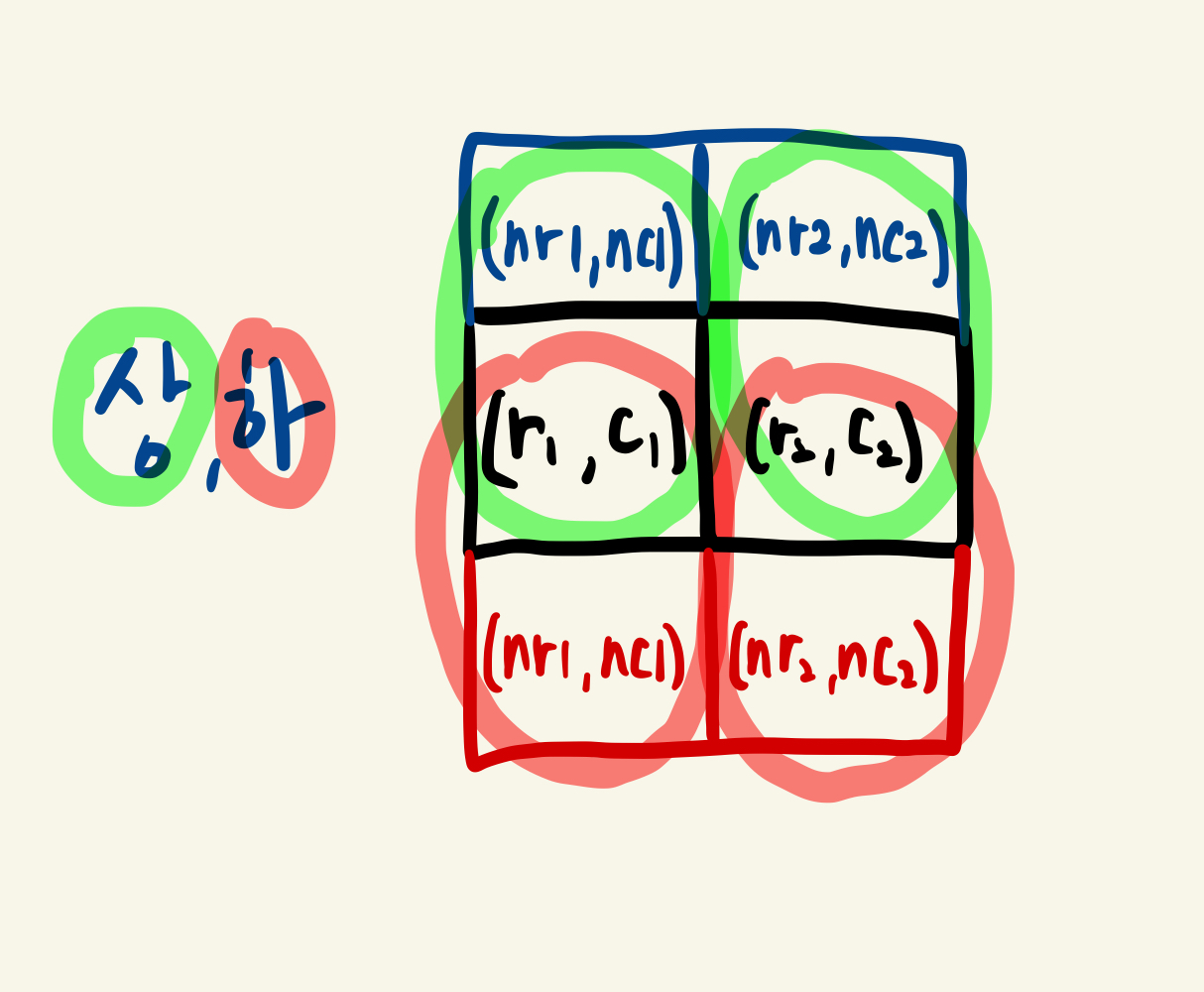
이렇게 네 가지 방향에 대해 모두 작업을 진행해주면 된다. 이를 코드로 표현하면 다음과 같다.
Integer BFS(){
boolean[][][] visited = new boolean[2][N][N];
Queue<Info> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new Info(0,0, 0,1, 0, 0));
visited[0][0][0] = true;
visited[0][0][1] = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Info cur = q.poll();
if( (cur.r1==N-1 && cur.c1==N-1) || (cur.r2==N-1 && cur.c2==N-1) ) return cur.cnt;
for(int dir=0; dir<4; dir++){
int next_r1 = cur.r1 + move[dir][0]; int next_c1 = cur.c1 + move[dir][1];
int next_r2 = cur.r2 + move[dir][0]; int next_c2 = cur.c2 + move[dir][1];
if(isValid(next_r1,next_c1,next_r2,next_c2)){ // 범위 안에 있고 벽이 아닌지 확인
if (!visited[cur.type][next_r1][next_c1] || !visited[cur.type][next_r2][next_c2]) {
visited[cur.type][next_r1][next_c1] = true;
visited[cur.type][next_r2][next_c2] = true;
q.offer(new Info(next_r1,next_c1, next_r2,next_c2, cur.type, cur.cnt+1));
}
int change_type = (cur.type==0 ? 1 : 0); // 회전 시키자
if( (cur.type==0 && dir<2) || (cur.type==1 && dir>1) ){ // 가로로 있을 때는 세로 방향으로 회전, 세로로 있을 때는 가로로 회전
if(!visited[change_type][next_r1][next_c1] || !visited[change_type][cur.r1][cur.c1]) {
visited[change_type][next_r1][next_c1] = true;
visited[change_type][cur.r1][cur.c1] = true;
q.offer(new Info(next_r1,next_c1, cur.r1,cur.c1, change_type, cur.cnt+1));
}
if(!visited[change_type][next_r2][next_c2] || !visited[change_type][cur.r2][cur.c2]) {
visited[change_type][next_r2][next_c2] = true;
visited[change_type][cur.r2][cur.c2] = true;
q.offer(new Info(next_r2,next_c2, cur.r2,cur.c2, change_type, cur.cnt+1));
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}isValid 메소드는 범위 밖인지 + 벽인지 를 체크해주는 메소드다.
Boolean isValid(int r1, int c1, int r2, int c2){
if(r1<0 || r1>=N || c1<0 || c1>=N || r2<0 || r2>=N || c2<0 || c2>=N) return false;
if(map[r1][c1]==1 || map[r2][c2]==1) return false;
return true;
}위의 코드들을 모두 합치면 다음과 같다. 내가 제출한 코드다.
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class MovingBlocks {
static int N;
static int[][] move = { {1,0}, {-1,0}, {0,1}, {0,-1} };
static int[][] map;
static int solution(int[][] board) {
N = board.length;
map = new int[N][N];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) map[i] = board[i].clone();
int answer = BFS();
return answer;
}
static Integer BFS(){
boolean[][][] visited = new boolean[2][N][N];
Queue<Info> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new Info(0,0, 0,1, 0, 0));
visited[0][0][0] = true;
visited[0][0][1] = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Info cur = q.poll();
if( (cur.r1==N-1 && cur.c1==N-1) || (cur.r2==N-1 && cur.c2==N-1) ) return cur.cnt;
for(int dir=0; dir<4; dir++){
int next_r1 = cur.r1 + move[dir][0]; int next_c1 = cur.c1 + move[dir][1];
int next_r2 = cur.r2 + move[dir][0]; int next_c2 = cur.c2 + move[dir][1];
if(isValid(next_r1,next_c1,next_r2,next_c2)){ // 범위 안에 있고 벽이 아닌지 확인
if (!visited[cur.type][next_r1][next_c1] || !visited[cur.type][next_r2][next_c2]) {
visited[cur.type][next_r1][next_c1] = true;
visited[cur.type][next_r2][next_c2] = true;
q.offer(new Info(next_r1,next_c1, next_r2,next_c2, cur.type, cur.cnt+1));
}
int change_type = (cur.type==0 ? 1 : 0); // 회전 시키자
if( (cur.type==0 && dir<2) || (cur.type==1 && dir>1) ){ // 가로로 있을 때는 세로 방향으로 회전, 세로로 있을 때는 가로로 회전
if(!visited[change_type][next_r1][next_c1] || !visited[change_type][cur.r1][cur.c1]) {
visited[change_type][next_r1][next_c1] = true;
visited[change_type][cur.r1][cur.c1] = true;
q.offer(new Info(next_r1,next_c1, cur.r1,cur.c1, change_type, cur.cnt+1));
}
if(!visited[change_type][next_r2][next_c2] || !visited[change_type][cur.r2][cur.c2]) {
visited[change_type][next_r2][next_c2] = true;
visited[change_type][cur.r2][cur.c2] = true;
q.offer(new Info(next_r2,next_c2, cur.r2,cur.c2, change_type, cur.cnt+1));
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
static Boolean isValid(int r1, int c1, int r2, int c2){
if(r1<0 || r1>=N || c1<0 || c1>=N || r2<0 || r2>=N || c2<0 || c2>=N) return false;
if(map[r1][c1]==1 || map[r2][c2]==1) return false;
return true;
}
static class Info{
int r1; int c1;
int r2; int c2;
int type;
int cnt;
Info(int r1, int c1, int r2, int c2, int type, int cnt){
this.r1 = r1; this.c1 = c1;
this.r2 = r2; this.c2 = c2;
this.type = type;
this.cnt = cnt;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] board = {{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0}, {0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}};
int res = solution(board);
System.out.println(res);
}
}내가 1시간 동안 위의 코드를 짜두고도 시간초과 때문에 계속 통과를 못했다. 나중에 너무 허망한 이유였는데 visited 정보를 큐에서 꺼낼 때 갱신해주는 것이 문제였다. 넣을 때 동시에 visited 정보를 갱신해줘야 했는데 큐에서 꺼내는 타이밍에 했더니 불필요한 Info들이 잔뜩 들어가게 된 것이다.
왜냐하면 아직 꺼내지지 않은 것들에 대해서 또다시 중복해서 들어가게 되기 때문이었다... 앞으로 visited 정보는 큐에 넣음과 동시에 갱신해주자.
오늘 배운 것
- 네카라쿠배를 과연 갈 수 있을까
- 구현은 졸라 어렵다
- 최단 경로 문제 풀 때
visited정보는 큐에 넣음과 동시에 갱신해주자
