Java Arrays Demystified: Examples, Code, and Use Cases
Arrays in Java
Introduction
Arrays in Java are one of the most fundamental and widely used data structures. Whether you're a beginner exploring your first Java tutorial or a seasoned developer brushing up on the basics, understanding arrays is essential to writing efficient Java code. This blog post will break down arrays in Java with detailed examples, code snippets, and real-world use cases to help demystify the concept.
What is an Array in Java?
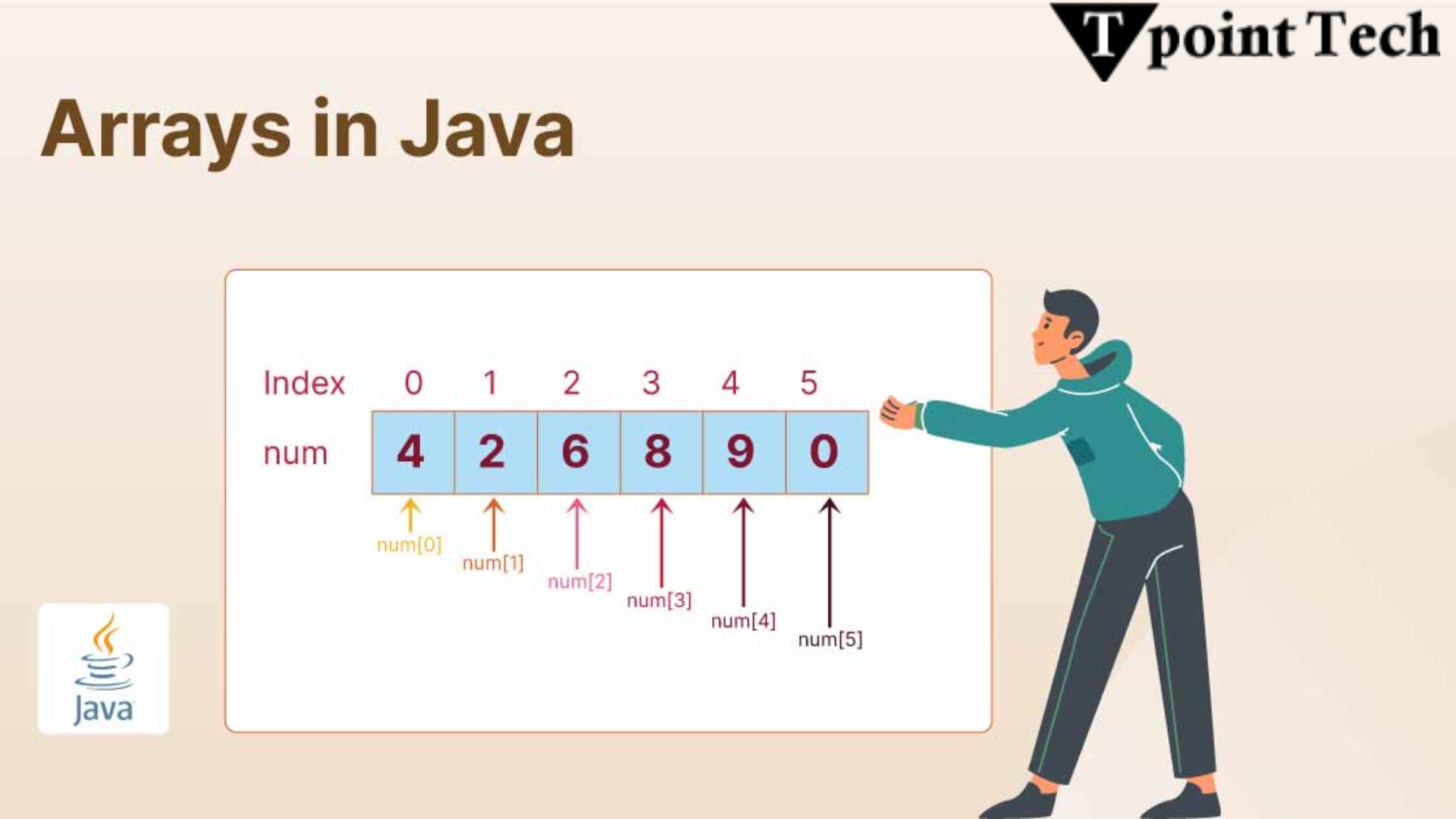
An array in Java is a container object that holds a fixed number of values of a single data type. The length of an array is established when the array is created, and it cannot be changed. Arrays are stored in contiguous memory locations, and elements are accessed using an index, starting from 0.
In simpler terms, an array allows you to store multiple values of the same type in a single variable, rather than declaring separate variables for each value.
Declaring and Initializing Arrays in Java
Here’s the basic syntax to declare and initialize arrays in Java:
// Declaration
int[] numbers;
// Initialization
numbers = new int[5]; // Array of 5 integers
// Declaration and Initialization combined
String[] fruits = {"Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"};You can also initialize an array with default values. Java arrays are automatically initialized to default values depending on the data type — 0 for integers, false for booleans, null for objects, etc.
Example: Integer Array
public class ArrayExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] marks = {85, 90, 78, 92, 88};
System.out.println("Student Marks:");
for (int i = 0; i < marks.length; i++) {
System.out.println("Subject " + (i + 1) + ": " + marks[i]);
}
}
}Output:
Student Marks:
Subject 1: 85
Subject 2: 90
Subject 3: 78
Subject 4: 92
Subject 5: 88Types of Arrays in Java
-
Single-dimensional Arrays
These are the most common types, as seen in the examples above. -
Multidimensional Arrays
Java supports multidimensional arrays, such as 2D arrays, which can be thought of as arrays of arrays.
Example: 2D Array
public class MatrixExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] matrix = {
{1, 2},
{3, 4},
{5, 6}
};
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
1 2
3 4
5 6Common Operations on Arrays in Java
Here are some frequently used operations involving arrays in Java:
- Traversing: Using loops to access each element.
- Sorting: Arrays can be sorted using
Arrays.sort()fromjava.utilpackage. - Searching: Linear or binary search to find an element.
- Copying: Using
System.arraycopy()orArrays.copyOf().
Example: Sorting an Array
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] data = {34, 12, 56, 78, 23};
Arrays.sort(data);
System.out.println("Sorted Array: " + Arrays.toString(data));
}
}Output:
Sorted Array: [12, 23, 34, 56, 78]Use Cases of Arrays in Java
Arrays are used in a wide range of applications. Here are a few real-world use cases:
1. Data Processing
Arrays are perfect for storing large datasets for processing, such as temperature logs, stock prices, or sensor data.
2. Game Development
Arrays can be used to store game state, such as positions on a chessboard or tiles in a grid-based game.
3. Image and Signal Processing
Pixels in images are typically stored in 2D arrays for manipulation and transformation.
4. Interview Questions
Arrays in Java are frequently used in coding interviews. Questions on reversing arrays, finding duplicates, and subarray sums are common.
Arrays vs. ArrayList
While arrays are powerful, they have limitations, such as fixed size. If you need a dynamic-sized structure, consider using ArrayList, which allows you to add or remove elements easily.
When to Use Arrays:
- When performance is critical.
- When size is known and constant.
- For fixed-size multi-dimensional data.
Conclusion
Arrays in Java are a foundational concept that every Java developer must master. They provide a simple and efficient way to group data and perform operations like sorting, searching, and traversal. As seen in this Java tutorial, arrays are easy to use and incredibly versatile.
By practicing with code examples and real-world use cases, you’ll quickly become proficient in working with arrays in Java. Whether you're preparing for interviews or developing enterprise applications, arrays will be one of your go-to tools in Java programming.
