- Spring 환경설정
- 기존 사용 이클립스 + 스프링코드 작성 + plugin 따로 설치
- 전용 ide설치 => sts(plugin) 설치
-
sts 설정
한글설정, 디폴트 브라우저 설정, 기존 디폴트 서버 삭제
서버 Tomcat 설치 => 3가지 설정 -
라이브러리(jar파일의 자동 다운로드)
환경설정문서(메이븐 : POM.XML, GRADLE:.GRADLE)
디펜던시 개념 사용 => 원격지에서 jar파일 자동 다운로드 사용
프로젝트 실행시 다운로드 완료 후 실행
C: -> user -> .m2 -> repository
pom.xml
0.java version 수정
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
- spring버전수정
<!-- Spring -->
<!-- Spring framework 버전 4.3.22로 수정 -->
<spring-framework.version>4.3.22.RELEASE</spring-framework.version>- complier 버전 수정
<configuration>
<!-- complier 버전 1.8로 수정 -->
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>-
필요시 사이에 디펜던시 추가 (.jar파일다운- jdbc, mybatis드라이버등...)
-
프로젝트 maven - update 실행 jar파일 업데이트 후 프로젝트 작성 진행
🔎Spring??
스프링이란 Java 엔터프라이즈(J2EE)개발을 편하게 해주는 오픈소스 경량급 어플리케이션 프레임워크이다.
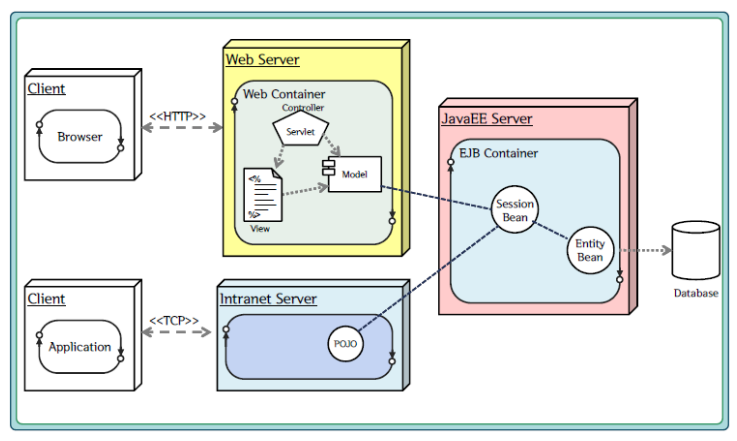
2003년 2월부터 오픈소스로 시작된 프로젝트로서 경량의 제어역행(IoC: Inversion of Control)과 관점지향(AOP: Aspect Object Programming)의 컨테이너 프레임워크이다.
Spring Framework 특징
- AOP (기능별 모듈화, 진정한 OOP 제공)
- AOP지원을 통해 주요 비즈니스 로직(핵심기능)과 시스템 전반에 걸쳐있는 기능모듈(부가기능)을 완벽히 분리해내도록 도와준다.
-
IoC컨테이너
- 애플리케이션 객체를 연결해주고 자동화된 설정 및 집중화된 설정을 제공하는 가장 완전한 경량 컨테이너
- 개발자가 직접 객체를 생성하지 않고, 객체의 생성에서 소멸까지 컨테이너가 관리
- Dependency Injection을 통해 객체간의 의존성 주입
-
트랜잭션
- 트랜잭션 관리를 위한 공통의 추상화된 레이어, 트랜잭션 관리자를 사용하여 저수준 트랜잭션 처리 가능
- 선언적인 트랜잭션을 지원하여 코드를 수정하지 않고도 트랜잭션을 적용 및 변경이 가능
-
JDBC 추상화 레이어
- 중요한 예외 계층을 제공하며, 예외처리를 단순화시켜 코드의 양이 감소
-
ORM 프레임워크 연동 제공
- hibernate, Mybatis, JPA등과 같은 ORM 프레임워크 연동 가능
-
좀 더 쉬운 J2EE개발 지향
- 계층화된 아키텍쳐를 갖고 있으며, 그 중 어떤 부분도 독립적으로 사용될 수 있도록 모듈화 되어있다.
- 비즈니스 객체들을 효과적으로 구성하고 관리할 수 있도록 지원한다.
- 자바 이외의 제이루비, 그루비같은 스크립트 언어를 지원한다.
- 다른 여러 프레임워크와의 연동을 지원한다.
-
서블릿 기반의 MVC 프레임워크를 지원
😮IoC (Inversion of Control)
단일 기능이 아닌 일반적인 자바의 컴포넌트는 협업객체와의 공동작업으로 해당 기능을 구현한다. 이때 각 컴포넌트와의 관계를 해당 작업 컴포넌트가 직접 찾는 것이 아니라 컨테이너에게 부여 받는다.
즉, 객체에 대한 의존성을 컨테이너로부터 부여 받는다.(INJECTION)
--> 의존하는 객체를 외부에서 주입한다는 의미에서 DI(Dependency Injection: 의존성 주입)이라고도 한다.
- IoC 철학
- 결합도를 낮추어 테스트와 재사용성을 높인다.
- 인터페이스를 이용하여 다른 클래스에 영향을 주지 않고도 실제 구현 클래스를 손쉽게 유지보수 가능하다.
- IoC 컨테이너
- IoC 방법으로 빈을 관리한다는 의미에서 IoC 컨테이너라고 한다.
- 개발자가 직접 객체를 생성하지 않고, 객체의 생성에서 소멸까지 컨테이너가 관리한다.
- 스프링은 모든 객체를 빈(bean)으로 관리한다. 단, DTO클래스는 일반적으로 제외.
- DI(Dependency Injection(의존성 주입)) 을 통해 객체간에 관계를 설정한다.
IoC 컨테이너
POJO(Plain Old Java Object)
- 스프링의 핵심이다.
- 특정 규약에 종속되지 않는다. (POJO는 자바 언어와 꼭 필요한 API외에는 종속되지 않는다.)
- 특정 환경에 종속되지 않는다. (특히 비즈니스 로직은 담고 있는 POJO 클래스는 웹 환경정보나 웹 기술을 담고있는 클래스나 인터페이스를 사용해서는 안된다.)
- 진정한 POJO는 객체지향적인 원리에 충실하면서, 환경과 기술에 종속되지 않고 필요에 따라 재활용될 수 있는 방식으로 설계된 오브젝트를 의미한다.
- MVC모델의 사용
!! Configuration Metadata 설정방법
- XML 기반 환경 설정
- Java annotation (2.5) 기반 환경설정
- Java Code(3.0) 기반 환경설정
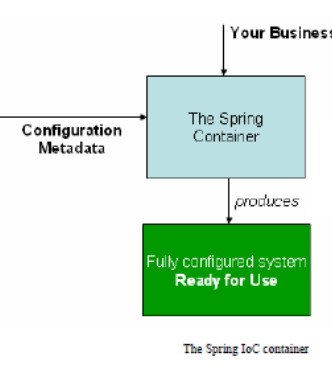
XML 이용한 환경설정
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id ="xxx" class="com.spring.Person">
<constructor-arg name="username" value="홍길동"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="10"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
IoC 계층구조
| - | - |
|---|---|
| UI 계층 | 서블릿 컨테이너 Web MVC 프레임워크 |
| 비즈니스 계층 | Lightweight 컨테이너 Transaction 관리 POJO 생명주기 관리 |
| 퍼시스턴스 계층 | DAO / OR Mapping |
| EIS 계층 | RDBMS |
Spring Framework 모듈
Spring Core
- 프레임워크의 가장 기본적인 부분
- 컨테이너의 기능을 수행하기 위해 의존성 주입 기능을 제공한다.
Spring Context
- Email, JNDI기능, EJB연계등과 같은 다수의 엔터프라이즈 서비스 제공
Spring DAO
- JDBC 추상화 API 제공
Spring AOP
- AOP 구현 API 제공
Spring ORM
- Mybatis, Hibernate, JPA등 지원
Sptring Web (Web MVC)
- 웹 기반 및 MVC 구현 API 제공
Maven
- Maven은 중앙 레포지토리(cental rpository)라고 불리우는 서버에서 필요한 jar파일을 다운로드 받아서 의존 모듈을 관리한다.
- 스프링 프로젝트 팀도 이런 의존 모듈 관리 방법에 맞추어, 스프링 프레임워크에 포함된 jar파일 및 스프링 프레임워크에서 필요로 하는 jar 파일을 하나의 파일로 묶어서 배포하기 보다는, Maven 중앙 레포지토리를 통해서 스프링 프레임워크 모듈(jar파일들)을 배포하고 있다.
🤔Dependency Injection
의존관계 주입(의존성 주입)이라고 한다.
스프링 프레임워크가 지원하는 핵심 기능 중 하나이다.
객체 사이의 의존관계가 객체 자신이 아닌 외부에 의해 결정된다는 개념이다.
컨테이너는 어떤 객체(A)가 필요로 하는 의존관계에 있는 다른 객체(B)를 직접 생성하여 어떤 객체(A)로 주입(설정)해주는 역할을 담당하게 된다.
결국 DI는 의존 관계의 구현을 어떻게 하느냐에 대한 내용이다.
의존하는 객체를 지정하는 방법
- 직접 의존하는 객체를 코드에 명시(가장 일반적)
- 단위 테스트가 어렵다.
- 의존 객체 변경시 코드 수정이 불가피하다.
Foo f = new Foo(); Bar b = new Bar(f);
- Factory나 JNDI를 이용하여 검색하는 방법 - 단위 테스트가 어렵다. - 실제 의존 객체와의 느슨한 의존성 대신 Factory나 JNDI와의 의존성이 생긴다.
📌XML기반 설정 방법
Constructor Injection
- 필수(mandatory) 의존성 설정이 가능하다.
- 간결한 사용법이 가능하다.
( 한 라인에 생성과 주입을 한꺼번에 가능하다. )
Setter Injection - <property> 사용
- 옵션(optional)으로 의존성 설정이 가능하다.
- 어떤 의존 객체를 설정 하는지를 메서드 이름으로 알 수 있다.
- 상속이 가능하다.
- 일반적으로 많이 사용되는 방법이며, 스프링에서도 권장된다.
( 많은 수의 생성자 인자 관리가 어렵다. Setter 메서드는 재구성하기가 쉽다.)
설정 방법1(Constructor Injection)
😁의존하는 객체를 생성자를 통해서 전달받는 방법
- 의존하는 객체를 전달받은 생성자를 작성한다.
- 설정파일에
<constructor-arg>태그를 이용하여 설정한다.
- 객체인 경우에는
<ref>태그를 사용한다.- 문자열이나 기본 데이터인 경우에는
<value>태그를 사용한다.
- 생성자로 전달할 객체나 값이 여러 개인 경우 index 사용 :
index 0부터 시작하여 지정한다.- 객체를 생성자에 지정할 경우 ref속성 사용
- 여러 객체를 생성 시 생성 후 생성자를 사용
- 모든 객체는 기본생성자를 포함하여야 함
설정 방법2(Settor Injection)
😁setXXX()형태의 설정 메소드를 통해서 전달받는 방법
프로퍼티 설정 방식이라고도 한다.
- 의존하는 객체를 전달받을 setter 메소드를 작성
- 설정파일에
<property>태그를 이용하여 설정
- 객체인 경우에는
<ref>태그를 사용- 문자열이나 기본 데이터인 경우에는
<value>태그를 사용- 오버로딩 생성자( overloading constructor)인 경우에는 반드시 기본생성자를 명시해야된다.
- setXXX함수의 이름을 통한 객체 주입, name속성값과 setXXX의 이름 일치
- 모든 객체는 기본생성자를 포함하여야 함
- Set뒤의 프로퍼티 이름은 첫 글자를 대문자로 치환한 이름 사용
- 여러 개의 객체를 주입시 property사용, 설정이 안된 값을 초기값으로 설정
- 기본 타입 설정시 컨테이너가 형변환을 해준다.
XML NameSpace의 p태그 이용
<property>태그를 사용하지 않고 프로퍼티의 값을 설정하는 방법이다.
다음과 같이 namespace를 지정해야 함
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">사용 예는 객체인 경우에는 p:프로퍼티명-ref = "참조값" 으로 설정
문자열이나 기본값일 경우에는 p:프로퍼티명="값" 형식으로 설정한다.
<bean id = "cat" class="com.spring.Cat" p:catName="야옹이" p:catAge="20"></bean>
<bean id = "dog" class="com.spring.Dog" p:dogName="멍멍이" p:dogAge="10"></bean>
<bean id = "person1" class="com.spring.Person" p:username="홍길동" p:age="30" p:cat-ref="cat" p:dog-ref="dog"></bean>🔎컬렉션 타입의 프로퍼티 설정
| tag | collecion type |
|---|---|
<list> | java.util.List나 배열 |
<set> | java.util.Set |
<map> | java.util.Map |
<props> | java.util.Properties |
- 컬렉션 원소가 객체인 경우에는
<ref>태그를 이용한다. - 컬렉션 원소가 기본타입인 경우에는
<value>태그를 이용한다.
(type 속성을 이용한 타입지정이 가능하며, 제네릭도 사용 가능하다.)
프로퍼티 설정 - List type
EchoBean 클래스의 멤버변수로 List타입을 갖는 set함수 설정이다.
<bean id="list" class="com.spring.EchoBean">
<property name="valueList">
<list>
<value>10</value>
<value>20</value>
<value>30</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>프로퍼티 설정 - Map type
.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id = "cat1" class="com.dto.Cat">
<property name="catName" value="나비"></property>
<property name="catAge" value="3"></property>
</bean>
<bean id = "cat2" class="com.dto.Cat">
<property name="catName" value="하늘"></property>
<property name="catAge" value="2"></property>
</bean>
<bean id = "student1" class="com.dto.Student">
<property name="name" value="홍길동"></property>
<property name="age" value="20"></property>
<property name="mapCat">
<map>
<entry key="one" value-ref="cat1"></entry>
<entry key="two">
<ref bean="cat2"/>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="phones">
<props>
<prop key="one">010</prop>
<prop key="two">011</prop>
<prop key="three">017</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
Student.java
public class Student {
String name;
int age;
Map<String, Cat> mapCat;
Properties phones;
.
.
.
StudentTest.java
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import com.dto.Cat;
import com.dto.Student;
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("classpath:stu.xml");
Student stu = ctx.getBean("student1", Student.class);
Map<String, Cat> map = stu.getMapCat();
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
for (String key : keys) {
System.out.println(map.get(key).getCatName());
}
Properties prop = stu.getPhones();
Set<Object> pkeys = prop.keySet();
for (Object key : pkeys) {
System.out.println(prop.get(key));
}
}
}독립형 컬렉션 구현
각 반에서 중복 처리되는 속성값을 재사용하기 위한 방법이다.
namespace의 util태그를 이용한다.
<util:list id="list">
<ref bean="anotherBean1"></ref>
<ref bean="anotherBean2"></ref>
<ref bean="anotherBean3"></ref>
</util:list>
<bean id ="echoBean" class="com.spring.EchoBean">
<property name="valueList" ref="list"></property>
</bean>👌빈 객체 스코프
😮빈 객체 생성 방식
- 기본적으로 컨테이너 한 개의 빈 객체를 생성하여 재사용된다.( per Container )
- 빈의 스코프(scope)를 설정할 수 있는 방법을 제공한다.
<bean>태그의 scope속성을 사용한다.
ex)
<bean id="" class="" scope="설정값">
| 방식 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| singleton | 컨테이너 한 개의 빈 객체만 생성한다. |
| prototype | 빈을 요청할 때 마다 빈 객체를 생성한다. |
.xml
<bean id="stu" class="com.dto.Student" scope="prototype"></bean>
<bean id="stu2" class="com.dto.Student" scope="singleton"></bean>
main.java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import com.dto.Student;
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("classpath:student.xml");
Student stu = ctx.getBean("stu",Student.class);
Student stu2 = ctx.getBean("stu2",Student.class);
System.out.println(stu);
System.out.println(stu2);
Student stu11 = ctx.getBean("stu",Student.class);
Student stu22 = ctx.getBean("stu2",Student.class);
System.out.println(stu11);
System.out.println(stu22); //Singleton은 주소가 같다. 쓰지 않아도 묵시적으로 적용됨
}
}
📌의존 관계 자동 설정
의존하는 빈 객체의 타입이나 이름을 이용하여 의존 객체를 자동으로 설정할 수 있는 기능
자동설정과 직접설정의 혼합도 가능하다.
<bean>태그의 autowire 속성을 이용한다.
<bean id="" class="" autowire="설정값">
| 방식 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| byName | 프로퍼티의 이름과 같은 이름을 갖는 빈 객체를 설정한다. |
| byType | 프로퍼티 타입과 같은 타입을 갖는 빈 객체를 생성한다. |
| constructor | 생성자 파라미터 타입과 같은 타입을 갖는 빈 객체를 생성자에 전달한다. |
byName 방식
id값과 일치하는 setter 메소드 가진 빈과 injection 된다.
.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
default-autowire="byName"
>
<bean id = "cat" class="com.spring.Cat">
<constructor-arg name="catName" value="야옹이"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="catAge" value="10"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id = "cat2" class="com.spring.Cat">
<constructor-arg name="catName" value="야옹이2"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="catAge" value="102"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id = "dog" class="com.spring.Dog" >
<property name="dogName" value="멍멍이"></property>
</bean>
<!-- default-autowire="byName" 선언으로 자동 주입됨 -->
<bean id = "onePerson" class="com.spring.Person">
<property name="username" value="홍길동"></property>
</bean>
<!-- id가 같은 클래스를 소문자로 바꾼 이름과 같은 cat, dog자동 주입됨 byName -->
</beans>Main.Java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import com.spring.Person;
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] arge) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("classpath:bean.xml");
Person p = ctx.getBean("onePerson",Person.class);
System.out.println(p.getUsername());
System.out.println(p.getCat());
System.out.println(p.getDog());
}
}
byType 방식
같은 타입의 빈이 여러 개 있으면 에러 발생된다.
- 해결방법1 :
primary="true"설정
.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
default-autowire="byType"
> <!-- default-autowire. 모든 빈에 공통적으로 적용 -->
<bean id = "cat" class="com.spring.Cat">
<constructor-arg name="catName" value="야옹이"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="catAge" value="10"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id = "dog" class="com.spring.Dog" >
<property name="dogName" value="멍멍이"></property>
</bean>
<bean id = "dog2" class="com.spring.Dog" primary="true">
<property name="dogName" value="멍멍2"></property>
</bean>
<!-- default-autowire="byType" 선언으로 자동 주입됨 -->
<bean id = "onePerson" class="com.spring.Person">
<property name="username" value="홍길동"></property>
</bean>
<!-- cat, dog자동 주입됨 byType -->
</beans>
Main.java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import com.spring.Person;
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] arge) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("classpath:bean.xml");
Person p = ctx.getBean("onePerson",Person.class);
System.out.println(p.getUsername());
System.out.println(p.getCat());
System.out.println(p.getDog());
}
}
- 해결방법2 :
autowire-candidate="false"설정- autowire후보에서 제외시키는 방법
<bean id = "cat" class="com.spring.Cat" autowire-candidate="false">
<constructor-arg name="catName" value="야옹이"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="catAge" value="10"></constructor-arg>
</bean>😉Annotation 기반 설정
Spring에서 지원하는 빈 설정 방법으로 자바의 어노테이션을 사용한다.
자바 코드에 설정된 어노테이션을 활성화 시키기 위하여 다음과 같은 최소한의 XML 설정 정보 설정은 필요하다.
클래스에 @를 쓰려면 xml에 <context:annotaion-config/> 태그를 작성한다.
@Required
- org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Required.
- setter 메소드에 설정
- 필수 속성이 되게 한다.
❗@Autowired
- org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired.
- 속성 또는 생정자, setter 메소드에 설정, 필수 속성이다.
(required=false로 필수 속성 해제 가능)- autowire="byType"과 동일한 기능
❗@Qualifier
- org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired.
- @ AutoWired와 같이 사용한다.
- 같은 타입의 빈이 여러 개 있는 경우 예외가 발생된다.
따라서 특정 빈을 사용하도록 설정 가능하게 한다.(byType)이므로
@Resource
- autowire="byName"과 동일한 기능.(즉, 빈의 id값과 일치한다)
@❗Value
- 특정 값을 주입해야 되는 용도이다.
- 대표적인 용도로는 자바 코드 외부의 리소스나 환경정보 설정값을 사용하는 경우이다.
$: 외부 /#: 내부
.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:com/spring/test.properties"/>
<bean id="person" class="com.spring.Person">
<property name="username" value="${value.name}"></property>
<property name="age" value="${value.age}"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
test.properties
value.name=\uD64D\uAE38\uB3D9
value.age=203@Required와 @Autowired를 같이 사용할 수 없는 이유🤔:
@Autowired을 사용하면 스프링은 해당 타입의 빈을 주입하려고 하지만,
@Required 어노테이션은 해당 프로퍼티가 필수로 설정되어야 한다고 요구한다.
--> 만약 프로퍼티가 필수로 설정되어야 하고, 동시에 의존성 주입을 수행해야 한다면, @Autowired 어노테이션만 사용하면 된다.
CoC 개념
멤버객체에 @Autowired 어노테이션을 주고 xml파일에 해당 객체에 대한 빈을 2개 이상 생성하면 @Autowired는 byType과 동일한 기능이기 때문에 에러가 생겨야 한다. 그러나 에러가 생기지 않는 이유는 xml에서 해당 객체의 클래스 이름이 빈의 id값과 동일하거나 유사하기 떄문에 자동으로 해당 빈으로 반영되어서 에러가 안터진다.
--> 에러가 터지게 하려면 Autowired의 대상이 되는 bean의 id를 클래스 이름과 겹치는 것이 없게, 아예 다르게 설정하면 된다.
❗❗빈 객체 스캔❗❗
설정 파일에 <context:component-scan> 태그의 base-package 속성으로 지정된 패키지 내의 클래스를 검색하여 자동으로 빈으로 등록하는 기능을 제공한다.
(내부적으로 <context:annotation-config/> 기능을 포함한다.)
XML 설정 파일에 여러 빈 정보를 명시적으로 추가하지 않고 자동으로 빈들을 등록시킨다.
(빈의 이름은 첫 글자는 소문자인 클래스명으로 지정된다.)
단, 패키지에 있는 모든 클래스들이 빈으로 등록되는 것은 아니며 반드시 다음과 같은 어노테이션으로 지정된 빈만 해당된다.
Step 1. 아래 어노테이션 보기 중 선택하여 클래스 선언 위(꼭대기)에 달아준다.
@Component
: @Scope('prototype')으로 스코프 지정 가능
@Service
@Repository
@Controller
@Configuration
Step 2. Context_Component 스캔으로 패키지만 지정해주면 알아서 클래스를 찾아 빈을 생성 해준다.
Step 3. 아이디를 지정하지 않았을 경우 소문자로 시작하는 클래스 이름의 아이디로 자동 지정된다.
LifeCycle
3가지 방법
- xml
- implements
- annotation