📌 이터레이터 패턴(Iterator)
⭐ 개념
Iterator를 사용하여 컨테이너 요소들에 순차적으로 접근하는 디자인 패턴- 각기 다른 자료구조(List, Set, Map...)들을 똑같은 인터페이스로 순회를 할 수 있음
- Iterator 패턴을 사용하는 가장 큰 이유는 하나씩 꺼내서 처리하는 과정을 구현과 분리할 수 있기 때문
- 주 아이디어는 컬렉션의 순회 동작을
반복자라는 별도의 객체로 추출하는 것
⭐ 코드
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BookShelf bookShelf = new BookShelf(10);
Book book1 = new Book("Java");
Book book2 = new Book("CS");
Book book3 = new Book("Algorithm");
bookShelf.appendBook(book1);
bookShelf.appendBook(book2);
bookShelf.appendBook(book3);
System.out.println("현재 꽂혀있는 책 : " + bookShelf.getLength() + "권");
Iterator it = bookShelf.createIterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Book book = (Book) it.next();
System.out.println(book.getName());
}
}
}
public class Book {
private String name;
public Book(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
public interface Aggregate {
public abstract Iterator createIterator();
}
public class BookShelf implements Aggregate {
private Book[] books;
private int last = 0;
public BookShelf(int size) {
books = new Book[size];
}
public Book getBook(int index) {
return books[index];
}
public int getLength() {
return last;
}
public void appendBook(Book book) {
if (last < books.length) {
this.books[last] = book;
last++;
} else {
System.out.println("책꽂이가 꽉 찼습니다!");
}
}
@Override
public Iterator createIterator() {
return new BookShelfIterator(this);
}
}
public class BookShelfIterator implements Iterator<Book> {
private BookShelf bookShelf;
private int index = 0;
public BookShelfIterator(BookShelf bookShelf) {
this.bookShelf = bookShelf;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return index < bookShelf.getLength();
}
@Override
public Book next() {
Book book = bookShelf.getBook(index);
index++;
return book;
}
}
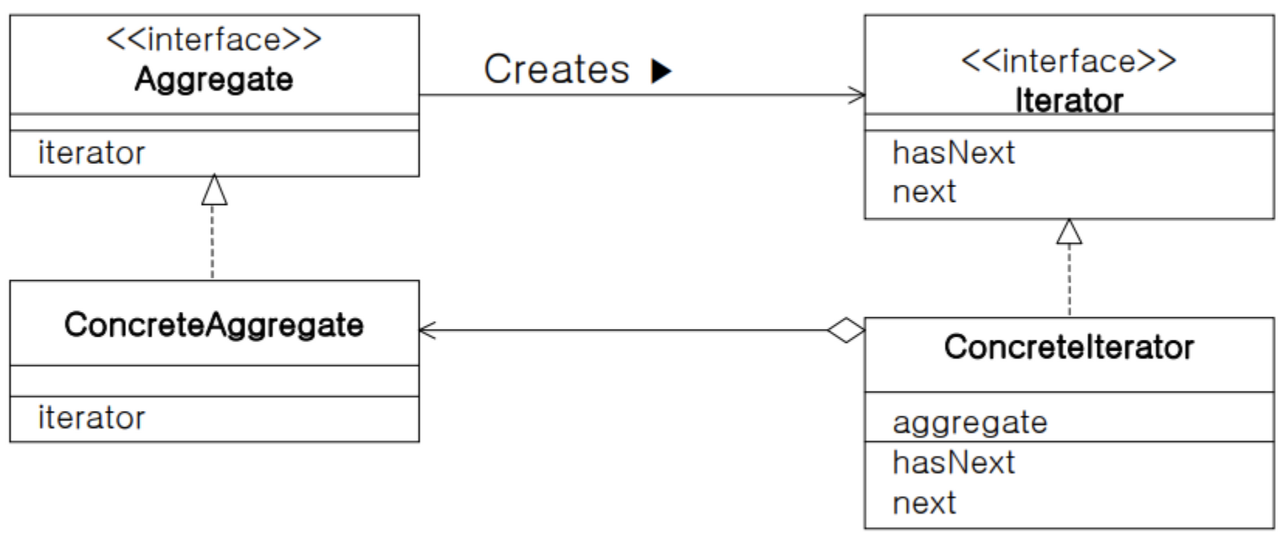
- Iterator(반복자) : 요소를 순서대로 검색하는 인터페이스를 결정
- ConcreteIterator(구체적인 반복자) : Iterator가 결정한 인터페이스를 실제로 구현한다. 검색하기 위해 필요한 정보를 가지고 있어야 한다.
- Aggregate(집합체) : Iterator 역할을 만드는 인터페이스를 결정한다.
- ConcreteAggregate(구체적인 집합체) : Aggregate 역할이 결정한 인터페이스를 실제로 구현한다.



