Spring Framework Core
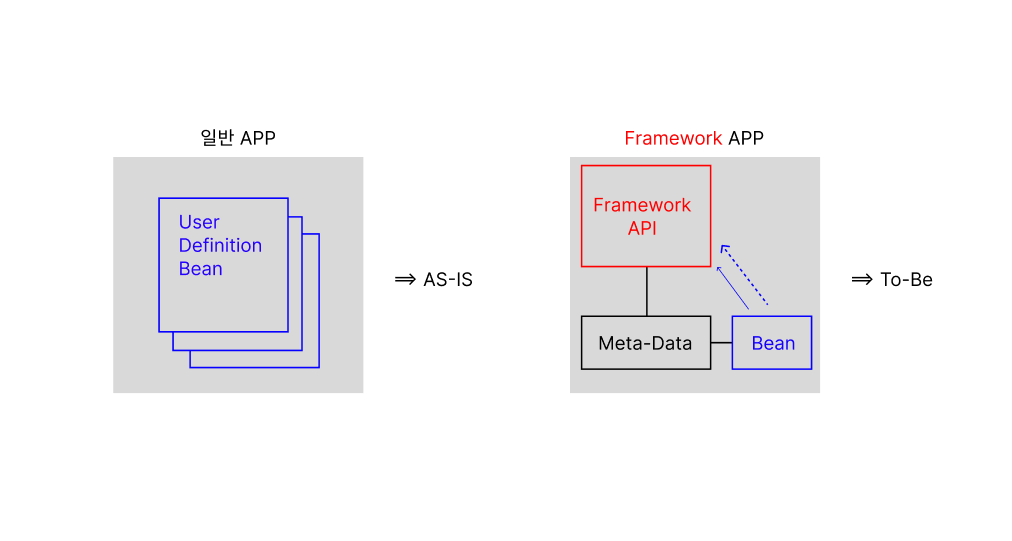
Spring Framework Structure
Spring Framework의 기초인 Core에 대해서 Araboza!
필수단어
-
POJO(Plain Old Java Object)
- 순수한 자바 객체
- 특정 프레임워크, 라이브러리에 종속되지않고 자바기능만 사용
-
FQCN(Fully Qualified Class Name)
- 패키지를 포함한 클래스 네임
- 패키지를 포함한 클래스 네임
- Meta-date에서 import 시 사용
-
Bean
- 애플리케이션의 핵심적인 부분을 구성하는 객체
- 스프링 IoC(Inversion of Control) 컨테이너에 의해 관리
-
Annotation
- 코드에 메타데이터를 추가하는 방법을 제공하는 기능
- XML 설정을 대체하거나 보완하여 코드를 더 간결하고 가독성 있게 작성
-
Meta-data
- 데이터에 대한 데이터, 다른 데이터의 특성이나 정보를 나타냄
-
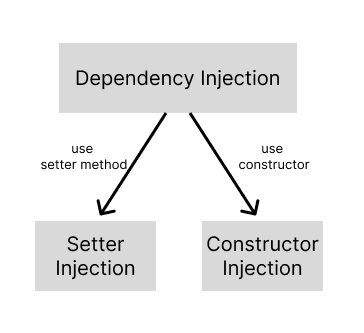
DI(Dependency Injection)
- 의존성 주입(생성자, setter 메소드를 통한 인스턴스 주입)
- Loose Coupling 발생
-
DL(Dependency LookUp)
- 사용할 인스턴스를 찾는 것
-
OGNL(Object-Graph Navigation Language)
- 웹 애플리케이션에서 객체의 속성 값을 읽거나 설정하는 등의 작업을 간단하게 처리
-
JNDI(Java Naming and Directory Interface)
- 메타데이터(이름 기반의 리소스 정보)를 관리하고 검색하는 데 사용
- DL이 포함됨
-
Framework
- 특정문제 OR 개념을 해결한 재사용, 확장가능한 lib(~.jar)
- 특정문제: new를 사용한 인스턴스 생성문제 / 클래스 간 Coupling 문제
Objective : 빠른퇴근, 유지보수의 용이함
Point 1: 다른 빈을 사용하고자할때 수정없이 대응할수있다면??
↓
Point 2: 코드수정없이 대응하는방법은??
- 빈컨테이너는 고려하지않는다
- 다형화개념으로 접근해서 해결한다
↓
Point 3: class 간 Coupling Relation에서 Polymorphism 적용 시 Loose Coupling이 발생
- Has A Relation 시 Coupling 강함(A 클래스변경 시 B클래스도 변경)
- Dependency Relation 시 Loose Coupling(A클래스가 B를 ‘사용함’)
- Dice 예제(Interface기반 인스턴스 활용) 참고
↓
**다형화를 적용시키면 약간 유연해진다 여기에 IOC개념이들어가야 완벽**↓
Point 4:
- IoC: 내가 생성하면 내가책임진다 → 내가 책임안지고 상태값을 설정한다
- Bean Container : new의 문제 → 내가 생성할 Bean을 Meta-date에 서술적으로 기술 → Parshing 후 Bean을 return
↓
Spring Framework
- Bean의 생성, 소멸, 객체간 관계설정 등을 관리 / DI 지원 / API제공하는 IoC Container
Spring Framework의 장점: 다른 Framework 연동이 쉽다, view만 지원하는 프레임워크에비해 MVC를 모두 지원한다
↓
사용법
-
~.xml에 태그 내에 Attribute로 사용할 클래스를 정의
<bean id="ex1" class="spring.service.ex1"/>
-
IoC Container를 사용하여 DI 수행
<bean id="player1" class="spring.service.Player1"> <property name="ex"> <ref bean="ex1"/> ===> <property name="ex" ref="ex1"/> </property> </bean> <property> 태그는 객체의 속성 값을 설정하거나 의존성을 주입하는 데 사용됨 name은 setter method를 뜻함 ex일경우 setEx와 같음 <bean id="player1" class="spring.service.Player1"> <constructor-arg> <ref bean="ex1"/> ===> <constructor-arg ref="ex1"/> </constructor-arg> </bean> <constructor-arg>태그는 ref의 객체를 player1의 생성자 인자로 주입함
-
Bean Container를 추상화한 인터페이스 사용으로 IoC Container 사용
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(new FileSystemResource("xml FQCN")); //Bean의 생성, 관리, 검색을 수행하는 인터페이스. ==> Bean Container //BeanFactory는 IoC 컨테이너의 핵심 역할을 담당. //Bean의 메타데이터를 읽어와 객체를 생성하고 관리하는 역할. //getBean을 통해 meta-data에 기술되어있는 객체를 가져오는 LookUp의 과정이 IoC //전체적인 과정을 통틀어 IoC Container = SpringFramework라고함 ApplicationContext factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("xml FQCN"); //ApplicationContext Interface를통해 인스턴스를 pre-loading
- Bean LifeCycle
- Spring Container에 의해 Bean 객체 생성
- DI를 통한 인스턴스 주입
- init method를통한 상태값 설정
- service method로 사용
- destroy method로 소멸
<bean id="lifeCycle1"
class="spring.service.LifeCycle01"
init-method="init" <!-- LifeCycle01 내 O/R된 init method 호출 -->
destroy-method="destroy" <!-- LifeCycle01 내 O/R된 destroy method 호 -->
depends-on="lifeCycle02,lifeCycle03" <!--DI 순서 정의-->
scope="singleton" /> <!-- 패턴정의, 싱글톤:최초한번만 생성-->
<bean id="lifeCycle02" class="spring.service.LifeCycle02"/>
<bean id="lifeCycle03" class="spring.service.LifeCycle03"/>
<bean id="lifeCycle04"
class="spring.service.LifeCycle04"
scope="prototype"/>
<!--위의 코드에서 Wiring에 해당하는 부분은 depends-on이다. -->
<!--Wiring: 객체간의 의존성을 설정하고 주입하는 과정-->-
개발자정의 및 API 인스턴스 생성
<!--개발자정의 인스턴스 생성의 기존코드--> <!--User user = new User() user.setUserId("유저") user.setAge(10)--> <!--개발자정의 인스턴스 생성--> <bean id="user" class="spring.service.User"> <property name="userId" value="유저"/> <property name="Age" value="20"/> </bean> <!--API 인스턴스 생성의 기존코드--> <!--String password = new String("7777")--> <!--API 인스턴스 생성--> <bean id="password" class="java.lang.String"> <construtor-arg value="7777"> </bean> <!--생성자 주입에의한 인자전달 시 모호한 순서 발생--> <!--이를 해결하기위해 index or type Attribute사용-->
Point : Bean의 속성값을 변경하려면 전부 바꿔야하는가???
- PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer API를 사용하여 프로퍼티(Bean의 속성값) Loose-Coupling
<!--properties 파일의 내용-->
db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb
db.username=myuser
db.password=mypassword
<!--=======================-->
<!-- PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 빈 등록 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>classpath:app.properties</value>
<!--classpath: 는 생략해도되지만 꼭!!! 써주도록하자(가독성)-->
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 빈 정의 및 프로퍼티 사용 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="url" value="${db.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${db.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${db.password}" />
<!--대치변수의 형태인 ${}로 접근 가능 ==> jsp의 EL과 유사-->
</bean>
Point : 프로퍼티마다 같은 이름의 속성이 있다면??
- xml의 스키마(xml문서의 정보 및 규칙) 위치 지정
- XSD (XML Schema Definition)는 XML 스키마를 정의하기 위한 파일 형식
- nameSpace = 문서 내 요소와 속성의 이름 중복을 피하기위한 것 = java의 패키지
- nameSpce로 먼저 위치를 잡고 xsd를 통해 스키마 위치 지정
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- util:properties를 사용하여 정적인 프로퍼티 값 정의 --> <util:properties id="staticProperties"> <prop key="key1">Value 1</prop> <prop key="key2">Value 2</prop> </util:properties> <!-- util:properties를 이용하여 프로퍼티 값을 빈에 주입 --> <bean id="staticBean" class="spring.service.MyBean"> <property name="propertyMap" ref="staticProperties" /> </bean> <!-- context:property-placeholder를 사용하여 외부 프로퍼티 파일 로드 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:app.properties" /> <!-- context:property-placeholder를 이용하여 프로퍼티 값을 빈에 주입 --> <bean id="dynamicBean" class="spring.service.MyBean"> <property name="propertyMap"> <map> <entry key="db.url" value="${db.url}" /> <entry key="db.username" value="${db.username}" /> </map> </property> </bean> </beans>
util:properties를 통해 외부 프로퍼티 파일을 로드하고#{}표현식을 사용하여 프로퍼티 값을 접근하는 것은 스프링의 SpEL (Spring Expression Language)의 기능. 이는 OGNL (Object-Graph Navigation Language)과는 유사한 개념- SpEL은 스프링에서 제공하는 표현 언어로서, 런타임 중에 객체 그래프를 탐색하고 조작하는 기능을 제공.
#{}표현식을 사용하여 빈의 프로퍼티 값을 참조하거나 연산을 수행할 수 있다. - OGNL은 다른 프레임워크인 Struts와 같이 사용되는 표현 언어로서, 주로 웹 애플리케이션에서 사용되는 사용자 입력과 모델 객체 간의 데이터 바인딩 및 연산에 사용된다.
- 따라서,
util:properties를 통해 로드한 프로퍼티 값을#{}표현식을 사용하여 접근하고 조작하는 것은 SpEL의 기능이며, OGNL과는 개념적으로 유사하지만 다른 기술이다.
객체 간의 필드를 통해 의존성을 주입하거나 연결하는 작업 ⇒ Wiring
폼 데이터를 객체의 속성에 매핑하는 작업⇒Binding
Point : Bean 생성 시 매번 init과 destroy를 지정해야하는가??
-
스키마의 bean root elements에 default-method 작성
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" default-init-method="init" default-destroy-method="destroy"> <!-- 빈 정의 --> <bean id="bean1" class="spring.service.Bean1" /> <bean id="bean2" class="spring.service.Bean2" /> <!-- ... -->
