1. 추상클래스
추상클래스란 추상메서드를 포함한 클래스이며 추상메서드는 선언만 있고 "구현"이 없다. 따라서 내용이 없어 추상클래스로 객체를 만들 수 없고 서브클래스를 만드는 용도로만 사용된다.
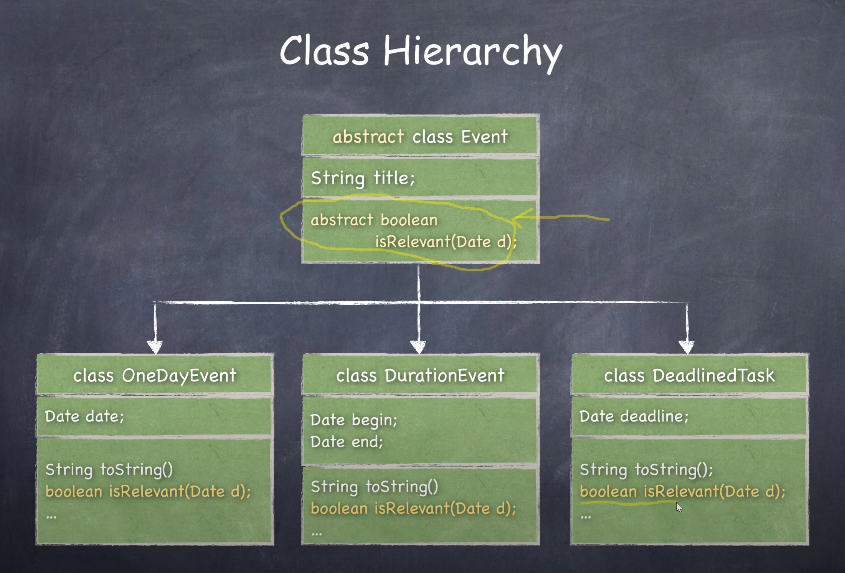
예)
// abstract메서드를 하나라도 가지면 클래스 자체도 추상클래스가 되기 때문에 abstract를 붙여줘야한다.
// 추상클래스는 객체를 만들 수 없다.
public abstract class Event {
public String title;
public Event (String title) {
this.title = title;
}
// 추상메서드
// 다이나믹바인딩으로 서브클래스에서 제각각의 방식대로 오버라이딩하므로
// 여기에서는 구현을 할 필요가 없다 그러므로 추상메서드로정의 해버린다.
public abstract boolean isRelevant(MyDate theDate);
}
...
public class OneDayEvent extends Event {
public MyDate date;
public OneDayEvent(String title, MyDate date) {
super(title);
this.date = date;
}
public String toString() {
return title + ", " + date.toString();
}
// 이벤트가 해당 날짜에 걸리는지 확인하는 메서드
public boolean isRelevant(MyDate date) {
if(this.date.compareTo(date) == 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
2. 인터페이스
자식클래스가 여러 부모클래스를 상속받을 수 있다면 다양한 동작을 수행할 수 있지만 자바에서는 클래스를 통한 다중 상속은 지원하지 않는다.
다만 인터페이스라는 것을 통해 다중 상속을 지원하고 있다.
특징
추상클래스 뿐만아니라 생성자, 필드, 일반메소드까지 포함할 수 있는 추상클래스와 달리 인터페이스는 오로지 상수와 추상클래스만을 가진다.
추상클래스와 마찬가지로 자신이 직접 인스턴스를 생성할 수 없다. 따라서 인터페이스가 가지고 있는 추상메소드를 구현해 줄 클래스를 만들어야한다.
예1)
interface Animal { public abstract void cry(); }
class Cat implements Animal {
public void cry() {
System.out.println("냐옹냐옹!");
}
}
class Dog implements Animal {
public void cry() {
System.out.println("멍멍!");
}
}
public class Polymorphism03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat c = new Cat();
Dog d = new Dog();
c.cry();
d.cry();
}
}예2) 다중상속
interface Animal { public abstract void cry(); }
interface Pet { public abstract void play(); }
class Cat implements Animal, Pet {
public void cry() {
System.out.println("냐옹냐옹!");
}
public void play() {
System.out.println("쥐 잡기 놀이하자~!");
}
}
class Dog implements Animal, Pet {
public void cry() {
System.out.println("멍멍!");
}
public void play() {
System.out.println("산책가자~!");
}
}
public class Polymorphism04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat c = new Cat();
Dog d = new Dog();
c.cry();
c.play();
d.cry();
d.play();
}
}
