
위 책을 보면서 정리한 글입니다.
조건에 따라 분리되는 객체 생성 로직 개선
비슷한 객체를 조건에 따라 별도로 생성하여 관리하는 것은 매우 비효율적이다.
- 많은 기능이 조건에 따라 결정되는 경우 조건이 빈번하게 변경된다면 변경된 객체에 대한 생성, 관리, 코드의 가독성 등에서 어려움이 생길 수 있다.
- 객체 생성을 별도의 객체에서 관리하면 객체 생성 호출자는 객체 생성에 관여하지 않게 된다.
- 객체 생성과 변경되는 조건들도 생성 관리 객체에서만 관리하면 되므로 확장성과 가독성이 좋아진다.
- 팩토리 메서드 패턴(Factory Method Pattern) : 생성자를 사용하지 않고 객체 생성을 담당하는 함수를 이용하여 객체를 생성하는 방식
- 팩토리 패턴(Factory Pattern) : 동일한 인터페이스나 객체를 상속받은 객체를 특정 조건에 따라 생성하게 하는 것
- 팩토리 객체(Factory Object) : 생성을 관리하는 객체
개선방향
비슷한 기능의 객체 생성을 별도의 관리 객체에게 위임
예를 들어, 결제 시스템에서 시스템의 확장으로 결제 방식이 변경되는 경우 분기문 내부 코드도 수정되어야 하면, 이는 코드의 결합도가 매우 높은 구조라고 할 수 있다.
이릴 경우 객체 생성이 객체 추가와 삭제 등의 수정에 유연하지 않게 된다.
해결 방법 : 결제 방식에 따른 결제 객체 생성과 관리를 별도의 관리 객체에 위임하여 객체의 추가나 삭제시 유연하게 대처 가능하다.
- 결제 처리 객체에서는 결제 방식과는 상관없이 관리 객체로부터 전달받은 결제 객체에 해당하는 기능을 수행하기만 하면 된다.
- 결제 방식의 수정에 유연하게 대처 가능하고, 결제 처리 객체의 내부 코드 결합도가 낮아지게 된다.
질문답
결제 방식에 따라 결제 객체의 생성과 수행이 분기문 내에서 처리되는건 나쁜 방식일까
- 조건에 따라 결제 방식이 달라지는건 어쩔 수 없지만, 결제 방식에 따라 결제를 담당하는 클래스가 모두 영향을 받는다면 결제 방식이 변경될 때마다 검증이 필요하게 된다.
- 의도하지 않은 예외 사항이 발생하며 수정이나 개선에 대한 확신과 정확성을 보장 불가능.
생성만 별도로 분리하면 결제 실행은 어떻게 진행할까
- 결제 객체들은 공통의 인터페이스로 상속하면 결제 요청 객체에서는 인터페이스로 결제 실행을 처리.
- 결제 객체를 받는 요청객체에서는 어떤 객체를 반환하는지 알 필요 없이 결제만 수행 가능
별도의 생성 관리 개체를 사용하지 않고, 기존의 결제 요청 객체 내에서 결제 객체를 생성하는 메서드를 사용해도 되지 않을까
- 기존의 객체는 결제를 요청하고 응답을 처리하는 기능을 가졌는데 이는 결제 객체 생성과는 무관한 기능
- 나중에 다른곳에서 객체 생성을 재사용하는 상황이 생기면 엉뚱한 곳에서 객체 생성을 담당한다고 생각할 수 있다.
레거시 코드
TotalPaymentGate는 결제 요청 시 전달받은 결제 방식에 따라 그에 맞는 객체를 생성하여 결제를 처리하는 구조
레거시 코드의 결제 객체 호출자와 결제 객체와의 관계
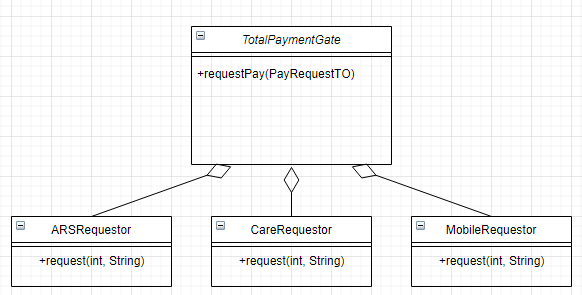
TotalPaymentGate 클래스
-
결제 정보를 받아 결제 처리를 관리하는 클래스
-
requsetPay()로 결제를 요청하면 결제 방식에 해당하는 객체(ARSRequestor, MobileRequestor, CardRequestor)를 생성
-
결제 객체의 request()를 호출하여 결제 처리를 위임
-
사용자가 결제를 요청하면 해당하는 결제를 처리한 후 결과를 반환
-
전달받은 결제 방식을 추출하여 분기문을 통해 객체를 생성하고 처리를 요청
public class TotalPaymentGate {
public PayResultTO requestPay(PayRequestTO requestTO) {
String payMethod = rquestTo.getPaymethod();
Map<String, Object> options = new HashMap<String, Object>();
int amount = requstTO.getAmount();
String productName = requestTO.getProductName();
Map<String, Onject> result;
if(payMethod.eqauls("card")) {
// 카드 결제 요청
CardRequestor cardRequestor = new CardRequestor();
result = cardRequestor.request(amount, productName);
} else if(payMethod.eqauls("mobile")) {
// 모바일 결제 요청
MobileRequestor MobileRequestor = new MobileRequestor();
result = mobileRequestor.requset(amount, productName);
} else if(payMethod.eqauls("ars")) {
// ARS 결제 요청
ARSRequestor arsRequestor = new ARSRequestor();
result = arsRequestor.request(amount, productName);
} else {
// 무응답 처리
result = new HashMap<String, Object>();
}
PayResultTO payResultTO = parsePayResultTO(payMethod, result);
return payResult;
}
private PayResultTO parsePayResultTO(String payMethod, Map<String, Object> result) {
// 중략
}
}ARSRequestor 클래스
public class ARSRequestor { // 대표로 ARS만
public Map<String, Object> request(int amount, String ProductName) {
// 결제 처리
// 중략
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<String, Object>();
result.put("code", 0);
result.put("msg", productName + "을 " + amount + "에 ARS로 구매");
return result;
}
}위 코드의 문제점
1. 결제 방식에 따른 결제 객체의 생성과 처리 요청을 TotalPaymentGate에서 관리.
2. 결제 방식에 따라서 결제 객체를 생성하고 관리하므로 TotalPaymentGate는 결제 객체의 수정에 의존적.
3. 결제 방식에 따른 생성과 처리가 분기문에 의한 처리로 관리되는 로직은 결제 방식이 증가하거나 수정이 잦으면 손 댈수 없는 클래스로 변하게된다.
레거시 코드 개선 과정
기존 호출자에 존재하는 분기에 의한 객체 생성을 관리 객체로 이동
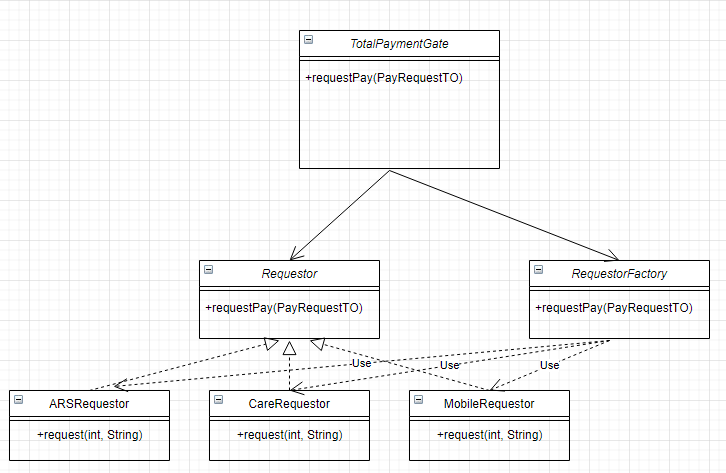
개선 후, 결제 객체와는 상관없이 RequestorFactory와 연관되어, 결제 객체와의 결합도가 제거된다.
추상화 도출
- 결제를 수행하는 추상화 객체(Reqeusetor)를 선언한 후
- 공통 정보를 처리하는 추상화 메서드 (Requestor.request(PayResultTO))를 생성
- 각 결제 객체는 추상화 객체를 상속받게 한다.
public interface Requsetor {
public Map<String, Object> request(PayResultTO payResultTO);
}
public class ARSRequestor implements Requsetor{ // 대표로 ARS만
// 결제 처리
@Override
public Map<String, Object> request(PayRequestTO payRequestTO) {
int amount = payRequestTO.getProductName();
String ProductName = payRequestTO.getProductName();
return reqeust(amount, productName);
}
public Map<String, Object> request(int amount, String ProductName) {
// 중략
}
}결제 객체의 생성과 추출 RequestFactory 클래스
기존 TotalPyamentGate에서 다음과 같이 결제 객체를 생성하는 로직을 추출하여 분리
- RequestFactory 클래스를 만든다.
- 생성 로직을 분리한 후 RequestorFactory.createRequesor() 메서드로 이동.
- 결제 객체의 동작 코드는 삭제하고, 생성된 객체를 반환하도록 수정.
public class RequestFactory {
public static Requestor createRequestor(String payMethod) {
// 반환 객체
Requestor requestor;
if(payMethod.eqauls("card")) {
// 카드 결제 요청
requestor = new CardRequestor();
} else if(payMethod.eqauls("mobile")) {
// 모바일 결제 요청
requestor = new MobileRequestor();
} else if(payMethod.eqauls("ars")) {
// ARS 결제 요청
requestor = new ARSRequestor();
} else {
// 무응답 처리
requestor = null;
}
return requestor;
}
}RequestFactory 테스트 코드
public class RequestorFactoryTest {
@Test
public void testCreateRequsetor() throws Exception {
// Card 결제 객체 생성
Requestor cardRequsetor = RequestorFactory.testCreateRequsetor("card");
// Null 체크
Assert.assertNotNull(cardRequsetor);
// 예상한 클래스 타입인지 확인
Assert.assertEquals(CareRequestor.class, requestor.getClass());
}
}생성된 객체를 전달받아 처리
public class TotalPaymentGate {
public PayResultTO requestPay(PayRequestTO requestTO) {
String payMethod = rquestTo.getPaymethod();
// 생성 관리 객체로부터 결제 수단별 결제 객체 전달
Requestor requestor = RequestorFactory.createRequestor(payMethod);
// 전달받은 추상화 객체로 결제 수행
Map<String, Object> result = requestor.request(requestTO);
PayResultTO payResultTO = parsePayResultTO(payMethod, result);
return payResult;
}
private PayResultTO parsePayResultTO(String payMethod, Map<String, Object> result) {
// 중략
}
}개선된 레거시 코드
Requestor 클래스
- 기존 결제 요청 객체들에 대한 공통의 인터페이스를 정의한 객체.
- 기존의 결제 수행 객체는 Requestor 인터페이스를 상속
RequestorFactory 클래스
- TotalPaymentGate에서 조건에 따라 생성하던 결제 수행 객체를 대신 생성
- Reqeuestor로 반환하고, 요청자가 좀 더 유연하게 이용할 수 있어 새로운 결제 객체가 추가되더라도 쉽게 확장 가능
TotalPaymentGate 클래스
- 기존 결제 수행 객체의 생성 로직을 RequestorFactroy에 위임
- 생성된 결제 객체에서 결제를 처리
- 생성 부분을 제거함으로써 코드의 가독성을 높이고, 인터페이스르 통해 결제를 수행함으로써 유연성을 높임.
요약 및 정리
팩토리 패턴은 비슷한 특성을 지닌 객체들의 생성을 관리할 때 주로 사용.
- 생성을 관리하는 객체를 별도로 만들 경우의 이점
- 객체의 생성을 외부에 위임함으로써 호출자는 객체의 생성에 대해 알 필요 없이 생성된 객체를 받아와 동작
- 객체 생성을 일일이 구현할 경우 추가되는 객체가 있거나 생성 요소가 변경된다면 객체 생성에 관여했던 모든 코드를 수정해야함
- 한곳에서 객체를 생성함으로써 한곳에서만 객체 생성을 관리하여 생성에 대한 캡슐화가 보장
- 팩토리 객체의 변환형이 추상화된 형태임으로 같은 추상화 객체를 상속받은 객체라면 언제든지 객체를 추가 가능. 확장을 쉽게 할 수 잇다.
팩토리 패턴을 이용하여 개선하기 위한 생각의 흐름
- 분기문을 통한 객체의 생성 로직과 비즈니스 로직이 혼재되어 있는지 확인
- 조건문에 따른 생성 객체의 유사성을 확인한 후 추상 객체를 생성.
- 객체 생성을 관리하는 팩토리 객체를 생성하여 해당 객체에서 객체의 생성을 관리.
- 기존 분기문을 제거하고 팩토리 객체를 통해 객체를 전달받아 사용.
