인천대학교 최대진 교수님 강의를 개인적으로 정리한 글입니다.
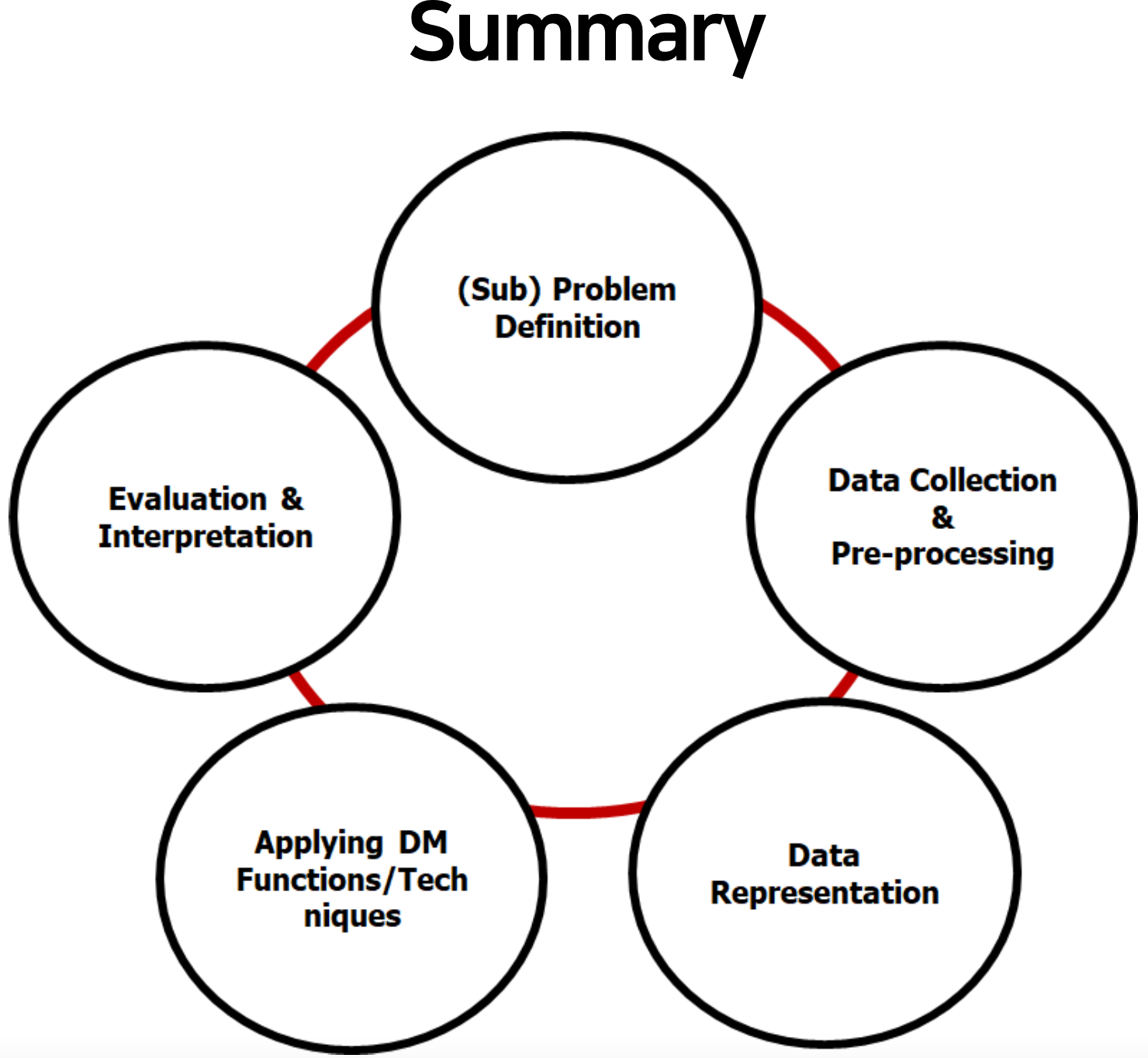
Data Mining
- Problem Definition
- Define the problem as a scientific form
- Require domain knowledge as well as scientific problem solving capability
- Data Collection
- Collecting data via
- Data Representation
- Transforming a high-dimensional raw data into problem-relevant data
- Quantifying data with various techniques
MapReduce
Large scale computing for Data Mining
-> Using machine clusters is essential
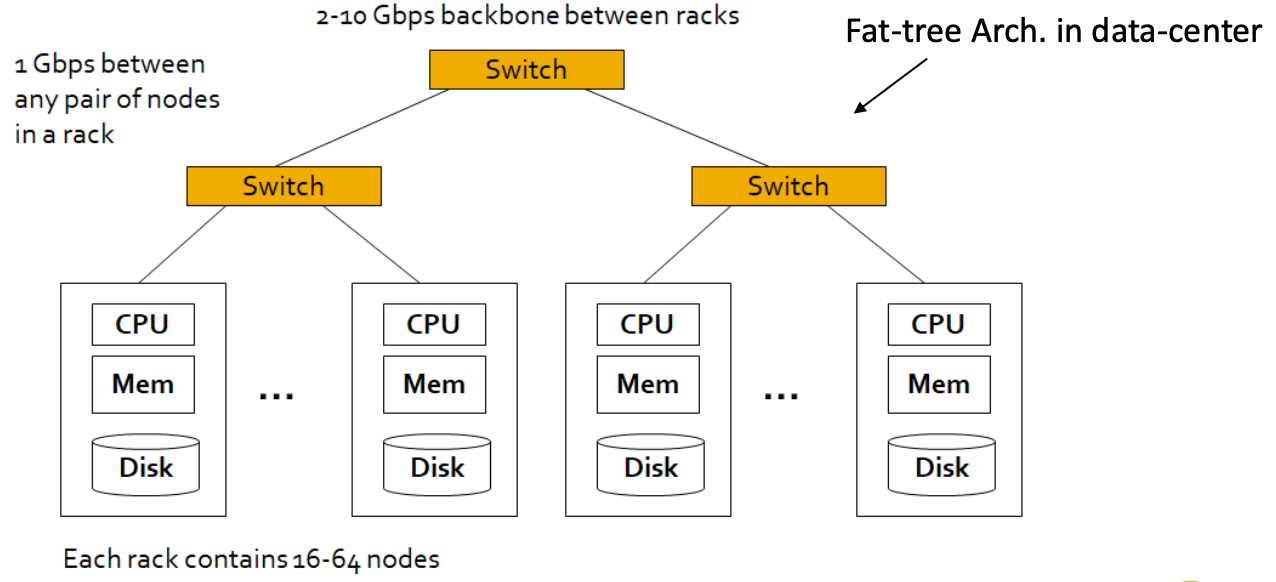
- Mining big data requires large-scale computing whose key component is Parallel programming
- MapReduce is Framework
Apache Hadoop MapReduce, Amazon Elastic MapReduce
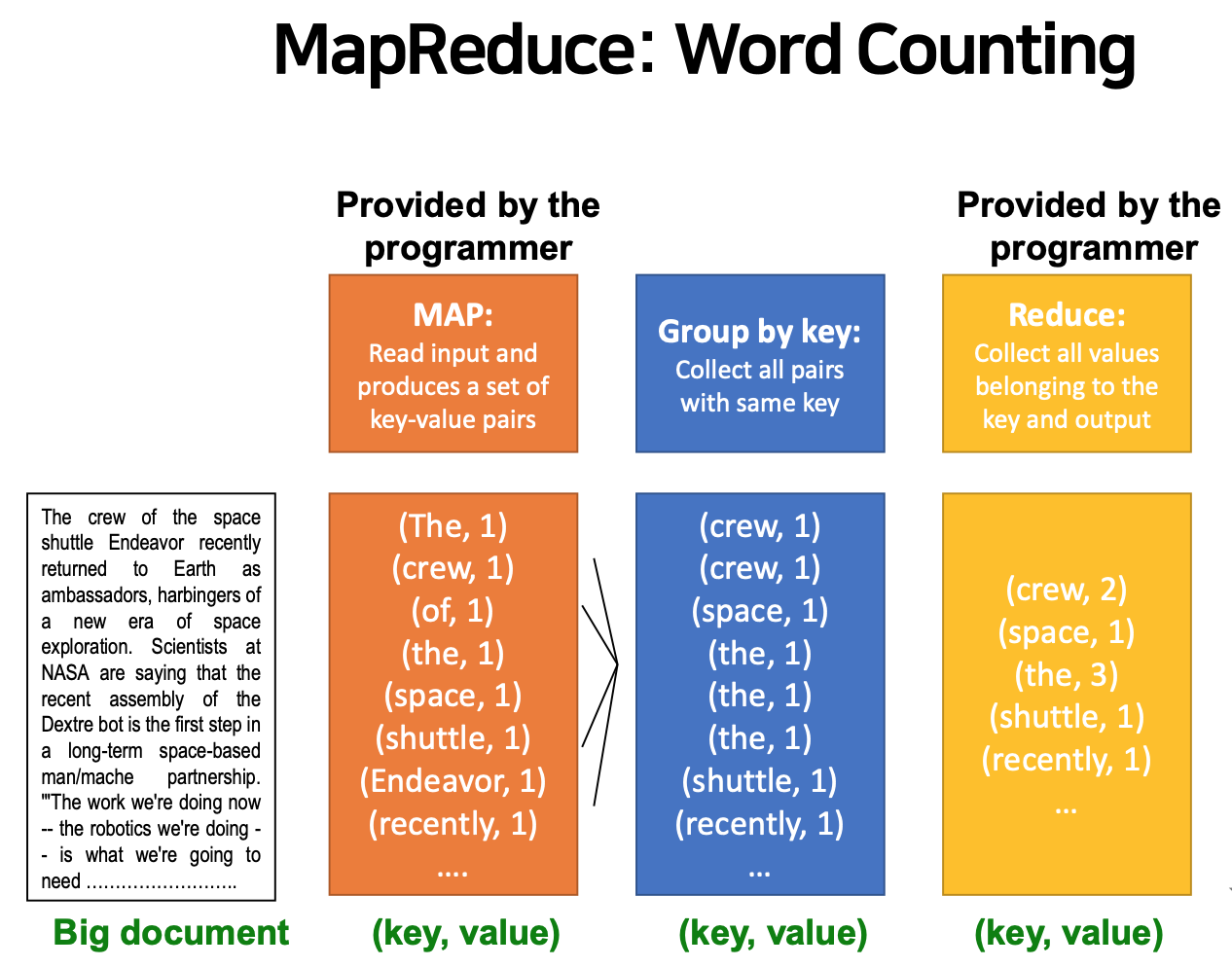
ex) Word Counting
MapReduce Environment
Partitioningthe input dataSchedulingthe program's excution across of a set of machines- Performing the
group by keystep - Handling machine
failures - Managing required inter-machine
communication
Using MapReduce Framework
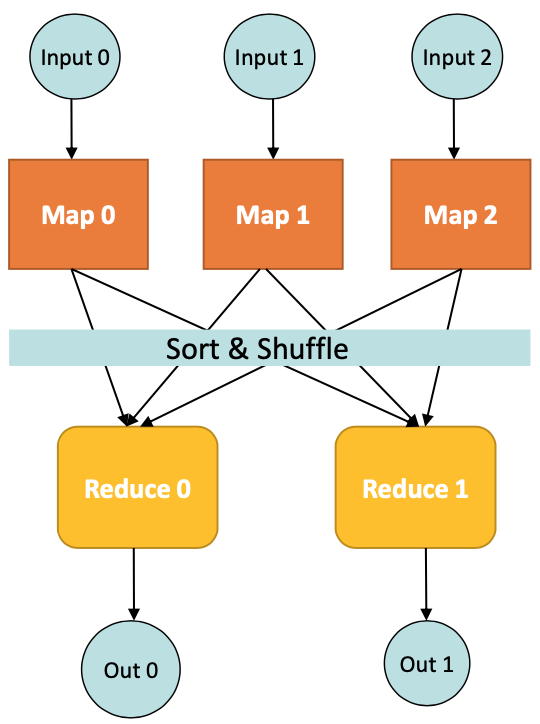
Data Flow
Input and final outputare stored on adistributed file system (DFS)
Stream Data
Big Data - Volumn, Velocity, Variety
high Velocity - Stream Data
Characteristics of Stream Data
- Size - Infinite, Burst (not equal speed, non-predictable) , Non-stationary
- only INSTATLY accessible
- Stream Management is important when the input rate is controlled externally
Applications
- Mining query streams
ex) Google wants to know what queries are more frequent today than yesterday - Mining click streams
ex) Yahho wants to know which of its pages are getting an unusual number of hits in the past hour - Mining social network news feeds
look for trending topics on Twitter, Facebook - Sensor Networks
Many sensors feeding into a central controller - IP packets monitored at a switch
Gather information for optimal routing
Detect denial-of-service attacks
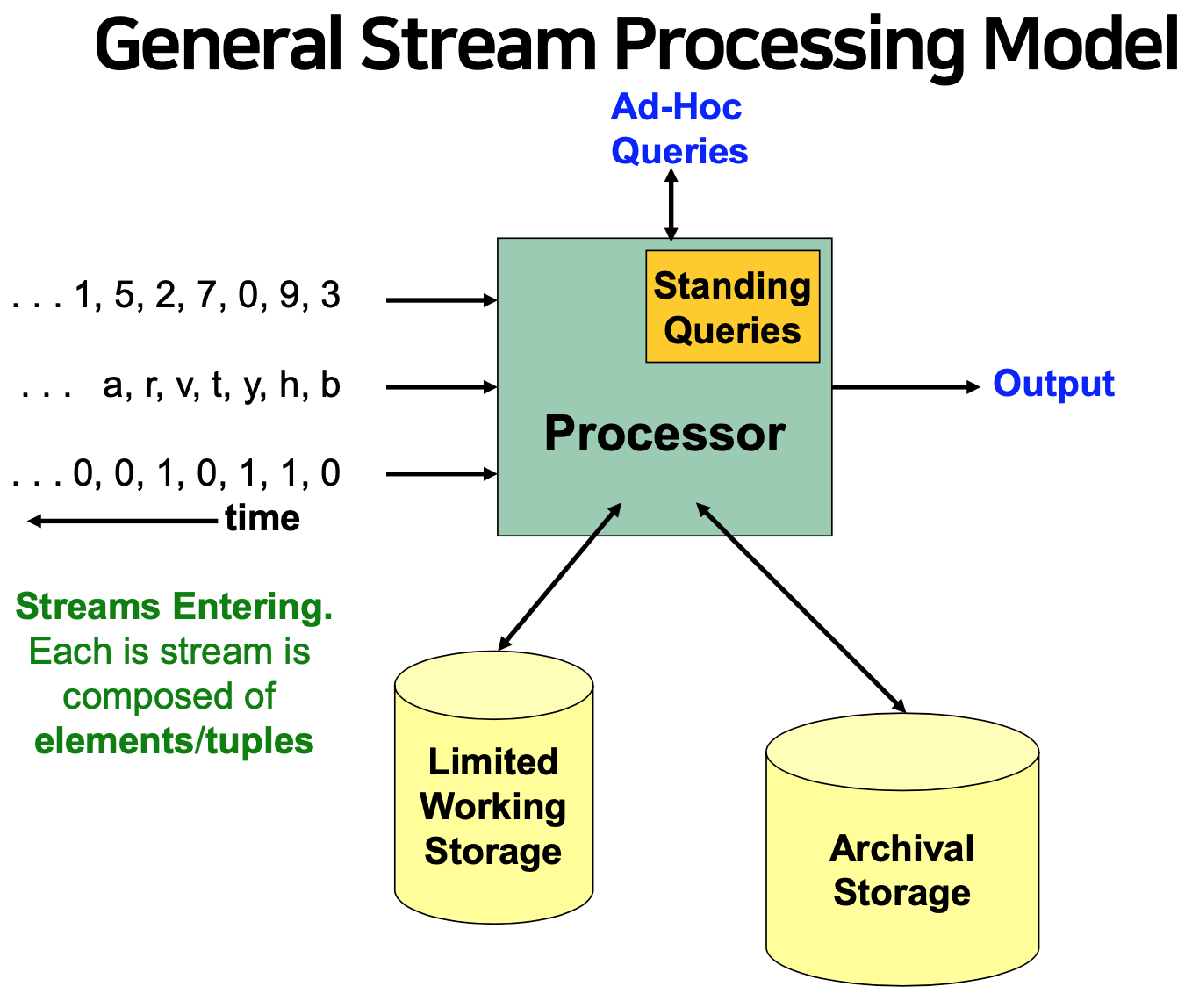
The Stream Model
- Input elements enter at a rapid rate, at one or more input ports
- The system cannot store the entire stream
SIDE NOTE : Online Learning
Online Learning enables a machine learning model to continously learn from the recent data stream
Example : Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD)
Idea : Do slow updates to the model
Operations on Data Streams
- In conclusion, we have to choose a subset of input streams
- Sampling data from a stream,
- Construct a random sample.
- Queries over sliding windows,
- Number of ~~
- Filtering a data stream,
- Counting distinct elements,
- Estimating moments,
- Counting itemsets.
- Sampling data
fixed-size tuples
Why? Don't know length of stream in advance
Suppose at time n we havve seen s items
Reservoir Sampling
Algorithm
- Store all first s elements of the stream ot S
- Suppose we have seen n-1 elements, and now the n^th element arrives (n>s)
Sliding Window
- A useful model of stream processing is that queries are about a window of length N, the N most recent elements recieved.
Example Problem - Counting Bits
- Given a stream of 0s and 1s
- Be prepared to answer queries of form "How many 1s are in the last k bits? where K <= N
Real Problem :
- What if we cannot afford to store N bits?
DGIM Method does not assume uniformity
Exponential Windows
- Sampling a fixed propotion of stream
Sample size grows as the stream grows - Sampling a fixed-size sample
Reservior Sampling - Counting the number of 1s in the last N elements
Exponentially
Filtering a Data Stream : Bloom Filter
Filtering Data Streams
- Each element of data stream is a tuple
- Given a list of keys S
- Determine which tuples of stream are in S
+ NOTE : It's different from from user-based sampling
Example Application: Email Spam Filtering
수 많은 이메일 중에서 정상으로 판정 된 메일은 스팸처리 X, 정상 처리된 이메일은 검색 없이 바로 보내고 싶다.
Bloom Fiter consists of
- An array of bits
- A number of hash functions
Two processes
-
Setup process
-
Lookup process
B[h(2)] = 1 : 내 이메일 (keys S)을 해쉬함수로 나온 숫자를 N 개 비트 배열의 위치를 구하고 1로 설정
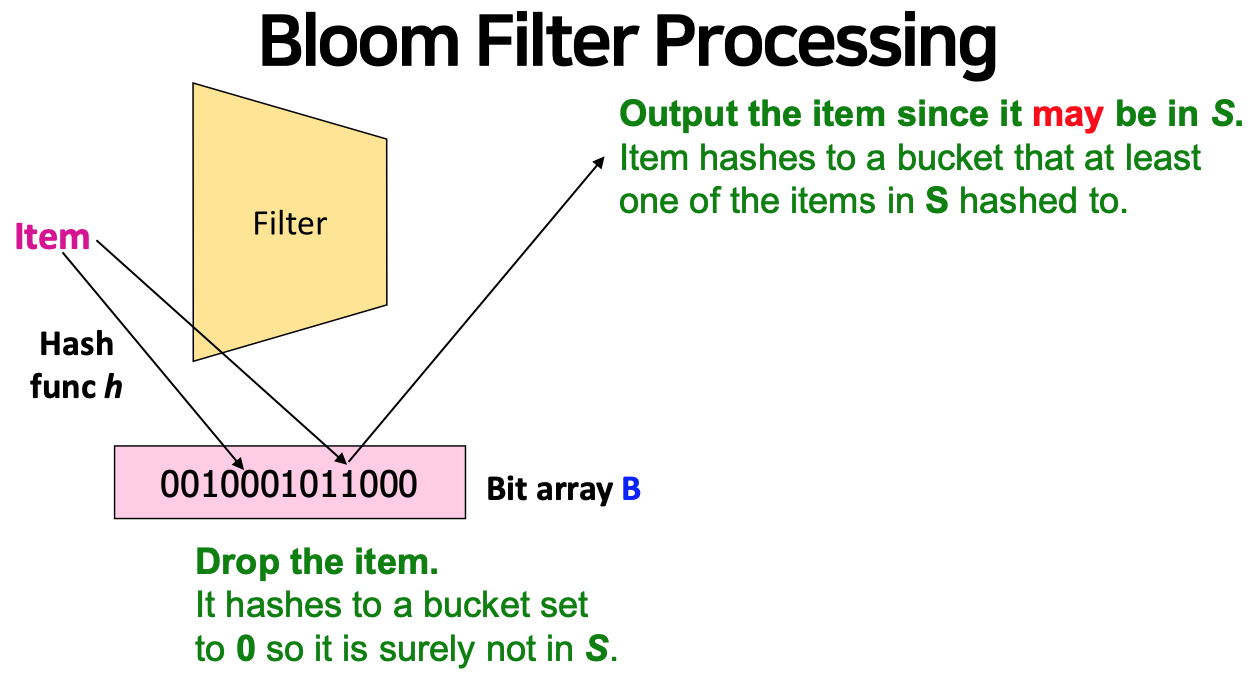
Creates false positives but no false negatives
- 정상 계정이 통과해야하는데 통과하지 못했다는 경우는 존재(create false positives), 비정상 계정이 통과하지 말아야 하는데 통과하는 경우는 없다.(no false negatives)
setup function에 여러 개의 hash function 존재.
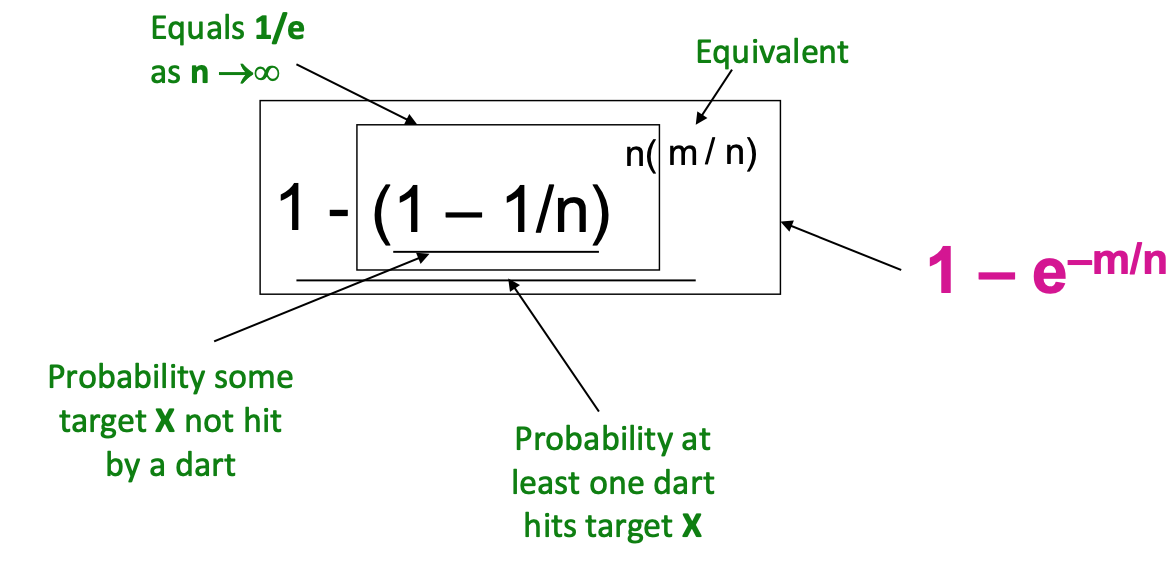
- 하나의 다트가 과녁에 맞을 확률 (1-1/n)
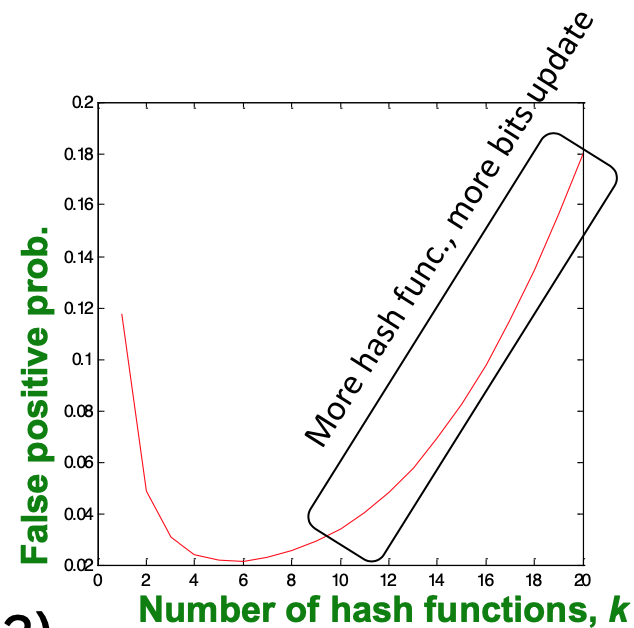
"Optimal" value of K: (n/m in(2))
Bloom filters guarantee no false negatives, and use limited memory
- Great for pre-processing before more expensive checks
Suitable for hardware implementation
- Hash function computations can e parallelized
hash function을 쓰는 이유 : 하드웨어딴에서 간단한 연산을 통해 쉽게 구현이 가능하기 때문이다 -> 속도가 매우 빠르다.
Counting Distinct Elements
Flajolet-Martin Approach
- Pick a hash function h that maps each of the N elements to at least log2 N bits
- For each stream element a, let r(a) be the number of trailing 0s in h(a)
- Record R
새롭게 들어온 아이템을 hash running,
r(a) = 오른쪽에서부터 연속적인 0의 갯수
R= max r(a)

Computing Moments
i라는 아이템이 들어온 횟수 mi
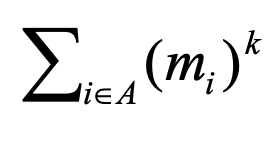

2nd moment : 아이템들이 얼마나 불균등하게 들어왔는가 (양)
AMS Method
공간이 한정하는 곳 까지 아이템을 최대한 저장하겠다.
Stream은 무한하지만 N개의 갯수를 안다고 가정하자,
N은 우리가 보고싶어하는 길이의 크기
0~N까지의 시간중 t라는 시점을 잡고 발견된 i의 갯수를 세어보자
-> 측정할수 있는 범위를 구하고 카운팅을 센 다음 식에 대입한다.

그렇다면 Stream은 무한한데 어떻게 측정하냐

Q. 미분 -> 기울기-> 지속적인 변경??
Counting Itemsets
item은 사실 tuple로 들어온다. 그럴 때 Itemset에 How to 적용
ex) 3개의 i가 있을 때 7개의 스트림 발생 -> i가 늘어남에 따라 다 저장이 불가능
Exponentially Decaying Windows

한 스탭이 넘어갈 떄 마다 1-c를 곱한다
빅데이터의 정의
주로 Volume, Velocity 에 대해서 배움
Stream 데이터에 대해서 어떤 식으로 샘플링, 추산, 계산한다.
