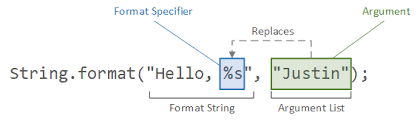
- String은 static 메서드인 format()을 통해 지정 형식의 문자열 리턴
| 포맷지정자 | 인자 | 설명 |
|---|
| 'b', 'B' | general | If the argument arg is null, then the result is "false". If arg is a boolean or Boolean, then the result is the string returned by String.valueOf(arg). Otherwise, the result is "true". |
| 'h', 'H' | general | If the argument arg is null, then the result is "null". Otherwise, the result is obtained by invoking Integer.toHexString(arg.hashCode()). |
| 's', 'S' | general | If the argument arg is null, then the result is "null". If arg implements Formattable, then arg.formatTo is invoked. Otherwise, the result is obtained by invoking arg.toString(). |
| 'c', 'C' | character | The result is a Unicode character |
| 'd' | integral | The result is formatted as a decimal integer |
| 'o' | integral | The result is formatted as an octal integer |
| 'x', 'X' | integral | The result is formatted as a hexadecimal integer |
| 'e', 'E' | floating point | The result is formatted as a decimal number in computerized scientific notation |
| 'f' | floating point | The result is formatted as a decimal number |
| 'g', 'G' | floating point | The result is formatted using computerized scientific notation or decimal format, depending on the precision and the value after rounding. |
| 'a', 'A' | floating point | The result is formatted as a hexadecimal floating-point number with a significand and an exponent |
| 't', 'T' | date/time | Prefix for date and time conversion characters. See Date/Time Conversions. |
| '%' | percent | The result is a literal '%' ('\u0025') |
| 'n' | line separator | The result is the platform-specific line separator |
| 포맷지정자 | 설명 |
|---|
| 'H' | Hour of the day for the 24-hour clock, formatted as two digits with a leading zero as necessary i.e. 00 - 23. |
| 'I' | Hour for the 12-hour clock, formatted as two digits with a leading zero as necessary, i.e. 01 - 12. |
| 'k' | Hour of the day for the 24-hour clock, i.e. 0 - 23. |
| 'l' | Hour for the 12-hour clock, i.e. 1 - 12. |
| 'M' | Minute within the hour formatted as two digits with a leading zero as necessary, i.e. 00 - 59. |
| 'S' | Seconds within the minute, formatted as two digits with a leading zero as necessary, i.e. 00 - 60 ("60" is a special value required to support leap seconds). |
| 'L' | Millisecond within the second formatted as three digits with leading zeros as necessary, i.e. 000 - 999. |
| 'N' | Nanosecond within the second, formatted as nine digits with leading zeros as necessary, i.e. 000000000 - 999999999. |
| 'p' | Locale-specific morning or afternoon marker in lower case, e.g."am" or "pm". Use of the conversion prefix 'T' forces this output to upper case. |
| 'z' | RFC 822 style numeric time zone offset from GMT, e.g. -0800. This value will be adjusted as necessary for Daylight Saving Time. For long, Long, and Date the time zone used is the default time zone for this instance of the Java virtual machine. |
| 'Z' | A string representing the abbreviation for the time zone. This value will be adjusted as necessary for Daylight Saving Time. For long, Long, and Date the time zone used is the default time zone for this instance of the Java virtual machine. The Formatter's locale will supersede the locale of the argument (if any). |
| 's' | Seconds since the beginning of the epoch starting at 1 January 1970 00:00:00 UTC, i.e. Long.MIN_VALUE/1000 to Long.MAX_VALUE/1000. |
| 'Q' | Milliseconds since the beginning of the epoch starting at 1 January 1970 00:00:00 UTC, i.e. Long.MIN_VALUE to Long.MAX_VALUE. |
| 포맷지정자 | 설명 |
|---|
| 'B' | Locale-specific full month name, e.g. "January", "February". |
| 'b' | Locale-specific abbreviated month name, e.g. "Jan", "Feb". |
| 'h' | Same as 'b'. |
| 'A' | Locale-specific short name of the day of the week, e.g. "Sun", "Mon" |
| 'a' | Minute within the hour formatted as two digits with a leading zero as necessary, i.e. 00 - 59. |
| 'C' | Four-digit year divided by 100, formatted as two digits with leading zero as necessary, i.e. 00 - 99 |
| 'Y' | Year, formatted as at least four digits with leading zeros as necessary, e.g. 0092 equals 92 CE for the Gregorian calendar. |
| 'y' | Last two digits of the year, formatted with leading zeros as necessary, i.e. 00 - 99. |
| 'j' | Day of year, formatted as three digits with leading zeros as necessary, e.g. 001 - 366 for the Gregorian calendar. |
| 'm' | Month, formatted as two digits with leading zeros as necessary, i.e. 01 - 13. |
| 'd' | Day of month, formatted as two digits with leading zeros as necessary, i.e. 01 - 31 |
| 'e' | Day of month, formatted as two digits, i.e. 1 - 31. |
| 포맷지정자 | 설명 |
|---|
| 'R' | Time formatted for the 24-hour clock as "%tH:%tM" |
| 'T' | Time formatted for the 24-hour clock as "%tH:%tM:%tS". |
| 'r' | Time formatted for the 12-hour clock as "%tI:%tM:%tS %Tp". The location of the morning or afternoon marker ('%Tp') may be locale-dependent. |
| 'D' | Date formatted as "%tm/%td/%ty". |
| 'F' | ISO 8601 complete date formatted as "%tY-%tm-%td". |
| 'c' | Date and time formatted as "%ta %tb %td %tT %tZ %tY", e.g. "Sun Jul 20 16:17:00 EDT 1969". |
- 플래그
- -(왼쪽 정렬)
- 기본적으로 숫자는 오른쪽정렬, 문자열은 왼쪽정렬. 이 플래그 사용하면 숫자도 왼쪽 정렬
- 예 : "%-10d"는 10자리 공간을 할당하고 숫자를 왼쪽으로 정렬
- +(부호 표시)
- 숫자 앞에 부호 표시. 양수일 경우 +가 앞에 붙고, 음수일 경우 -가 붙는다.
- 예 : "%+d"는 +10, -5와 같은 출력 생성
- 0(제로 패딩)
- 출력 너비가 지정된 경우, 빈 공간을 0으로 채움
- 예 : "%05d"는 숫자 3을 출력할 때 00003으로 출력
- ,(천 단위 구분자)
- 숫자를 출력할 때 천 단위 구분 기호(쉼표)를 추가
- 예 : "%,d"는 숫자 1000000을 1,000,000으로 출력
- ((음수 괄호로 감싸기)
- 금융 및 회계에서 자주 사용
- 예 : "%(.2f"는 음수를 (-100.50)처럼 괄호로 출력
- #(유효한 접두어)
- 숫자 형식에서 접두어 포함. 0x(16진수), 0(8진수) 등을 출력할 때 사용
- 예 : "%#x"는 255를 0xff로 출력
- space(부호 없이 양수에 공백 추가)
- 양수 앞에 부호 대신 공백 추가. 음수는 그대로 -가 출력됨
- 예 : "% d"는 +10을 출력할 때 10으로 출력
예시코드
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date now = new Date();
System.out.println(String.format("현재 날짜와 시간: %tF", now));
System.out.println(String.format("현재 시간: %tT", now));
System.out.println(String.format("현재 날짜: %tD", now));
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(String.format("%-10d", 42));
System.out.println(String.format("%+d", 42));
System.out.println(String.format("%05d", 42));
System.out.println(String.format("%,d", 1000000));
System.out.println(String.format("%(.2f", -100.50));
System.out.println(String.format("%#x", 255));
System.out.println(String.format("% d", 42));
}
}
String.format()을 사용하지 않아도 SimpleDateFormat을 사용한 날짜/시간 포맷팅이 가능하다 ! 날짜 및 시간을 더 세밀하게 포맷할 수 있고 SimpleDateFormat은 Date 객체를 원하는 형식의 문자열로 변환한다.
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date now = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String formattedDate = dateFormat.format(now);
System.out.println("포맷된 날짜와 시간: " + formattedDate);
}
}

