🔍 접근 제한자, Access Modifier
객체의 멤버필드(고유한 속성), 멤버 메소드(고유한 기능)에 대한 정보나 기능을 객체의 외부에서 함부로 접근할 수 없게 제한
- 객체는 추상화를 통해 중요하고 필수적인 정보만 추출하여 코드로 만든 것 👉🏻 객체의 멤버들을 함부로 접근할 수 있게 공개하면 프로그램에 악영향을 미칠 수 있음 ❗ 접근 제한의 필요성 ❗
➰ 접근제한자의 종류
멤버필드, 멤버메소드에 적용하며, 종류에 따라 공개범위가 단계적으로 달라짐
private < default < protected < public
-
private같은 객체 내부에서만 접근 가능 -
default같은 패키지의 다른 클래스까지 접근 가능- package 접근 제한자 라고도 함
- 키워드 따로 없이 접근 제한자 항목을 적지 않으면 적용
-
protected같은 패키지 + 상속 관계의 객체까지 접근 가능 -
public모든 접근 가능
➰ 접근제한자를 적용할 수 있는 위치
-
멤버필드 : 주로 private을 작성
-
멤버메소드 : 주로 public을 작성
-
클래스 정의코드 : public 또는 default만 가능
package java06_class;
public class Class_02 {
private int num1 = 100;
(default) int num2 = 200;
protected int num3 = 300;
public int num4 = 400;
-----------------------------------------------------
package java06_class.defaultTest; 👉🏻 패키지가 다름
public class Main_02_defaultTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class_02 cl = new Class_02();
System.out.println( cl.num4 ); ➡ public
//System.out.println( cl.num3 ); ➡ protected //패키지가 달라져서 값을 가져올 수 없음
//System.out.println( cl.num2 ); ➡ default //패키지가 달라져서 값을 가져올 수 없음
//System.out.println( cl.num1 ); ➡ private
}
}🔍 클래스, Class
➰ 작성방법
[접근제한자] [클래스식별자] class [클래스명] { //정의부, Head
//멤버필드
//멤버 메소드 //구현부, Body
//생성자
}- 클래스 명은 첫글자를 대문자로 시작하며 식별자 규칙에 맞게 작성되어야 함
- 클래스의 풀네임 : [패키지이름].[클래스명] 👉🏻 다른 소스파일이어도 같은 패키지 내에 같은 클래스명으로 작성 불가 ➡ public으로 선언하지 않고 여러 클래스 만드는 경우 같은 패키지 내에 같은 이름으로 클래스를 작성하는 오류가 생길 수 있음
➰ 접근 제한자
public 또는 default 두 가지만 적용할 수 있음
- public Class
- 어디에서든지 사용할 수 있는 클래스가 됨
- public 클래스의 이름은 .java 파일의 이름과 같아야 함 👉🏻 .java 파일 안에 딱 하나의 public 클래스만 존재 가능
- public 클래스는 해당 .java파일의 주 클래스로 사용됨 / primary / master
- default Class
- 같은 패키지에서만 사용할 수 있는 클래스가 됨
- public 클래스의 보조기능을 담당하는 클래스로 사용됨 / secondary / slave
➰ 클래스 식별자, 제한자(modifier)
클래스의 용도에 맞는 특별 기능을 부여할 때 사용
abstract, final, static, ...
➰ 멤버필드
👉🏻 메소드 밖에서 선언된 것
- 클래스가 객체로 생성되었을 때 공간을 가지게 될 변수, 상수
- 인스턴스마다 변수공간이 각각 만들어짐
➰ 멤버메소드
객체가 수행할 수 있는 기능, 동작을 정의
➰ 생성자
객체를 생성할 때 반드시 호출하도록 정의해놓는 코드
- 인스턴스를
초기화함
초기화: 변수의 기본값과 객체의 기능동작에 필요한 설정
🔍 메소드, Method
함수, Function + 객체지향 원리
[접근제한자] [제한자] [리턴타입] [메소드명] (매개변수) {
//실행코드
}- 객체(클래스)의 기능, 동작, 행위 등을 정의하는 코드
- 객체 변수(인스턴스의 주소를 저장하고 있는 참조변수)를 통해서 메소드를 호출(사용)할 수 있음
- 객체들이 서로 데이터를 교환하거나 상호작용할 때 사용
- 접근제한자 모두 적용 가능
- 메소드명은 첫글자를
소문자로 시작
➰ 메소드 제한자
메소드에 추가적인 역할, 기능을 부여할 때 사용
abstract, final, static, ...
➰ 리턴타입, Return type, 반환타입
메소드가 종료할 때 되돌려 주는 데이터(반환데이터, Return Data)의 자료형을 명시 👉🏻 메소드 출력 데이터
- 리턴값(반환값)이 없으면
void라고 적음
➰ 매개변수, Parameter
메소드 동작에 필요한 데이터를 저장하는 변수, 메소드 입력 데이터
👉🏻 입력할 매개변수가 없다면 () 괄호 안을 비워둠
ex) main(String[] args) 👉🏻 문자열 여러개가 필요
➰ 매개변수와 반환데이터
- 매개변수 x, 반환데이터 x
public void method() {
System.out.println("Hello");
}- 매개변수 o, 반환데이터 x
public void method( int parameter ) {
System.out.println("전달된 값 : " + parameter);
}- 매개변수 x, 반환데이터 o
public int method() {
return 123;
}- 매개변수 o, 반환데이터 o
public int method(int n1, int n2) {
return n1 + n2;
}➰ 메소드 작성법
- 메소드의 기본형태 작성하기
public void method() { } - 메소드 이름 정하기 ➡ 만들려는 기능을 대표하는 이름으로
- 매개변수 작성하기 ➡ 기능을 수행하기 위해 필요한 데이터를 저장할 수 있도록 선언
- 실행코드 작성하기 ➡ 메소드의 기능을 구형
- return코드 작성하기 ➡ 기능 수행 후 결과값을 반환해야 할때 작성
- return타입 작성하기 ➡ return 코드에 맞는 자료형으로 작성
Public class Method_01 {
public void method() {
System.out.println("메소드 호출 테스트");
}
//2개의 정수 뺄셈하는 메소드
public int sub(int num1, int num2) {
int result = num1 - num2;
return result;
}
--------------------------------------------------------
public class MethodEx { //Executor 실행기의 약자
public static void main(String[] args) {
//객체 생성
Method_01 m01 = new Method_01();
m01.method();
➡ 메소드 호출 테스트
System.out.println("뺄셈 결과 : " + m01.sub(3, 2));
➡ 1
}🔍 캡슐화, Encapsulation
객체지향프로그램의 특징 중 하나
✔ 결합도 : 객체끼리의 연결(의존)정도
✔ 응집도 : 객체 내부에 관련 사항들이 모여있는 정도
- 서로 연관있는 데이터(필드)와 기능(메소드)들을 하나의 클래스로 묶어서 작성
- 객체의 속성(필드)은 중요한 정보이므로 외부에서 함부로 접근할 수 없도록 처리 👉🏻 접근제한자를
private로 두고, 필요시 공개 ➡ 정보 은닉, Information Hiding
🔍 Setter Method
멤버필드의 값을 저장할 수 있도록 작성하는 메소드
- 멤버메소드의 이름을 "set"으로 시작해서 멤버필드의 첫 글자만 대문자로 바꿔서 작성
public void setXxxx( [멤버필드의 자료형] [멤버필드명] ) {
this.[멤버필드명] = [멤버필드명];
}
ex)
private int data; //멤버필드
public void setData( int data ) {
this.data = data;
}🔍 Getter Method
멤버필드의 값을 불러올 수 있도록 작성하는 메소드
- 멤버메소드의 이름을 "get"으로 시작해서 멤버필드의 첫 글자만 대문자로 바꿔서 작성
public [멤버필드의 자료형] getXxxx() {
return [멤버필드명];
}
ex)
private int data; //멤버필드
public int setData() {
return data;
}➰ Getter, Setter 단축키
alt + s, r- 퀵메뉴
alt + shift + s, r
(퀵메뉴를 이용할 땐 alt대신 alt + shift 이용)
🔍 메소드 오버로딩, Method Overloading
같은 이름의 메소드를 여러 개 중복정의 하는 것
➰ 오버로딩 성립 조건
💡 매개변수만 다르면 됨
- 메소드 이름이 같을 때 적용
- 매개변수의 자료형 종류 또는 개수 또는 순서가 달라야함
- 리턴타입, 접근제한자는 오버로딩과 상관없음
public void test() { }
vs 👉🏻 오버로딩❌ / 반환타입은 오버로딩의 조건이 되지 않음
public int test() {
return 0;
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------
public void test(String str, int i) { }
vs 👉🏻 오버로딩⭕ / 매개변수의 위치가 다르면 중복정의가 아님
public void test(int i, String str) { }🔍 생성자, Constructor
멤버 필드, 멤버 메소드와 함께 클래스를 구성하고 있는 요소
생성자의 이름 = 클래스 이름
[접근제한자] 클래스명 ( 매개변수 ) {
//객체를 생성하면서 수행할 작업(코드)
}- 객체를 생성(new)할 때 반드시 호출되는 특수한 형태의 메소드 👉🏻 new 연산자와 함께 사용(호출)
- 클래스에는 한 개 이상의 생성자가 반드시 존재해야 함
- 클래스 정의 코드에 생성자를 작성하지 않으면 자동으로 JVM이 추가 👉🏻 생성자를 하나라도 작성하면 자동으로 생성자를 추가해주지 않음
- 반환타입, 반환코드(return코드) 작성 금지
- 오버로딩 가능
➰ 생성자의 역할
- 멤버 필드들의 기본값(초기값)을 설정 👉🏻 객체가 생성될 때 기본으로 저장하고 있어야하는 값
- 멤버 필드의 초기값을 설정할 때 추가적인 작업이 필요하면 생성자로 작성한다
-> 예외 처리 코드 (try~catch 구문)
🔍 클래스 다이어그램, Class Diagram
클래스의 내부 구조, 유형, 클래스들 간의 관계 등을 그림으로 표현한 것
➰ 접근제한자 표현 기호
+: public#: protected~: default-: private
➰ 자료형 표시법
변수의 데이터타입, 메소드의 반환타입을 표현할 때에는 이름 뒤에 :을 붙이고 자료형을 명시
👀 example
- 멤버필드
- num : int ➡ private int num;
+ name : String ➡ public String name;- 멤버메소드
+ display(n1 : int, n2 : int) : void / + display(int, int) : void
➡ public void display(int n1, int n2) { }
💭 다음 다이어그램을 보고 코드를 작성하시오.
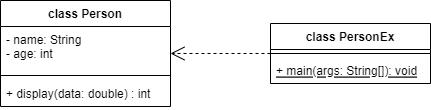
💡 밑줄 표시 ➡ static
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public int dislpay(double data) {
}
}
---------------------------------------------
public class PersonEx {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Person p = new Person();
}
}