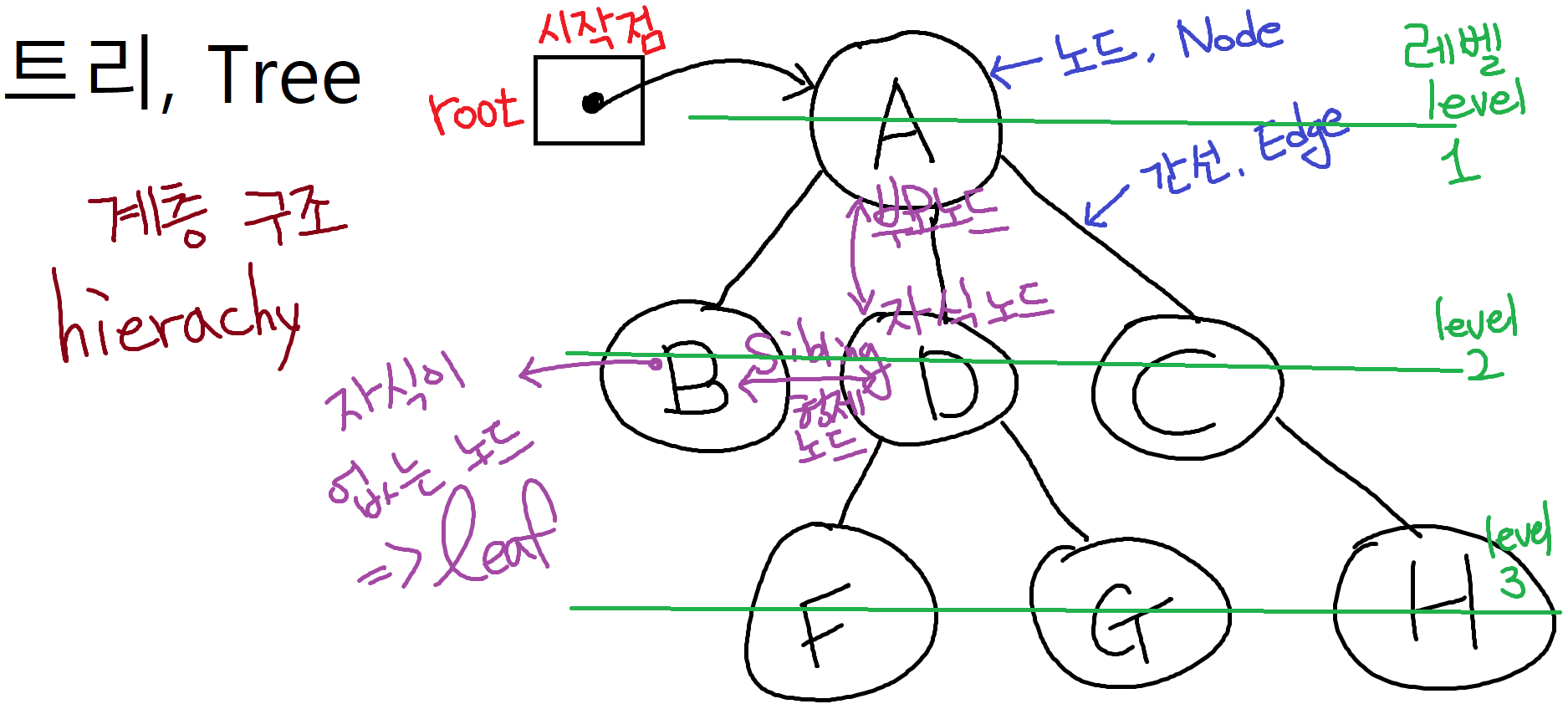
🔍 Iterator, 반복자
컬렉션(List, Set)의 모든 요소들에 순차적으로 접근할 때 사용
👉🏻 for-each 구문과 비슷한 역할을 수행(저장된 요소들을 읽어옴)
➰ 메소드()
hasNext(): 읽어올 요소가 남았는지 확인하는 메소드next(): 다음 요소를 읽어오는 메소드
List list = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C", "D", "E");
//반복자 변수 선언 및 생성
Iterater iter = list.iterator(); //메소드 호출만으로 Iterator 객체 생성
while(iter.hasNext()) { //요소가 존재하는만큼 반복
System.out.println(iter.next()); //요소를 반환하고 다음 요소를 반환할 수 있도록 준비
}
👉🏻 같은 동작을 for, for-each로도 구현 가능
💡 println에 오버로딩된 toString때문에 객체, 요소가 문자열로 출력될 수 있음🔍 Set 인터페이스
비선형 구조로 된 데이터의 모음(집합) 👉🏻 데이터의 입력된 순서를 유지하지 않으며 인덱스가 없음
💡 중복데이터를 허용하지 않음
➡ hashCode(), equals()를 이용해 요소의 중복검사 수행
- Interface Set의 구현체(구현된 class) :
class HashSet,class LinkedHashSet,class TreeSet - 메소드는 List와 거의 유사
➰ class HashSet
가장 기본이 되는 Set 구현체
➰ class LinkedHashSet
데이터의 입력순서를 유지하는 Set 👉🏻 인덱스는 없음
➰ class TreeSet
정렬기능이 포함된 Set 👉🏻 오름차순 정렬
- 트리구조의 Set이라 생성작업과 데이터를 추가, 삭제하는 작업이 느린 편
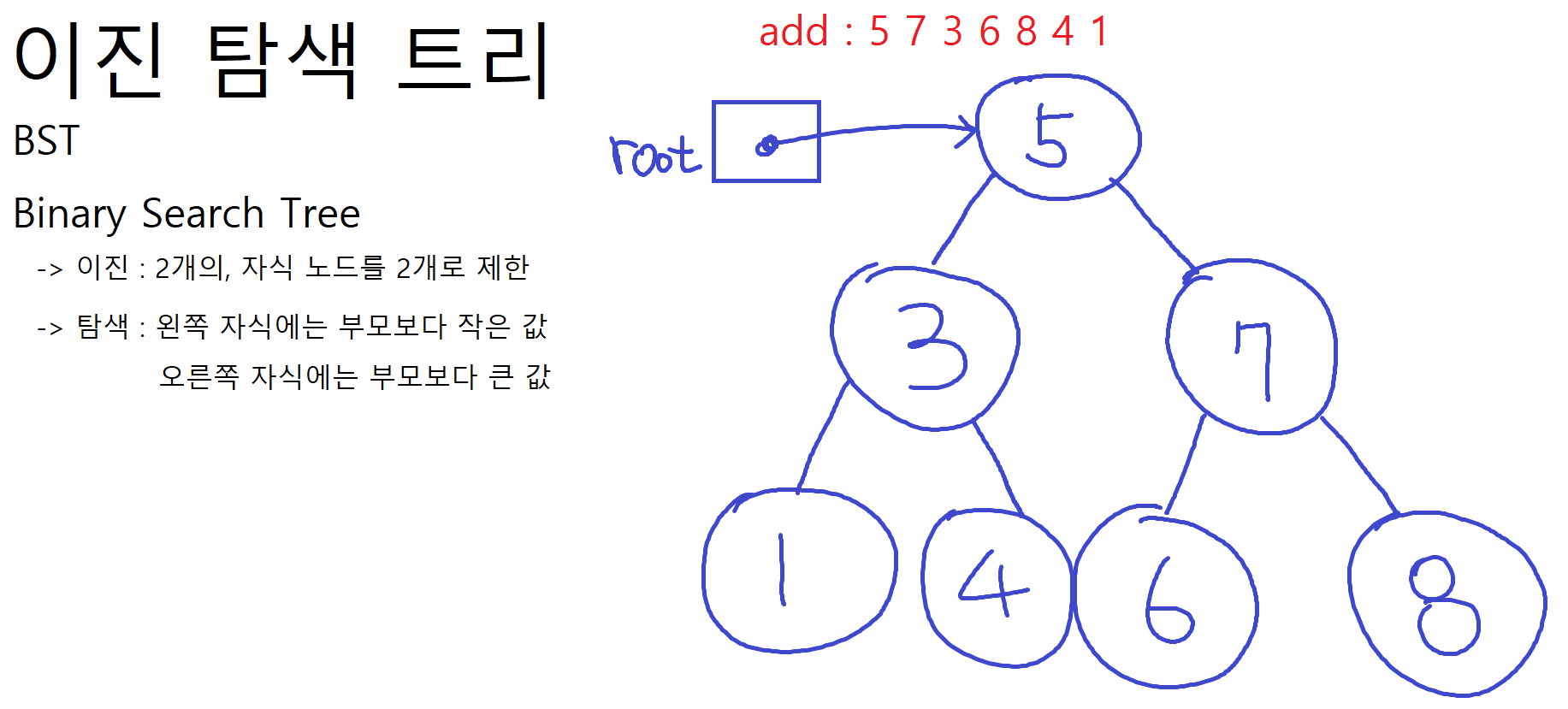
👉🏻 대신! 조회(탐색)이 단점을 무시할 수 있을 정도로 매우 빠른편 - BST, Binary Search Tree, 이진 탐색트리 👉🏻 자식 노드를 2개로 제한 / 왼쪽 자식에는 부모보다 작은 값, 오른쪽 자식에는 부모보다 큰 값을 저장
- 한쪽으로 치우치는 모양을 갖게될 수 있음 ➡ 밸런스를 잡아주는 알고리즘이 추가로 필요
🔍 Map 인터페이스
매핑되어있는 데이터를 요소로 가짐 ➡ Entry : 매핑된 쌍
- Map 자료구조는 Entry를 여러개 저장하는 구조로,
keyvalue두 데이터를 한 쌍(Entry)으로 묶어서 데이터를 관리 Key: Entry의 기준값으로, 데이터들을 식별할 때 사용 👉🏻 중복값으로 사용할 수 없음Value: Entry의 데이터로, key에 매핑된(대응하는) 값 👉🏻 중복값 사용 가능- key 중복 검사는
hashCode(),equals()로 판단 👉🏻 Set과 동일 - 출력시( System.out.println(map); ) { key=value, key=value, ... } 형태로 출력
- 모든 요소 출력시 key를
Set에 따로 저장 후 Iterator로 출력
👉🏻 value는 .get(key) 메소드를 통해 출력할 수 있지만 key는 메소드를 통해 출력 불가 ➡ .keySet()을 통해 Set변수에 key를 set 형태로 저장 - interface Map의 구현체 :
class HashMap,class Hashtable,class Properties
➰ 매핑, Mapping
두 집합을 구성하는 원소들 간의, 데이터와 데이터 사이의 대응 관계
- one to one, 1:1 / 일대일 매핑
- one to many, 1:m / 일대다 매핑
- many to one, m:1 / 다대일 매핑
- many to many, m:n / 다대다 매핑
➰ class HashMap
가장 기본이 되는 Map 객체
- key와 value로
null이 허용 ➡ 그래도 쓰지 않는 것이 좋음
➰ class Hashtable
HashMap + 동기화 처리
- key와 value로
null을 허용하지 않음
➰ 메소드()
Map map = new HashMap();
Map map = new Hashtable();
👉🏻 key와 value로 null값응 허용하느냐의 차이
map.put(key, value); / 데이터 삽입
map.get(key); / 데이터 출력
➡ 존재하지 않는 key를 이용하여 get()하면 null반환
❗ 중복키를 사용할 수 없음 ➡ 중복입력된 key에 매핑된 기존 데이터를 덮어씌움
map.containsKey(key); / 입력된 key를 이미 갖고있는지
➡ if(!map.comtainsKey(2)) { map.put(2, "Cherry"); }
➡ key를 확인하고 같은 key가 없으면 데이터 삽입
map.containsValue(value); / 입력된 value가 이미 존재하는지
map.remove(key); / 입력된 key 확인 후 Entry 제거
map.remove(key, value); / 입력된 Entry확인 후 일치하면 제거
map.values() / values 출력 ➡ 컬렉션 형태로 [3.345, Apple, Apple, Durian, Orange]
map.size(); / map.isEmpty(); /
<모든 요소 출력하기>
Set keys = map.keyset();
Iterator iter = keys.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iter.next() + " = " + map.get(key));
}
or
for(Object key : map.keyset()) {
System.out.println(key + " = " + map.get(key));
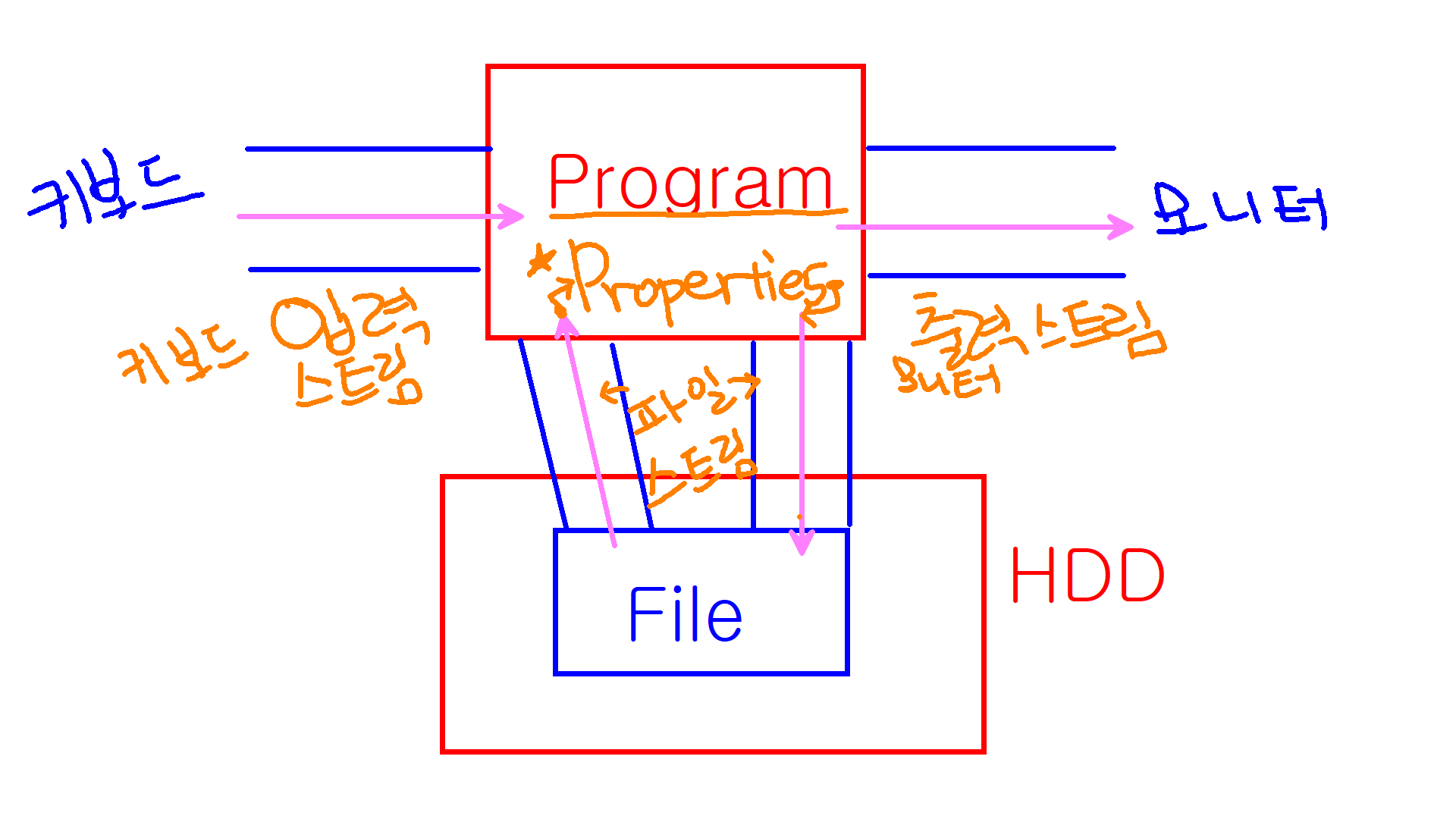
}➰ class Properties
💡 key와 value의 데이터타입이 String으로 제한됨 ➡ 문자열 타입의 Entry 관리
Hashtable의 자식 클래스 👉🏻 상속받은 기능 + 추가 특성
- 주로 프로그램의 설정값이나 기본값을 저장할 때 사용
- 파일(File)로
Entry(key-vlaue)를 저장하고 불러오는 기능이 추가되어있음 ➡ 파일의 확장자.properties - 파일스트림(입출력)을 통해 프로그램과 파일간 입출력 관장
- Map의 .put()메소드로도 값을 저장할 수 있지만 Properties의 고유한 메소드를 이용할 수 없음 👉🏻 고유메소드 :
.store(),.load() - 자바 API에서 기본으로 제공하는 Properties 클래스
Properties sys = System.getProperties();
sys.getProperty("java.version");
sys.getProperty("os.name");
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.setProperty(String, String); / prop.getProperty(String, String);
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
<파일 출력>
//파일 출력스트림 변수
FileWriter writer = null; 👉🏻 System.out(모니터 출력)과 같은 역할
//파일 출력스트림 생성 ➡ 입력된 주소에 파일이 없으면 파일을 생성
writer = new FileWriter("//파일 주소//") 👉🏻 이 문구만 작성시 예외 에러 발생 ➡ try-catch로 감싸주기
//Properties 객체의 데이터를 파일로 출력(파일로 저장)
prop.store(writer, "comment : User Information");
👇🏻
Properties propt = new Properties();
propt.setProperty("want", "vacation");
propt.setProperty("hope", "Holiday");
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("D:\\eclipse-workspace\\StudyAtHome\\src\\java10_collection");
propt.store(fw, "comment : study again");
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
<파일 입력>
//파일 입력 스트림 객체
FileReader read = null;
//입력받은 데이터를 확인할 Properties 객체
Properties again = new Properties();
//입력객체에 데이터 저장
read = new FileReader("D:\\eclipse-workspace\\StudyAtHome\\src\\java10_collection"); 👉🏻 예외 발생 / 파일 못찾은 경우 ➡ try-catch로 감싸주기
👇🏻
FileReader read = null;
Properties again = new Properties();
try {
read = new FileReader("D:\\eclipse-workspace\\StudyAtHome\\src\\java10_collection");
again.load(read); 👉🏻 불러온 파일 확인 / 예외발생 ➡ try-catch로 감싸주기
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//파일 확인
System.out.println(again);🔍 데이터타입 일반화
자료형들의 개별적인 특징, 특성을 하나의 공통적인 특성으로 바꿔서 표현
| int | ===일반화===> | 데이터타입 Type |
|---|---|---|
| double | T | |
| boolean | T | |
| String | T | |
| Point | T | |
| Person | T | |
| List | T | |
| ... | T |
클래스, 메소드 정의코드에서 사용되는 데이터타입들을 일반화시켜 프로그래밍
👉🏻 자바에서는 제네릭(Generic) 문법을 적용해서 구현
👀 Example
- 일반화가 필요한 상황 👉🏻 타입만 다른 같은 메소드
데이터 타입부분만 달라지며 같은이름, 같은 동작을 하는 중복코드가 작성되는 상황public void out(int data) { System.out.println("데이터 : " + data); } public void out(double data) { System.out.println("데이터 : " + data); } public void out(Point data) { System.out.println("데이터 : " + data); } public void out(Person data) { System.out.println("데이터 : " + data); } -------------------------------------------------------------------------- public <T> void out(!!T!! data) { System.out.println("데이터 : " + data); } ➡ 어떤 데이터를 대입해도 JVM이 오버로딩해서 자동으로 채워줌 ex) 123 -> int -> Integer✔ 개별적인 데이터타입으로 작성해야하는 정의코드들을 하나의 일반화된 데이터타입 T를 이용해 한번만 작성하고 활용할 수 있도록 👉🏻 제네릭 메소드
➰ 타입 파라미터, Type Parameter
특정 자료형으로 결정되기 전 상태의 일반화된 데이터타입
- 타입 파라미터를 결정하지 않으면 Object로 자동 결정되며, 이를
raw type이라고 함
👉🏻raw type으로 결정되면 형변환이 항상 필요 ➡ Object는 최상위 부모타입이므로 더 많은 기능을 가진 자식클래스타입이 될 수 없음 - 제네릭타입으로 기본형타입을 사용할 수 없음 ➡ int❌ Integer⭕
- 객체 선언 및 생성을 동시에 할 경우 생성코드에서 데이터타입 생략 가능 👉🏻 JDK 1.7이상 가능
ArrayList<String> list; //타입 파라미터를 String으로 결정하면서 객체변수 선언 👉🏻 int형은 값 저장 불가
list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Banana");
ArrayList list2; //타입 파라미터를 결정하지 않아 Object 타입으로 자동결정
//객체 선언 및 생성 동시에
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Iterator<Integer> iter = new Iterator<>();🔍 제네릭 클래스
제네릭 타입을 적용해 정의한 클래스
- 제네릭 클래스 타입으로 객체 변수를 선언하고 생성할 때 / 타입 파라미터를 결정하고 사용
class Class02 <T> {
//T 타입 멤버필드
private T data;
//T 타입 멤버메소드
//반환타입, 매개변수타입, 지역변수타입이 모두 T
public T display(T data) {
this.data = data;
return data;
}
//T 타입 게터세터
public T getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
👉🏻 클래스를 정의할 때 제네릭타입을 적용, 클래스 내부 코드에서 T를 자료형처럼 사용할 수 있음
------------------------------------------------------
public class GenericClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class02 c01 = new Class02(); 👉🏻 타입파라미터를 결정하지 않아 Object 타입으로 자동 결정 / raw type
c01.setData(1234); // 1234 ➡ int ➡ Integer ➡ Object
int num = (int)c01.getData(); //raw type이라 형변환 필수!
//제네릭 클래스 객체변수 선언 및 생성시 타입 파라미터 결정, 사용
Class02<String> c02 = new Class02<>();
c02.setData("Grape");
String fruit = c02.getData();
}🔍 제네릭 메소드
메소드 내부에서 사용할 수 있는 제네릭 타입(타입 파라미터)을 적용한 메소드
- 메소드를 호출하면서 타입 파라미터를 결정할 수 있음
class Class03 {
//일반메소드 + <T> 👉🏻 제네릭 메소드
public <T> void disply(int num) {
int data;
}
//제네릭 메소드 👉🏻 return타입, 매개변수타입, 지역변수타입
public <T> T out(T obj) {
T data = obj;
return data;
}
}
---------------------------------------------------
//일반 클래스 생성
Class03 cl = new Class03();
cl.out(1234);
👉🏻 타입파라미터를 결정하지 않고 호출 ➡ 매개변수의 전달인자를 보고 Integer타입으로 자동 결정
cl.<Double>out(3.14); 👉🏻 타입파라미터를 Double로 결정 후 호출