21. 스프링 XML AOP 구현
스프링 XML 설정을 통한 AOP 구현
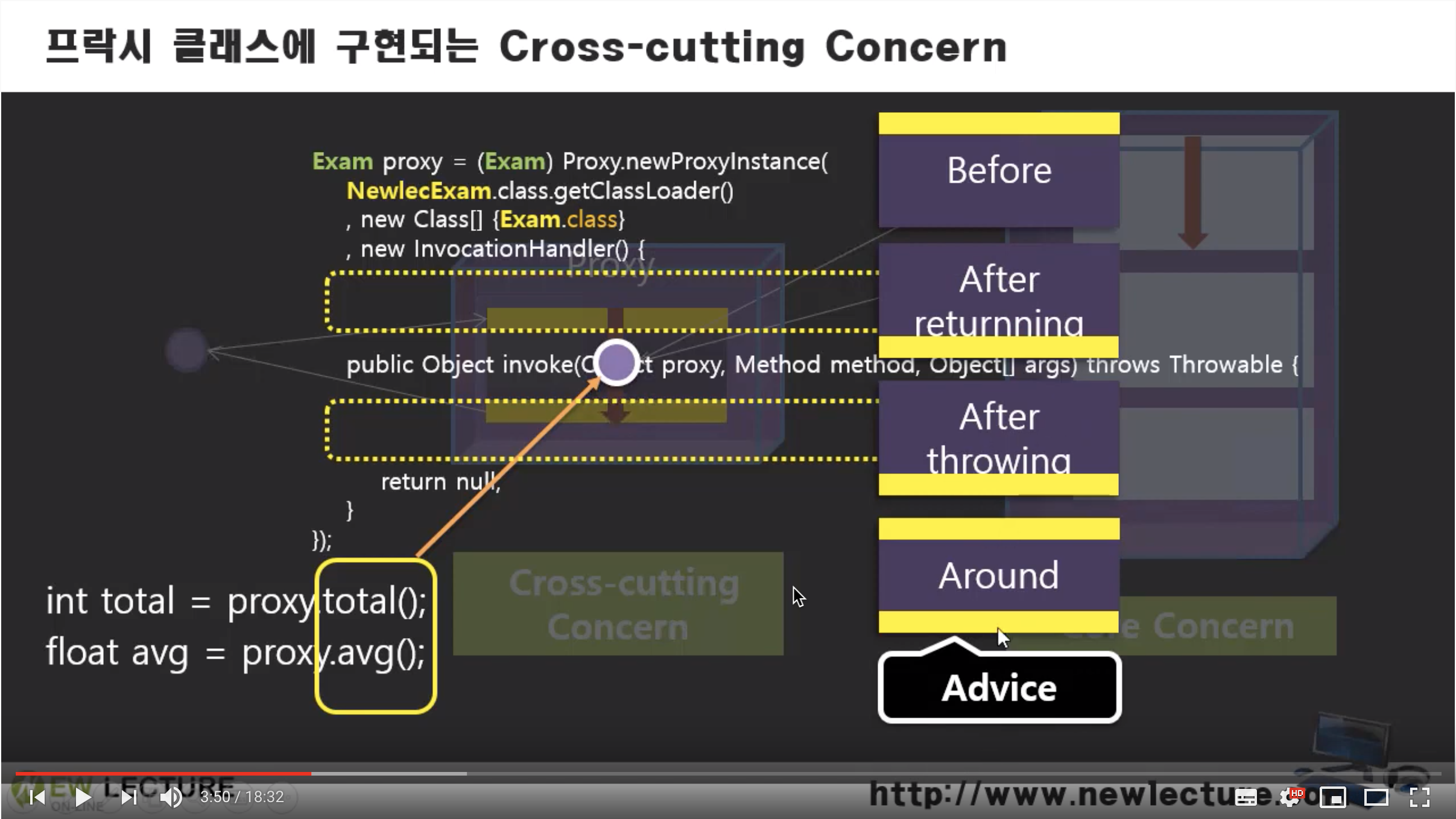
이제 자바 코드로만 AOP를 구현한 것을 스프링의 DI 장점을 활용하여 구현해본다. 스프링에서는 Cross-cutting Concern이 존재하는 방식을 Advice라고 하며 제공하는 4가지 Advice가 존재한다.
| 명칭 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| Before | Core Concern 앞 단에 보조 업무가 존재 |
| After returnning | Core Concern 뒷 단에 보조 업무가 존재 |
| After throwing | Core Concern 뒷 단에 보조 업무(에러 처리)가 존재 |
| Around | Core Concern 앞/뒷 단에 보조 업무가 존재 |
이전 내용을 Around Advice을 활용해 스프링으로 AOP를 구현해 본다.
LogAroundAdvice.java
아래와 같이 Program.java에 존재하던 보조 업무에 대한 코드를 따로 클래스를 생성해 옮긴다.
Exam exam = new NewlecExam(1, 1, 1, 1);
Exam proxy = (Exam) Proxy.newProxyInstance(NewlecExam.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] {Exam.class},
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = method.invoke(exam, args);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
String message = (end - start) + "ms 소요 ";
System.out.println(message);
return result;
}
});옮기면서 다른 점은 InvocationHandler 대신 MethodInterceptor를 구현했다는 점이다. 큰 차이는 없으나 Method 클래스의 invoke 메소드는 매개변수를 갖는 반면 MethodInvocation 클래스의 proceed 메소드는 매개변수를 갖지 않는다.
package spring.aop.advice;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
public class LogAroundAdvice implements MethodInterceptor{
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = invocation.proceed();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
String message = (end - start) + "ms 소요 ";
System.out.println(message);
return result;
}
}
setting.xml
Core Concern에 대해서만 실행할 때는 exam bean 객체만 생성하면 되며 Cross-cutting Concern을 통해 실행할 때에는 exam이 target으로 바뀌어 proxy 객체에 DI되는 형식으로 바꾼다. logAroundAdvice도 DI가 되도록 한다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.3.xsd">
<!-- Core Concern(주 업무 로직)만 사용할 경우 -->
<bean id="exam" class="spring.aop.entity.NewlecExam" p:kor="1" p:eng="2" p:math="1" p:com="3"/>
<!-- Cross-cutting Concern(보조 업무 로직)을 활용할 경우 -->
<bean id="target" class="spring.aop.entity.NewlecExam" p:kor="1" p:eng="2" p:math="1" p:com="3"/>
<bean id="logAroundAdvice" class="spring.aop.advice.LogAroundAdvice" />
<bean id="proxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="target" ref="target"></property>
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>logAroundAdvice</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
Program.java
이를 통해 주 업무만 남은 코드는 간결해 짐을 알 수 있다. 다만 setting.xml에서 proxy를 exam으로만 바꾸어 사용하면 되며 Core Concern에서는 이것이 real인지 proxy인지 판단할 길이 없게 된다.
package spring.aop;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import spring.aop.entity.Exam;
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring/aop/setting.xml");
Exam exam = (Exam) context.getBean("exam");
System.out.println("total is " + exam.total());
System.out.println("avg is " + exam.avg());
}
}
