04. 스택
스택 개요
- Stack은 한쪽으로 들어가서 한쪽으로 나오는 자료구조
- PUSH(데이터 삽입), POP(데이터 삭제) 등의 연산
스택의 연산 과정(배열)
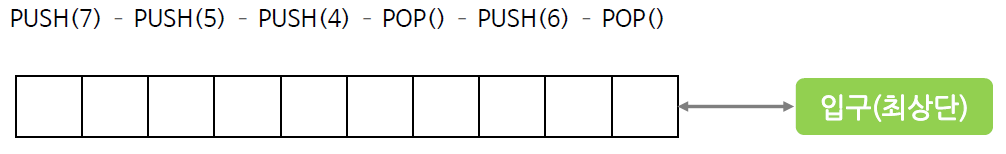
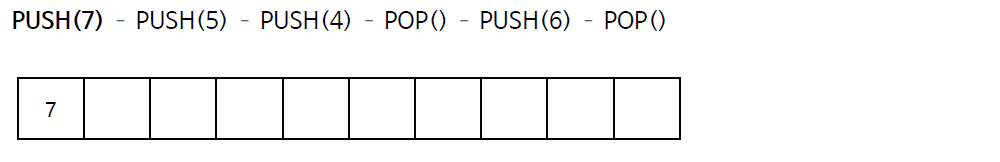
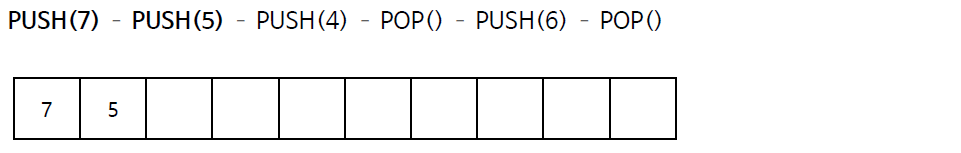
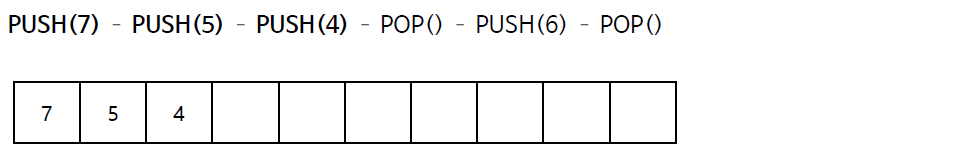
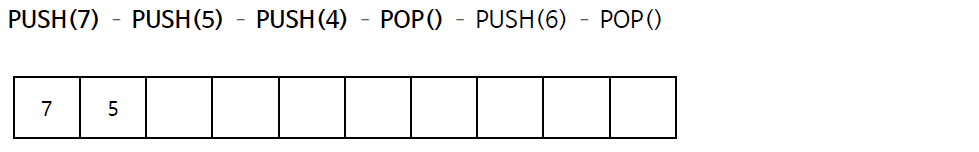
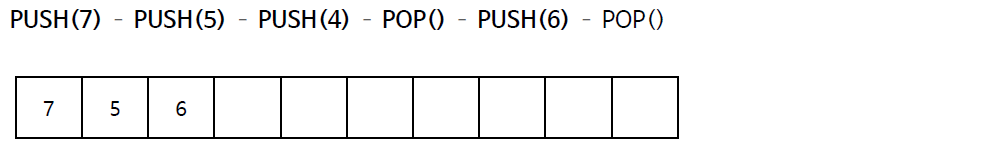
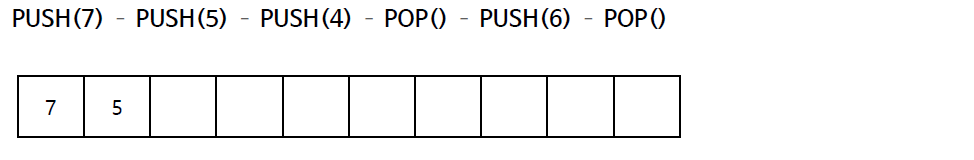
스택의 구현 (배열)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SIZE 10000
#define INF 99999999
int stack[SIZE];
int top = -1; // 스택의 입구(최상단) 의미
void push(int data) {
if (top == SIZE - 1) {
printf("Stack overflow");
return;
}
stack[++top] = data;
}
int pop() {
if (top == -1) {
printf("Stack underflow");
return -INF;
}
return stack[top--];
}
void show() {
printf("=== 스택의 최상단 ===\n");
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--) {
printf("%d\n", stack[i]);
}
printf("=== 스택의 최하단 ===\n");
}
int main(void) {
push(7);
push(5);
push(4);
pop();
push(6);
pop();
show();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
메모리를 크게 잡아두어 비효율적, 따라서 연결리스트 사용
스택의 연산과정 - 삽입 (연결 리스트)
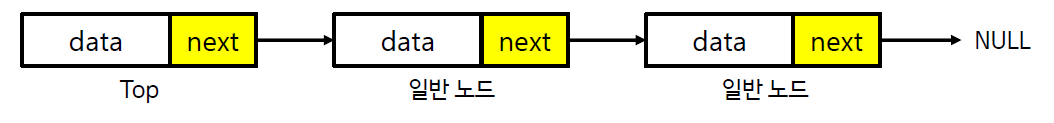
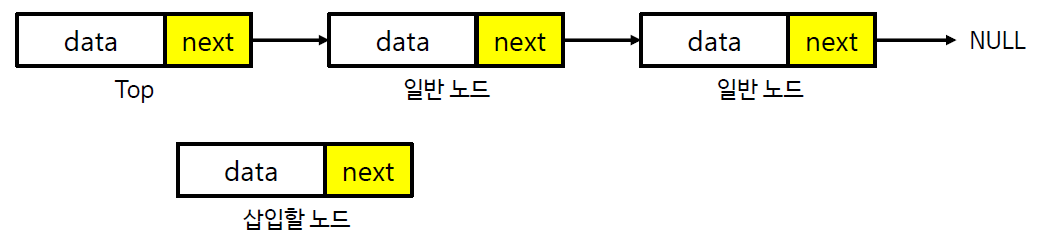
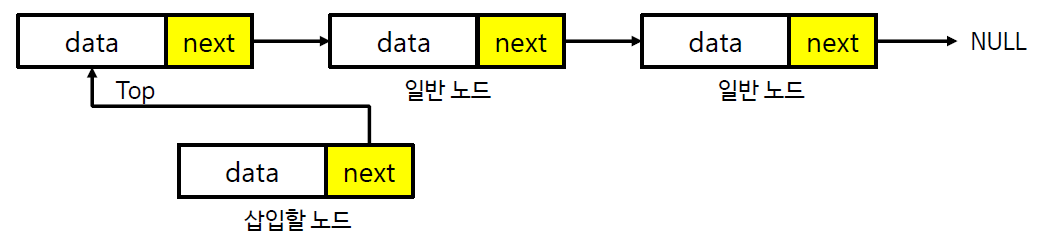
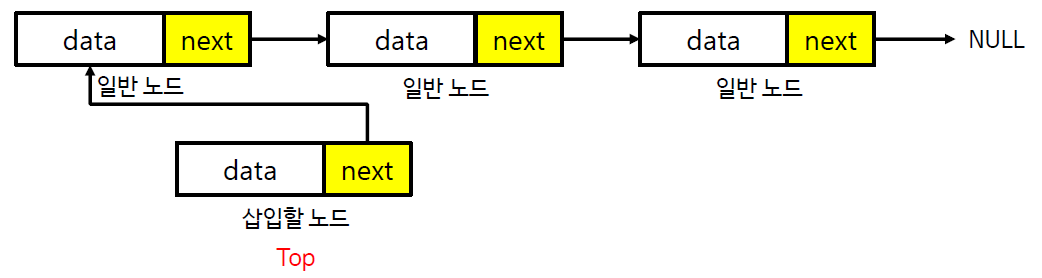
스택의 연산과정 - 추출 (연결 리스트)
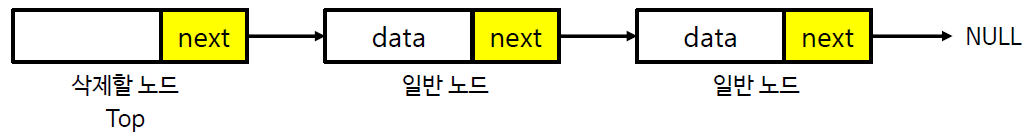
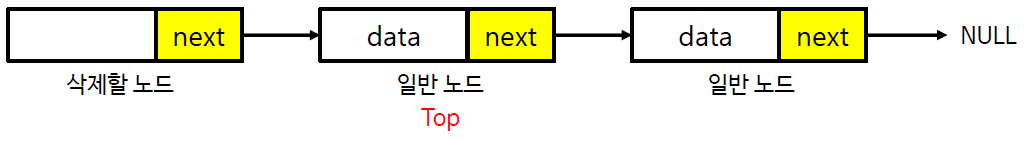
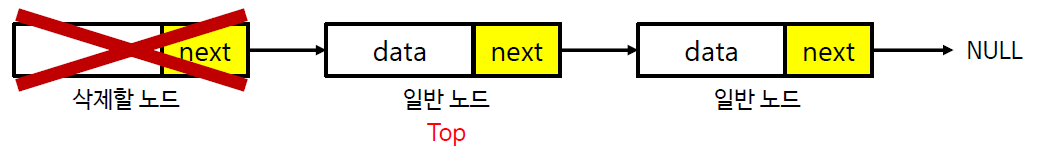
스택의 구현 (연결 리스트)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define INF 99999999
// 노드 정의
typedef struct {
int data;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
// 스택 정의(top)
typedef struct {
Node* top;
} Stack;
// push 함수 정의
void push(Stack* stack, int data) {
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); // 메모리 동적할당
node->data = data; // 노드의 데이터에 삽입하고자하는 데이터 삽입
node->next = stack->top; // 노드의 다음을 현 스택의 탑을 가리킴
stack->top = node; // 현 스택의 탑을 추가하는 노드로 변경
}
int pop(Stack* stack) {
if (stack->top == NULL) {
printf("Stack underflow");
return -INF;
}
Node* node = stack->top; // 스택 최상단(top)을 임시 노드에 담음
int data = node->data; // 임시 노드(top)의 데이터를 data에 저장
stack->top = node->next; // 임시 노드(top)의 다음 노드를 top으로 가리킴
free(node); // 최상단 노드 메모리 해제
return data;
}
void show(Stack* stack) {
Node* cur = stack->top;
printf("===== 스택의 최상단 =====\n");
while (cur != NULL) {
printf("%d\n", cur->data);
cur = cur->next; // cur이 다음 노드로 넘어가며 NULL을 만날 때까지 노드 값들 출력
}
printf("===== 스택의 최하단 =====\n");
}
int main(void) {
Stack s;
s.top = NULL;
push(&s, 7);
push(&s, 5);
push(&s, 4);
pop(&s);
push(&s, 6);
pop(&s);
show(&s);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
