문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7569
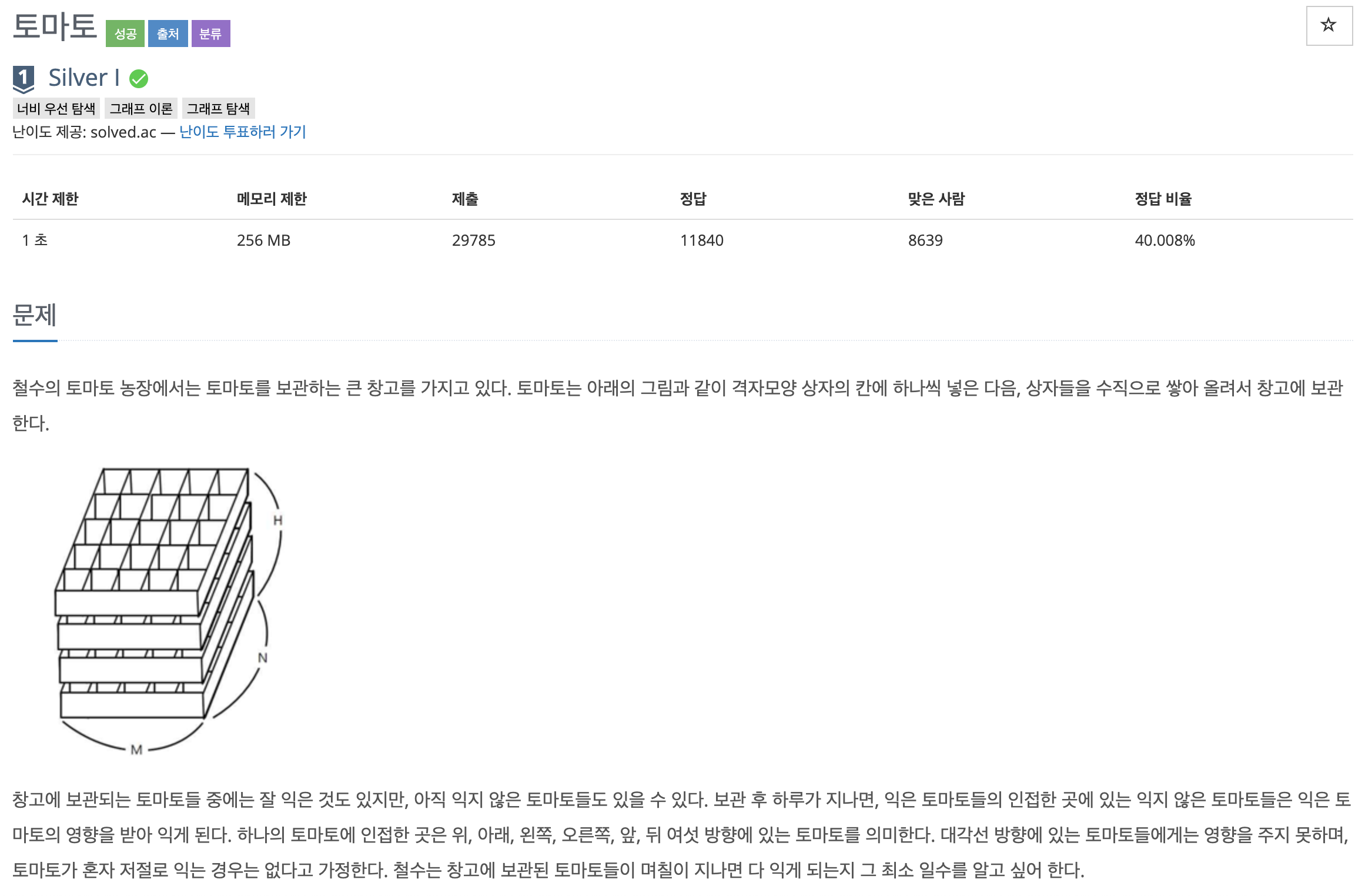
앞의 문제와 거의 동일하다.
다른게 있다면 토마토가 '상하좌우 + 앞뒤'의 영향을 받는다는 것이다.
문제보다는 3차원 배열을 쓰는 것이 거의 처음이라, 이게 더 어려웠던 것 같다.
3차원 배열을 만드는 방법
- numpy 모듈을 import 하기
import numpy
tomato = numpy.arange(m*n*h).reshape(z,x,y) - for문 사용하기
tomato = [[[0] * y for i in range(x)] for j in range(z)]상황과 취향에 맞게 사용하면 될 것 같다.
문제 풀이
- 익은 토마토이면 queue에 (z,x,y,cnt)를 넣어준다.
- 익은 토마토의 '상하좌우앞뒤'가 안익은 토마토일때, 익었다고 체크를 해주고 queue에 (nz,nx,ny,cnt+1)을 넣어준다.
- 전역변수 day에 cnt+1을 저장해준다.
- 모든 배열을 체크하면서 안익은 토마토가 나오면, -1을 리턴한다.
그렇지 않으면 day를 리턴한다.
코드
import sys
#import numpy
from collections import deque
input = sys.stdin.readline
m,n,h = map(int,input().rstrip().rsplit())
queue = deque([])
#tomato = numpy.arange(m*n*h).reshape(h,n,m) #z x y
tomato = [[[0] * m for i in range(n)] for j in range(h)]
day = 0
dx = [-1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0] #상, 하, 좌, 우 , 위, 아래
dy = [0, 0, -1, 1, 0, 0]
dz = [0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 1]
for hei in range(h):
for row in range(n):
temp = input().rstrip().rsplit()
for col,num in enumerate(temp):
tomato[hei][row][col] = num
if num == '1':
queue.append((hei,row,col,0))
while queue:
#익은 토마토의 위치와 cnt를 꺼냄
hei, row, col, cnt = queue.popleft()
for k in range(6):
nx = row + dx[k]
ny = col + dy[k]
nz = hei + dz[k]
if 0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < m and 0 <= nz < h:
# 익은 토마토 상하좌우에 안익은 토마토가 있으면 익게 해주고, queue에 위치와 cnt+1을 넣어줌
if tomato[nz][nx][ny] == '0':
tomato[nz][nx][ny] = '1'
queue.append((nz,nx,ny,cnt+1))
day = cnt + 1
def check(day):
for k in range(h):
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if tomato[k][i][j] == '0':
return -1
return day
print(check(day))
