1. Wrapper Class
1-1. Wrpper Class란?
-
Java는 데이터를 관리하기 위하여 기본 데이터 타입을
지원하지만, 클래스를 통해서 만들어진 객체를 통한 데이터
관리도 가능하다. -
어떤 상황에서는 기본 데이터 타입의 변수를 객체형태로
사용해야 하는 경우가 있는데, 이때 기본형 타입을 객체로
포장할 필요가 있다. -
포장 클래스(Wrapper class)는 특정 기본형 타입을
나타내는 용도로 사용된다.1-2. Wrapper Class
-
초창기 Java언어는 기본 자료형의 연산보다도
Wapper 클래스를 사용한 연산이 더 많이 이루어 졌으나,
Java언어가 발전함에 따라서 기본 자료형과 Wrapper 클래스
간의 연산에 차이가 없어졌다. -
최근의 Java 언어는 Wrapper 클래스와 기본 자료형을
구분하지 않고 사용하기 때문에 객체로서의 특별한
의미가 없어졌다고 볼 수 있다.
1-3. Wrapper 클래스의 객체 만들기
-
각각의 Wrapper 클래스의 객체는 자신과 대응되는 기본
자료형의 데이터를 파라미터로 전달받는다.
int num = 1;
Integer wrapper = new Integer(num);
-
기본 자료형과 Wrapper class간에는 서로 암묵적 형변환이
가능하다.
int num = 1;
Integer wrapper = num;Integer wrapper = new Integer(100); int num = wrapper;
1-4. Wrapper 클래스의 static 데이터
-
모든 Wrapper 클래스는 static 데이터 형태로 Wrapper
클래스에 대응되는 자료형에 대한 최소 값과 최대 값을
가지고 있다int max = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int min = Integer.MIN_VALUE;1-5. 문자열 데이터의 형변환
-
1과 "1"의 차이
-> 기본 자료형과 문자열 데이터간의 연산에서는
기본 자로형 데이터가 문자열로 변환된 후,
문자열간의 연산으로 처리된다.int a = 1;
String b = "1";
System.out.println(a + b); // "11" -
사용자 입력값에 대한 연산
-> 모든 프로그램 플랫폼에서 사용자의 입력값은
String 으로 처리된다
-> 만약, 인터넷 뱅킹에서 2개의 계좌로 송금할 금액을
각각 입력하였을 때, 총 금액을 계산한다면?String money1 = "3000";
String money2 = "5000";
moeny1 + money2 = "30005000"; -
문자열 데이터를 기본 데이터 형으로 변환하기
-> Wrapper 클래스에는 기본 자료형의 모양을 띄고
있는 문자열 데이터를 실제 기본 자료형으로 변환시키는
기능이 포함되어 있다
-> 오늘날의 Java Wrapper클래스의 가장 큰 의미는
바로 이 부분이다.String money1 = "3000";
String money2 = "5000";int m1 = Integer.parseInt(money1);
int m2 = Integer.parseInt(money2);System.out.println(m1 + m2); // 8000
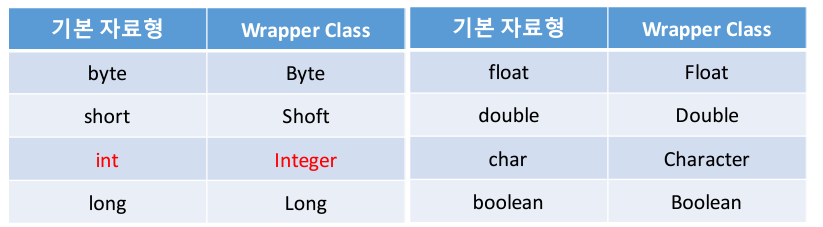
1-6. String을 기본 자료형으로 변환해 주는 기능들
2. Math 클래스
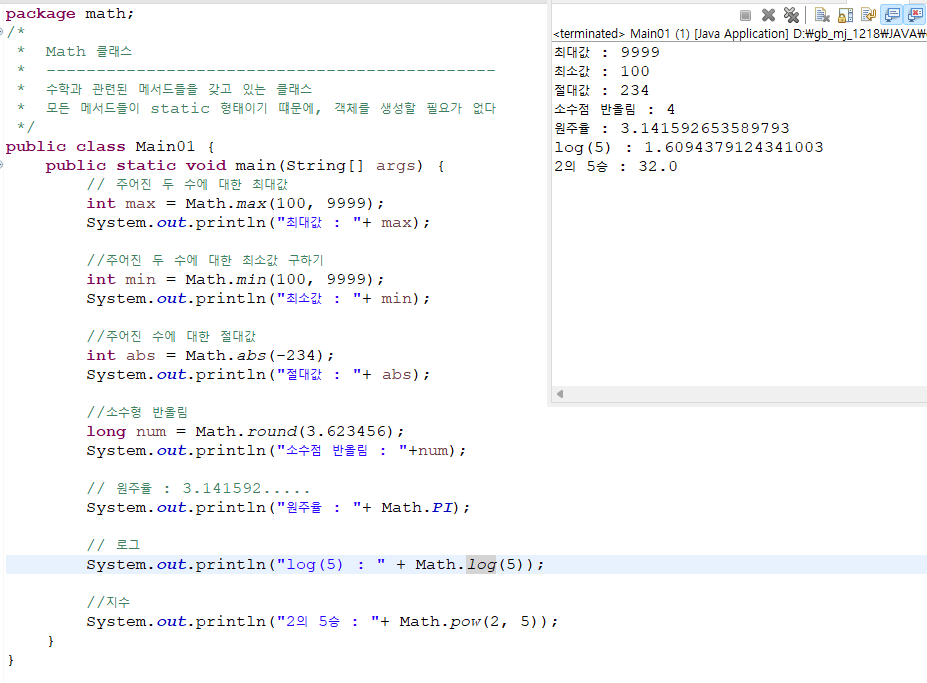
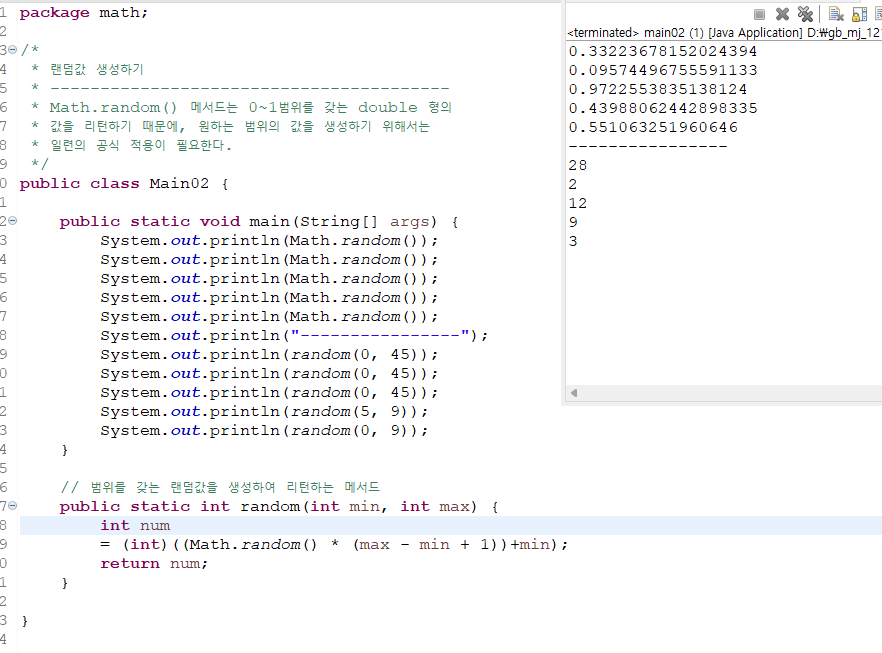
- Math 클래스는 흔히 계산을 하는데 도움이 되는 많은 수의
기본적 수학 함수들을 제공한다 - Math클래스는 Java 표준 클래스 라이브러리 java.lang
패키지에 정의되어있다. - Math클래스의 모든 메서드들은 static 메서드로, 클래스의
객체를 생성하지 않고 그 메서드가 정의된 클래스 이름을
통해 호출될 수 있다.
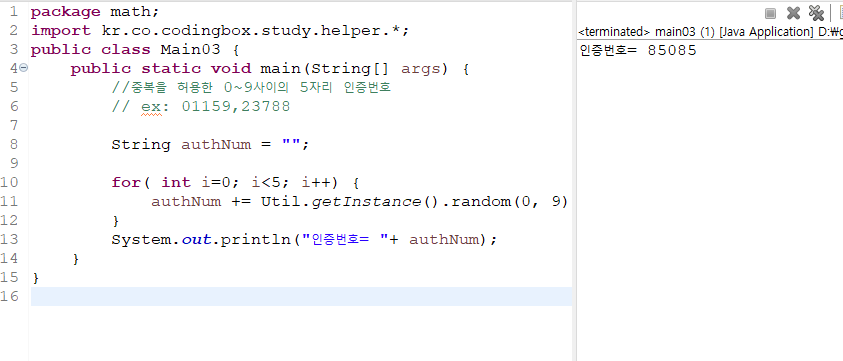
3. String
public class Main01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 객체생성 방법
String str1 ="자바 Programming";
String str2 = new String("Java");
System.out.println("str1 : "+str1);
System.out.println("str2 : "+str2);
// 문자열의 길이를 조회
int str1_len = str1.length();
int str2_len = str2.length();
System.out.println("str1_len : "+ str1_len);
System.out.println("str2_len : "+ str2_len);
System.out.println("=======================");
// 특정 문자열이 처음으로 나타나는 위치를 조회
int str1_pos = str1.indexOf(" ");
int str2_pos = str1.indexOf("a");
System.out.println("str1_pos : " +str1_pos);
System.out.println("str2_pos : " +str2_pos);
System.out.println("=======================");
// A를 B로,변경하기
String new_str1 = str1.replace(" ","-");
String new_str2 = str2.replace("a","A");
System.out.println("new_str1 : " +new_str1);
System.out.println("new_str2 : " +new_str2);
System.out.println("=======================");
//대소문자
String upper = new_str2.toUpperCase();
String lower = new_str2.toLowerCase();
System.out.println(new_str2);
System.out.println("upper : "+ upper);
System.out.println("lower : "+ lower);
System.out.println("=======================");
//문자열 앞뒤 공백 제거
String input = " enho eee zzzz pa a i sun h aha";
String output = input.trim();
System.out.println("input : "+ input);
System.out.println("output : "+output);
String output2 = input.replace(" ","");
System.out.println("output2 : "+output2);
System.out.println("=======================");
//문자열 비교
boolean isSam = str1.equals(str2);
if(isSam) {
System.out.println("같다");
}else {System.out.println("다르다");}
System.out.println("=======================");
//문자열 자르기
// -첫번째 파라미터 : 시작위치
// - 두번째 파라미터 : 끝 위치
String sub_str1 = str1.substring(0,2);
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println("sub_str1 : "+ sub_str1);
// 두번째 파라미터가 없는 경우 끝까지 자른다
String sub_str2 = str1.substring(3);
System.out.println("sub_str2 : "+ sub_str2);
System.out.println("=======================");
//형식에 따른 문자열 출력을 위한 String 메서드 사용
/*
* - %d : 정수
* - %s : 문자
* - %f : float형 소수
* - %3d : 숫자를 3자리로 맞춰서 출력
* - %03d : 자릿수가 맞지않으면 0을 출력
* - %3s : 문자열 3자리로 맞춰서 출력, 맞지않으면 앞에 공백 출력 (%03s와 같은 형식은 사용불가)
*/
int yy = 2024;
int mm = 1;
int dd = 5;
String gender = "남성";
String result = String.format("%d년 %02d월 %02d일 성별: %s", yy, mm, dd, gender);
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println("=======================");
//주어진 글자를 기준으로 잘라내어서 배열로 변환
String src = "C++/java/C#/Javascript/DB";
String[] data = src.split("/");
for(int i = 0; i<data.length; i++) {
System.out.println(data[i]);
}
}}