프로젝트 생성
프로젝트 선택
-
Project: Gradle Project
- Language: Java
- Spring Boot: 2.5.x
-
Project Metadata
- Group: hello - Artifact: thymeleaf-basic - Name: thymeleaf-basic - Package name: hello.thymeleaf - Packaging: Jar - Java: 11 -
Dependencies: Spring Web, Lombok , Thymeleaf
동작 확인 localhost:8000
홈 화면
/resources/static/index.html
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body> <ul>
<li>텍스트 <ul>
<li><a href="/basic/text-basic">텍스트 출력 기본</a></li>
<li><a href="/basic/text-unescaped">텍스트 text, utext</a></li> </ul>
</li>
<li>표준 표현식 구문
<ul>
<li><a href="/basic/variable">변수 - SpringEL</a></li>
<li><a href="/basic/basic-objects?paramData=HelloParam">기본 객체들</
a></li>
<li><a href="/basic/date">유틸리티 객체와 날짜</a></li> <li><a href="/basic/link">링크 URL</a></li>
<li><a href="/basic/literal">리터럴</a></li>
<li><a href="/basic/operation">연산</a></li>
</ul> </li>
<li>속성 값 설정 <ul>
<li><a href="/basic/attribute">속성 값 설정</a></li> </ul>
</li> <li>반복
<ul>
<li><a href="/basic/each">반복</a></li>
</ul> </li>
<li>조건부 평가 <ul>
<li><a href="/basic/condition">조건부 평가</a></li> </ul>
</li>
<li>주석 및 블록
<ul>
<li><a href="/basic/comments">주석</a></li> <li><a href="/basic/block">블록</a></li>
</ul> </li>
<li>자바스크립트 인라인 <ul>
<li><a href="/basic/javascript">자바스크립트 인라인</a></li> </ul>
</li>
<li>템플릿 레이아웃
<ul>
<li><a href="/template/fragment">템플릿 조각</a></li> <li><a href="/template/layout">유연한 레이아웃</a></li> <li><a href="/template/layoutExtend">레이아웃 상속</a></li>
</ul> </li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>2. 타임리프 소개
-
타임리프의 간단한 개념과, 실제로 동작하는 기본 기능 위주로 학습하는 시간을 가져보겠습니다
A. 타임리프 특징
- 서버 사이드 HTML 렌더링(SSR)
- 타임리프는 백엔드 서버에서 HTML을 동적으로 렌더링하는 용도로 사용됩니다
- 네츄럴 템플릿
- 타임리프는 순수 HTML을 최대한 유지하는 특징이 있습니다
- 타임리프로 작성한 파일은 HTML을 유지하기 때문에 웹 브라우저에서 파일을 직접 열어도 내용을 확인할 수 있고, 서버를 통해 뷰 템플릿을 거치면 동적으로 변경된 결과를 확인할 수 있습니다
- JSP를 포함한 다른 뷰 템플릿들은 해당 파일을 열면, 예를 들어서 JSP 파일 자체를 그대로 웹 브라우저에서 열어보면 JSP 소스코드와 HTML이 뒤죽박죽 섞여서 웹 브라우저에서 정상적인 HTML 결과를 확인할 수 없습니다
- 오직 서버를 통해서 JSP가 렌더링 되고 HTML 응답 결과를 받아야 화면을 확인할 수 있습니다
-반면에 타임리프로 작성된 파일은 해당 파일을 그대로 웹 브라우저에서 열어도 정상적인 HTML 결과를 확인할 수 있습니다 - 물론 이 경우 동적으로 결과가 렌더링 되지는 않습니다
- 하지만 HTML 마크업 결과가 어떻게 되는지 파일만 열어도 바로 확인할 수 있습니다
- 이렇게 순수 HTML을 그대로 유지하면서 뷰 템플릿도 사용할 수 있는 타임리프의 특징을 네츄럴 템플릿 (natural templates) 이라 합니다
- 스프링 통합 지원
- 타임리프는 스프링과 자연스럽게 통합되고, 스프링의 다양한 기능을 편리하게 사용할 수 있게 지원한다.
타임리프 기본 기능
-
타임리프 사용 선언
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> -
기본 표현식
-
타임 리프는 다음과 같은 기본 표현식들을 제공합니다
-
간단한 표현
➡️ 변수 표현식: ${...}
➡️ 선택 변수 표현식: *{...}
➡️ 메시지 표현식: #{...}
➡️ 링크 URL 표현식: @{...}
➡️ 조각 표현식: ~{...} -
리터럴
➡️ 텍스트: 'one text', 'Another one!',...
➡️ 숫자: 0, 34, 3.0, 12.3,...
➡️ 불린: true, false
➡️ 널: null
➡️ 리터럴 토큰: one, sometext, main,... -
문자 연산
➡️ 문자합치기: +
➡️ 리터럴 대체: |The name is ${name}| -
산술 연산
➡️ Binary operators: +, -, *, /, %
➡️ Minus sign (unary operator): - -
불린 연산
➡️ Binary operators: and, or
➡️ Boolean negation (unary operator): !, not -
비교와 동등
➡️ 비교: >,<,>=,<=(gt,lt,ge,le)
➡️ 동등 연산: ==, != (eq, ne) -
조건 연산
➡️ If-then: (if) ? (then)
➡️ If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
➡️ Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue) -
특별한 토큰
➡️ No-Operation: _
텍스트 - test,utext
- 타임리프의 가장 기본 기능인 텍스트를 출력하는 기능 먼저 알아보자.
- th:text
- 타임리프는 기본적으로 HTML 테그의 속성에 기능을 정의해서 동작한다. HTML의 콘텐츠(content)에 데이터를 출력할 때는 다음과 같이 th:text 를 사용하면 됩니다
➡️
(2) [[...]]
- HTML 테그의 속성이 아니라 HTML 콘텐츠 영역안에서 직접 데이터를 출력하고 싶을 때는 이와 같이 사용합니다
➡️ 컨텐츠 안에서 직접 출력하기 = [[${data}]]
BasicController
// ..
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/basic")
public class BasicController {
@GetMapping("text-basic")
public String textBasic(Model model){
model.addAttribute("data", "Hello <b>Spring!</b>");
return "basic/text-basic";
}
}/resources/templates/basic/text-basic.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
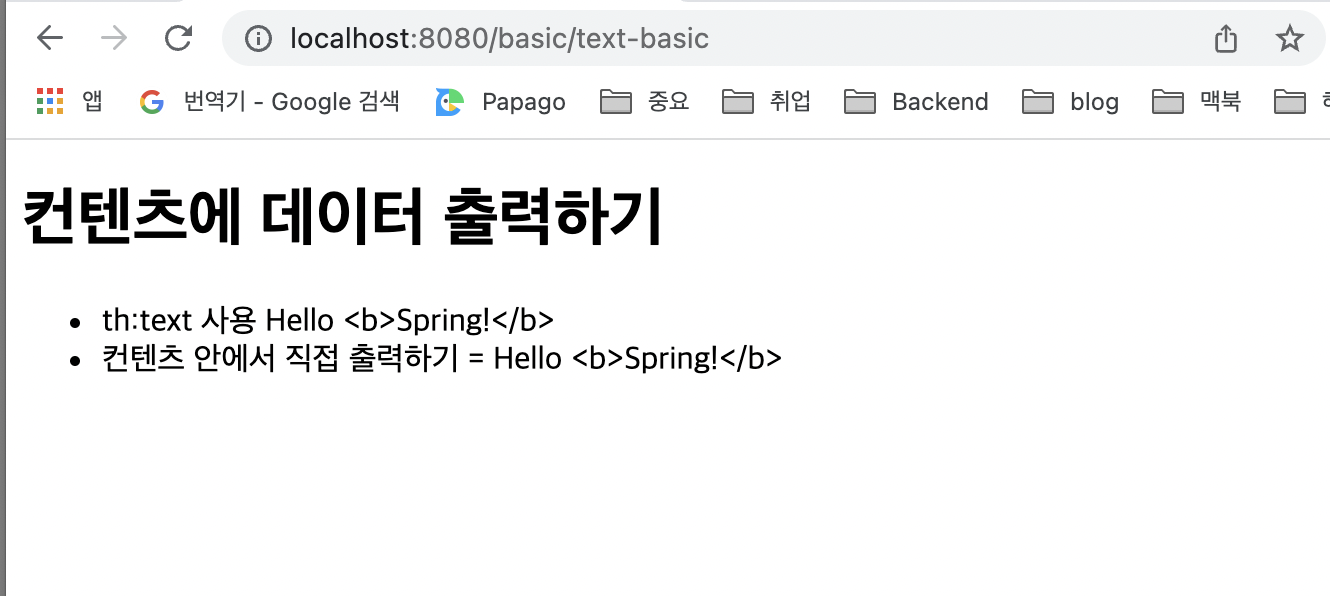
<h1>컨텐츠에 데이터 출력하기</h1>
<ul>
<li>th:text 사용 <span th:text="${data}"></span></li>
<li>컨텐츠 안에서 직접 출력하기 = [[${data}]]</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>실행
A. Escape
- HTML문서는 <, > 같은 특수 문자를 기반으로정의됩니다
- 따라서 뷰 템플릿으로 HTML 화면을 생성할 때는 출력하는 데이터에 이러한 특수 문자가 있는 것을 주의해서 사용해야 합니다
변경 전
"Hello Spring!"
변경 후
"Hello <b>Spring!</b>"상황1)
<b> 태그를 사용해서 Spring!이라는 단어가 진하게 나오도록 해보려는 개발자
실행 결과
웹 브라우저: Hello <b>Spring!</b>
소스 보기: Hello <b>Spring!</b>
개발자가 의도한 것은 <b> 가 있으면 해당 부분을 강조하는 것이 목적이었으나 <b> 태그가 그대로 나온다.
소스보기를 하면 < 부분이 <로 변경된 것을 확인할 수 있습니다
HTML 엔터티
-
HTML 문서는 <, > 같은 특수 문자를 기반으로 정의됩니다
-
웹 브라우저는 <를 HTML 태그의 시작으로 인식합니다
-
HTML 엔터티: <를 테그의 시작이 아니라 문자로 표현할 수 있는 방법
-
이스케이프(escape): HTML에서 사용하는 특수 문자를 HTML 엔터티로 변경하는 것
-
타임리프가 제공하는 th:text , [[...]] 는 기본적으로 이스케이스(escape)를 제공합니다
-
<➡️< -
>➡️> -
기타 수 많은 HTML 엔티티가 있다
참고
- HTML 엔티티와 관련해서 더 자세한 내용은 HTML 엔티티로 검색해보겠습니다
C. Unescape
- 이스케이프 기능을 사용하지 않으려면 어떻게 해야하나요?
- 즉, HTML 엔터티로 변경하지 않고, HTML 태그로 사용하고 싶다면?
- 의도적으로 태그를 강조할 때 unescaped를 사용합니다
타임리프는 다음 두 기능을 제공합니다
- th:text ➡️ th:utext
- [[...]] ➡️ [(...)]
BasicController에 추가
@GetMapping("text-unescaped")
public String textUnescaped(Model model){
model.addAttribute("data", "Hello <b>Spring!</b>");
return "basic/text-unescaped";
}/resources/templates/basic/text-unescape.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
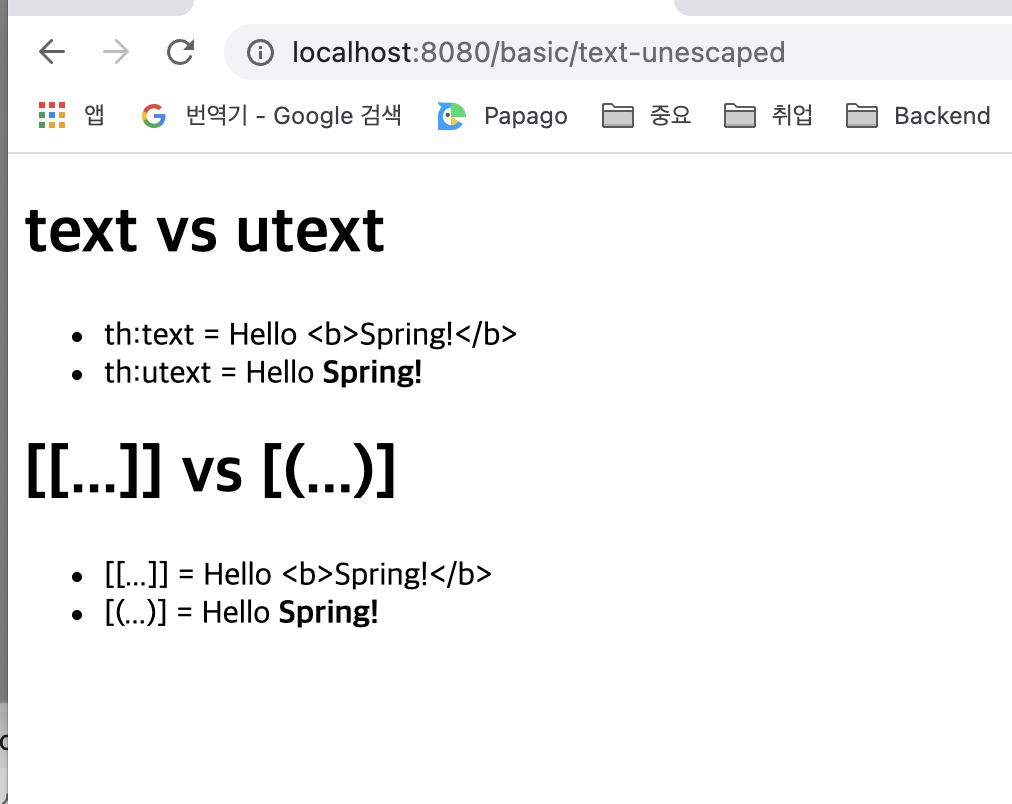
<h1>text vs utext</h1>
<ul>
<li>th:text = <span th:text="${data}"></span></li>
<li>th:utext = <span th:utext="${data}"></span></li>
</ul>
<h1><span th:inline="none">[[...]] vs [(...)]</span></h1>
<ul>
<li><span th:inline="none">[[...]] = </span>[[${data}]]</li>
<li><span th:inline="none">[(...)] = </span>[(${data})]</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>- th:inline="none" : 타임리프는 [[...]] 를 해석하기 때문에, 화면에 [[...]] 글자를 보여줄 수 없습니다
- 이 태그 안에서는 타임리프가 해석하지 말라는 옵션입니다
실행
실행해보면 다음과 같이 정상 수행되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다
- 웹 브라우저: Hello Spring!
- 소스보기: `Hello Spring!
th:utext와 [(...)]을 사용하면 escape 되지 않게 할 수 있습니다
⚠️ 주의!
실제 서비스를 개발하다 보면 escape를 사용하지 않아서 HTML이 정상 렌더링 되지 않는 수 많은 문제가 발생합니다
escape를 기본으로 하고, 꼭 필요한 때만 unescape를 사용하는 것을 권장합니다
변수 - SpringEL
변수 표현식: {...}
- 타임리프에서 변수를 사용할 때 변수 표현식을 사용합니다
- 변수 표현식에서는 SpringEL이라는 스프링이 제공하는 표현식을 사용할 수 있습니다
BasicController에 추가
@GetMapping("/variable")
public String variable(Model model){
User userA = new User("userA", 10);
User userB = new User("userB",20);
List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(userA);
list.add(userB);
Map<String, User> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("userA", userA);
map.put("userB", userB);
model.addAttribute("user", userA);
model.addAttribute("users", list);
model.addAttribute("userMap", map);
return "basic/variable";
}
@Data
static class User{
private String username;
private int age;
public User(String username, int age) {
this.username = username;
this.age = age;
}
}- /resources/templates/basic/variable.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
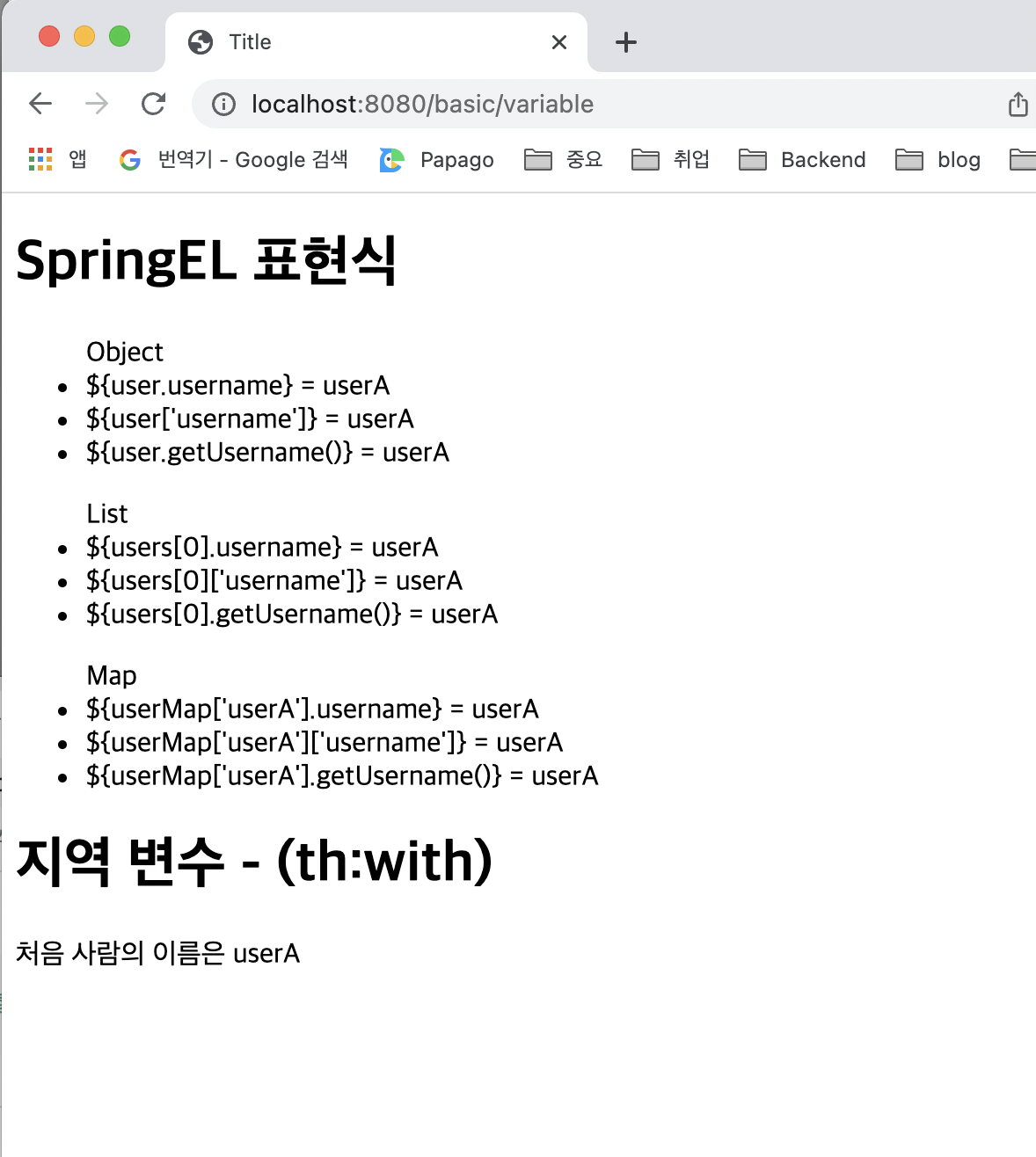
<h1>SpringEL 표현식</h1>
<ul>Object
<li>${user.username} = <span th:text="${user.username}"></span></li>
<li>${user['username']} = <span th:text="${user['username']}"></span></li>
<li>${user.getUsername()} = <span th:text="${user.getUsername()}"></span></
li>
</ul>
<ul>List
<li>${users[0].username} = <span th:text="${users[0].username}"></span></li>
<li>${users[0]['username']} = <span th:text="${users[0]['username']}"></span></li>
<li>${users[0].getUsername()} = <span th:text="${users[0].getUsername()}"></span></li>
</ul>
<ul>Map
<li>${userMap['userA'].username} = <span th:text="${userMap['userA'].username}"></span></li>
<li>${userMap['userA']['username']} = <span th:text="${userMap['userA']['username']}"></span></li>
<li>${userMap['userA'].getUsername()} = <span th:text="${userMap['userA'].getUsername()}"></span></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>SpringEL 다양한 표현식 사용
- Object
- user.username: user의 username을 프로퍼티 접근 → user.getUsername()
- user['username'] : 위와 같음 → user.getUsername()
- user.getUsername() : user의 getUsername() 을 직접 호출
- List
- users[0].username : List에서 첫 번째 회원을 찾고 username 프로퍼티 접근 → list.get(0).getUsername()
- users[0]['username'] : 위와 같음
- users[0].getUsername() : List에서 첫 번째 회원을 찾고 메서드 직접 호출
- Map
- userMap['userA'].username : Map에서 userA를 찾고, username 프로퍼티 접근 → map.get("userA").getUsername()
- userMap['userA']['username'] : 위와 같음
- userMap['userA'].getUsername() : Map에서 userA를 찾고 메서드 직접 호출
실행
B. 지역 변수 선언
- th:with 를 사용하면 지역 변수를 선언해서 사용할 수 있습니다
- 지역 변수는 선언한 테그 안에서만 사용할 수 있습니다
/resources/templates/basic/variable.html에 추가
<h1>지역 변수 - (th:with)</h1>
<div th:with="first=${users[0]}">
<p>처음 사람의 이름은 <span th:text="${first.username}"></span></p>
</div>실행 결과
5. 기본 객체들
타임 리프는 기본 객체들을 제공합니다
- ${#request}
- ${#response}
- ${#session}
- ${#servletContext}
- ${#locale}
그런데 #request 는 HttpServletRequest 객체가 그대로 제공되기 때문에 데이터를 조회하려면 request.getParameter("data") 처럼 불편하게 접근해야 합니다
편의 객체
이런 점들을 해결하기 위해 편의 객체도 제공합니다
- HTTP 요청 파라미터 접근:
param
➡️ 예)${param.paramData} - HTTP 세션 접근:
session
➡️ 예)${session.sessionData} - 스프링 빈 접근:
@
예)${@helloBean.hello('Spring!')}
BasicController에 추가
@GetMapping("/basic-objects")
public String basicObjects(HttpSession session){
session.setAttribute("sessionData", "Hello Session");
return "basic/basic-objects";
}
@Component("helloBean")
static class HeeloBean{
public String hello(String data){
return "Hello " + data;
}
}/resources/templates/basic/basic-objects.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
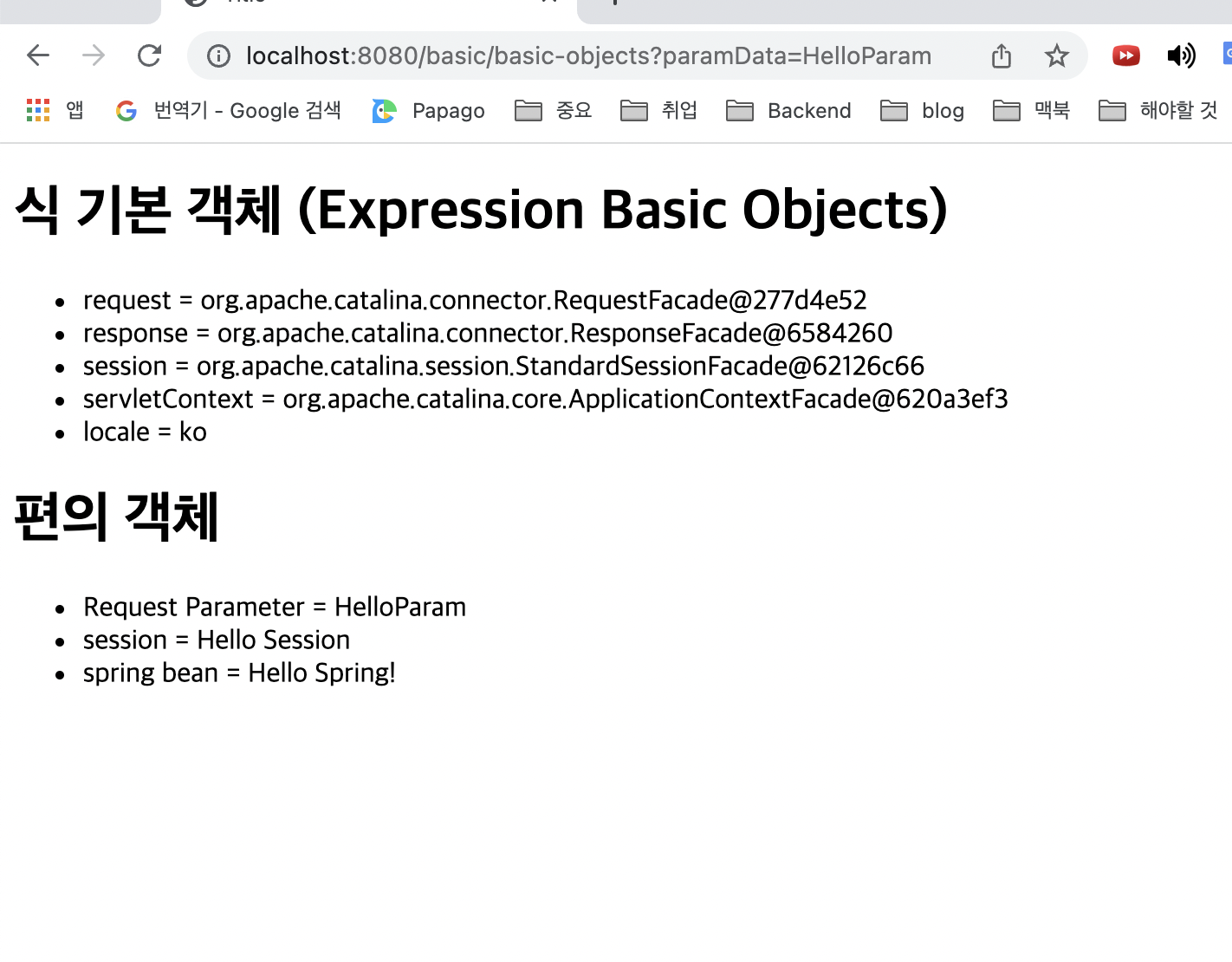
<h1>식 기본 객체 (Expression Basic Objects)</h1>
<ul>
<li>request = <span th:text="${#request}"></span></li>
<li>response = <span th:text="${#response}"></span></li>
<li>session = <span th:text="${#session}"></span></li>
<li>servletContext = <span th:text="${#servletContext}"></span></li>
<li>locale = <span th:text="${#locale}"></span></li>
</ul>
<h1>편의 객체</h1>
<ul>
<li>Request Parameter = <span th:text="${param.paramData}"></span></li>
<li>session = <span th:text="${session.sessionData}"></span></li>
<li>spring bean = <span th:text="${@helloBean.hello('Spring!')}"></span></
li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>실행
6. 유틸리티 객체와 날짜
타임리프는 문자, 숫자, 날짜, URI등을 편리하게 다루는 다양한 유틸리티 객체들을 제공합니다
타임리프 유틸리티 객체들
- #message : 메시지, 국제화 처리
- #uris : URI 이스케이프 지원
- #dates : java.util.Date 서식 지원
- #calendars : java.util.Calendar 서식 지원
- #temporals : 자바8 날짜 서식 지원
- #numbers : 숫자 서식 지원
- #strings : 문자 관련 편의 기능
- #objects : 객체 관련 기능 제공
- #bools : boolean 관련 기능 제공
- #arrays : 배열 관련 기능 제공
- #lists , #sets , #maps : 컬렉션 관련 기능 제공
- #ids : 아이디 처리 관련 기능 제공, 뒤에서 설명
타임리프 유틸리티 객체
유틸리티 객체 예시
- https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html#appendix-b-expression- utility-objects
💡 참고
이런 유틸리티 객체들은 대략 이런 것이 있다 알아두고, 필요할 때 찾아서 사용하면 된다고 합니다
A. 자바8 날짜
- 타임리프에서 자바8 날짜인 LocalDate, LocalDateTime, Instant 를 사용하려면 추가 라이브러리가 필요합니다
- 스프링 부트 타임리프를 사용하면 해당 라이브러리가 자동으로 추가되고 통합됩니다
타임리프 자바8 날짜 지원 라이브러리
thymeleaf-exttras-java8time
자바8 날짜용 유틸리티 객체
#temporals
사용 예시
<span th:text="${#temporals.format(localDateTime, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}"></
span>BasicController에 추가
@GetMapping("/date")
public String data(Model model){
model.addAttribute("localDateTime", LocalDateTime.now());
return "basic/date";
}/resources/templates/basic/date.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
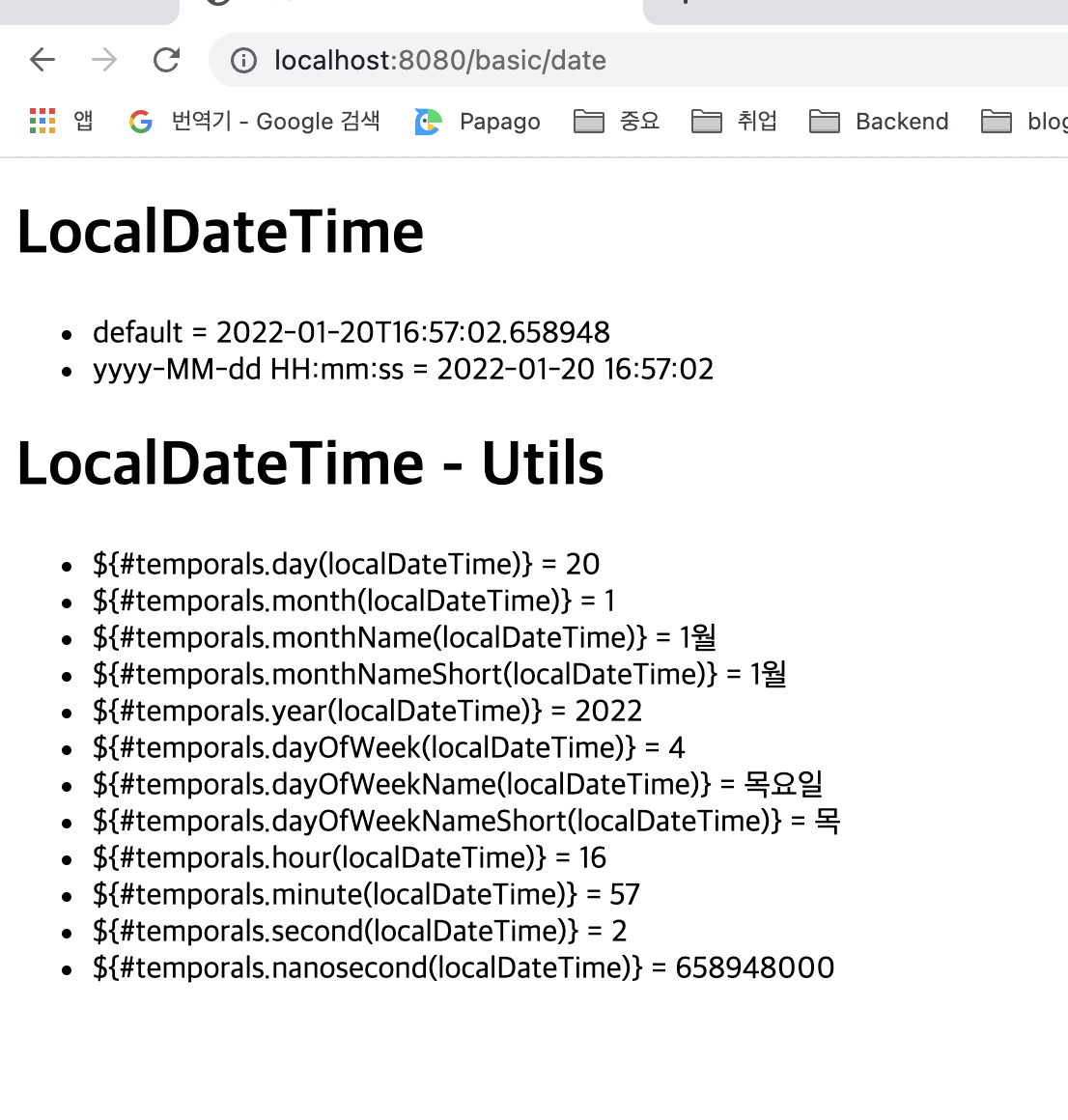
<h1>LocalDateTime</h1>
<ul>
<li>default = <span th:text="${localDateTime}"></span></li>
<li>yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss = <span th:text="${#temporals.format(localDateTime, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}"></span></li>
</ul>
<h1>LocalDateTime - Utils</h1>
<ul>
<li>${#temporals.day(localDateTime)} = <span th:text="${#temporals.day(localDateTime)}"></span></li>
<li>${#temporals.month(localDateTime)} = <span th:text="${#temporals.month(localDateTime)}"></span></li>
<li>${#temporals.monthName(localDateTime)} = <span th:text="${#temporals.monthName(localDateTime)}"></span></li>
<li>${#temporals.monthNameShort(localDateTime)} = <span th:text="${#temporals.monthNameShort(localDateTime)}"></span></li>
<li>${#temporals.year(localDateTime)} = <span th:text="${#temporals.year(localDateTime)}"></span></li>
<li>${#temporals.dayOfWeek(localDateTime)} = <span th:text="${#temporals.dayOfWeek(localDateTime)}"></span></li>
<li>${#temporals.dayOfWeekName(localDateTime)} = <span th:text="${#temporals.dayOfWeekName(localDateTime)}"></span></li>
<li>${#temporals.dayOfWeekNameShort(localDateTime)} = <span th:text="${#temporals.dayOfWeekNameShort(localDateTime)}"></span></li>
<li>${#temporals.hour(localDateTime)} = <span th:text="${#temporals.hour(localDateTime)}"></span></li>
<li>${#temporals.minute(localDateTime)} = <span th:text="${#temporals.minute(localDateTime)}"></span></li>
<li>${#temporals.second(localDateTime)} = <span th:text="${#temporals.second(localDateTime)}"></span></li>
<li>${#temporals.nanosecond(localDateTime)} = <span th:text="${#temporals.nanosecond(localDateTime)}"></span></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>실행 결과
URL 링크
- 타임리프에서 URL을 생성할 때는 @{...} 문법을 사용하면 된다고 합니다
BasicController에 추가
@GetMapping("link")
public String link(Model model){
model.addAttribute("param1", "data1");
model.addAttribute("param2", "data2");
return "basic/link";
}/resources/templates/basic/link.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
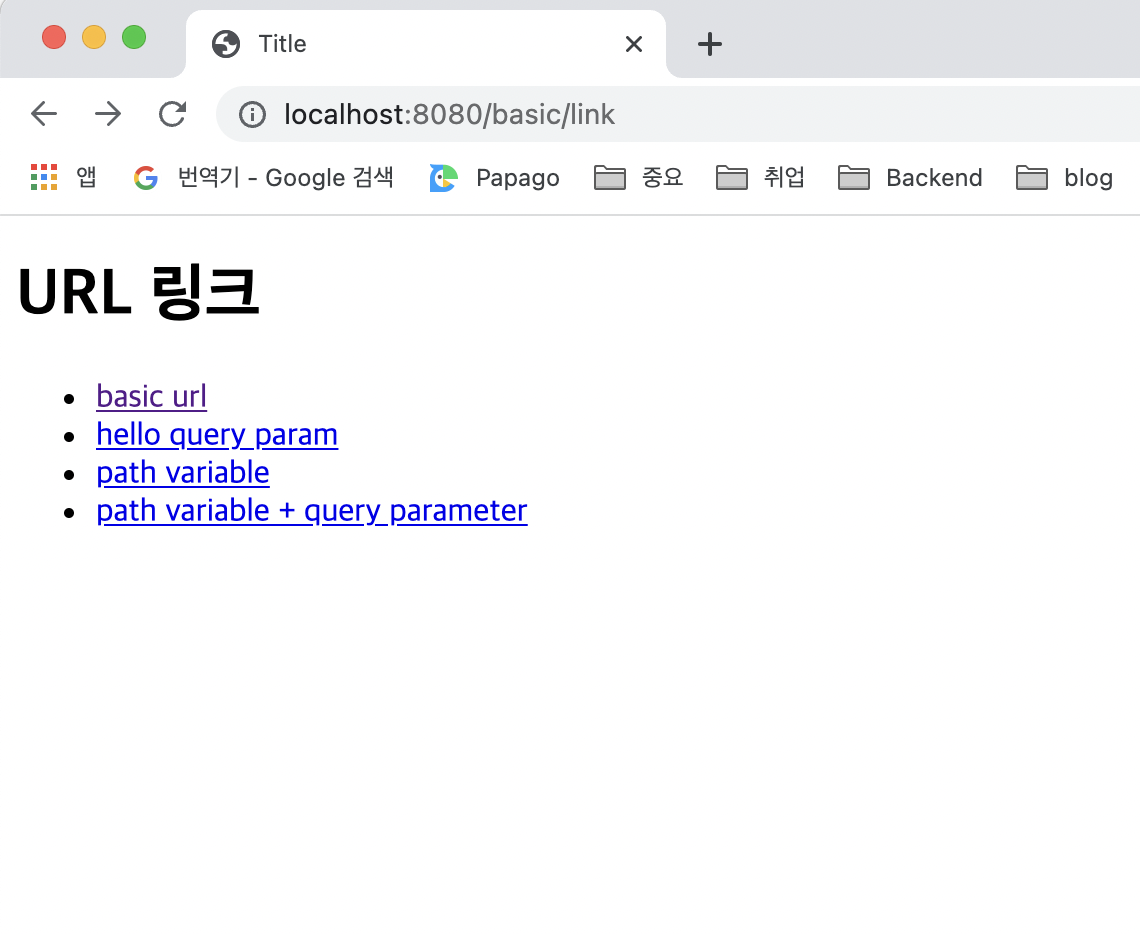
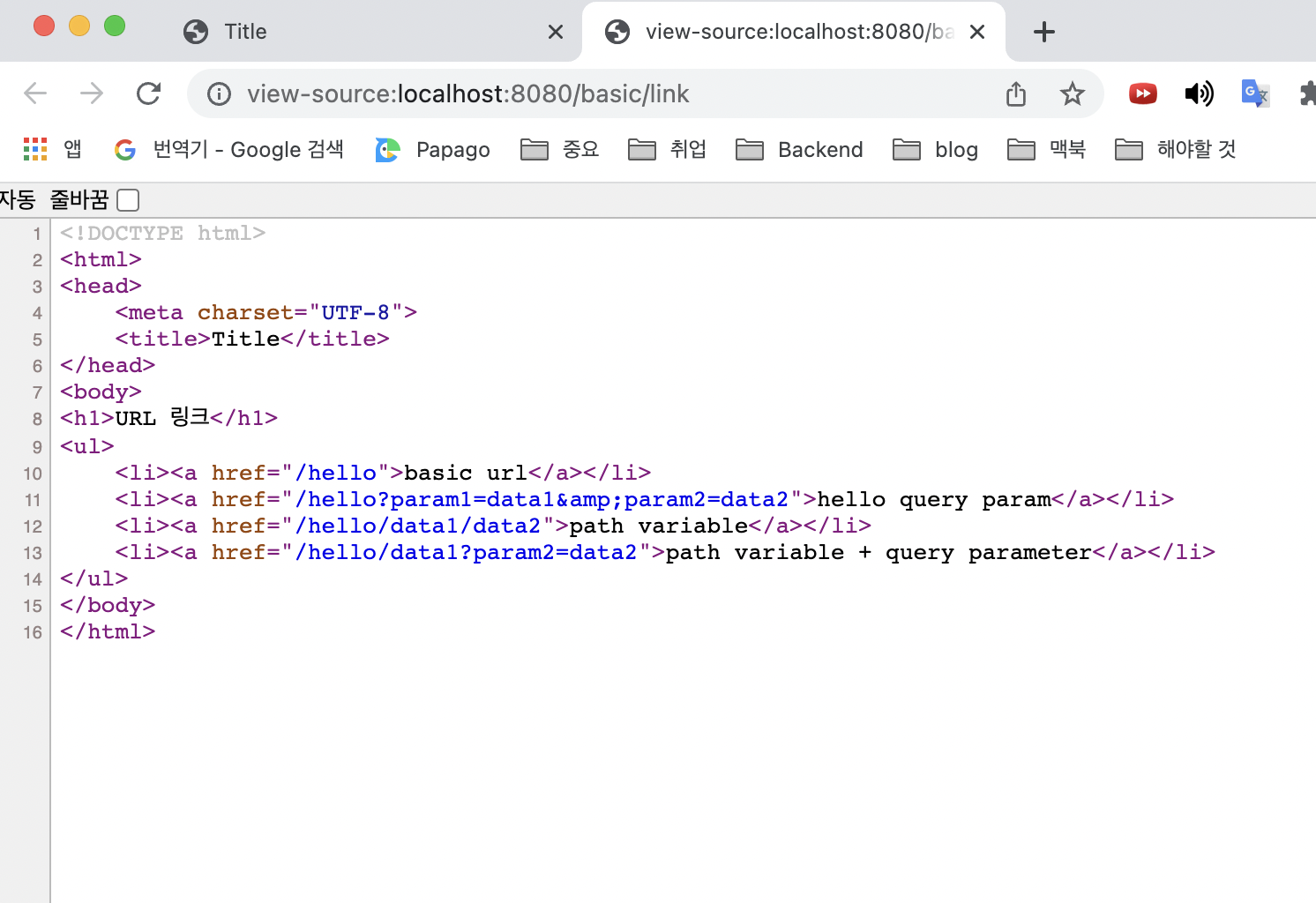
<h1>URL 링크</h1>
<ul>
<li><a th:href="@{/hello}">basic url</a></li>
<li><a th:href="@{/hello(param1=${param1}, param2=${param2})}">hello query param</a></li>
<li><a th:href="@{/hello/{param1}/{param2}(param1=${param1}, param2=${param2})}">path variable</a></li>
<li><a th:href="@{/hello/{param1}(param1=${param1}, param2=${param2})}">path variable + query parameter</a></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>단순한 URL
-
@{/hello} → /hello
쿼리 파라미터
-
@{/hello(param1={param2})}
➡️ http://localhost:8080/hello?param1=data1¶m2=data2
➡️ ()에 있는 부분은 쿼리 파라미터로 처리됩니다경로 변수
-
@{/hello/{param1}/{param2}(param1={param2})}
➡️ http://localhost:8080/hello/data1/data2
➡️ URL 경로상에 변수가 있으면 () 부분은 경로 변수로 처리된다.
경로 변수 + 쿼리 파라미터
- @{/hello/{param1}(param1={param2})}
➡️ http://localhost:8080/hello/data1?param2=data2
➡️ 경로 변수와 쿼리 파라미터를 함께 사용할 수 있다고 합니다
실행 결과
상대경로, 절대경로, 프로토콜 기준을 표현할 수도 있습니다
- /hello: 절대경로
- hello : 상대 경로
💡 참고
https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html#link-urls
리터럴
리터럴은 소스 코드 상에 고정된 값을 말하는 용어입니다
String a = "hello"
int a = 10 * 20
예를 들어 다음 코드에서 "Hello" 는 문자 리터럴, 10 , 20 는 숫자 리터럴입니다
💡 참고
이 내용이 쉬워 보이지만 처음 타임리프를 사용하면 많이 실수하니 잘 보아두어야 한다고 합니다
A. 타임리프에 있는 리터럴
- 문자: 'hello'
- 숫자: 10
- 불린: true , false
- null: null
B. 문자 리터럴
- 타임리프에서 문자 리터럴은 항상 `(작은 따옴표)로 감싸야 합니다
- 그런데 문자를 항상 `로 감싸는 것은 너무 귀찮은 일입니다
- 공백이 없이 이어진다면 하나의 의미있는 토큰으로 인지해서 작은 따옴표를 생략할 수 있습니다
➡️ 룰: A-Z, a-z, 0-9, [], ., -, _
➡️ 위 예시:<span th:text="hello">
- 공백이 없이 이어진다면 하나의 의미있는 토큰으로 인지해서 작은 따옴표를 생략할 수 있습니다
오류
<span th:text="hello world!"></span>
➡️ 문자 리터럴은 원칙상 ' 로 감싸야 합니다
- 위와 같이 ' 감싸지 않고 중간에 공백이 있으면 하나의 의미있는 토큰으로 인식되지 않는다고 합니다
수정
<span th:text="'hello world!'"></span>
➡️ 이렇게 ' 로 감싸면 정상 동작합니다
BasicController에 추가
@GetMapping("/literal")
public String literal(Model model){
model.addAttribute("data", "String");
return "basic/literal";
}/resources/templates/basic/literal.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
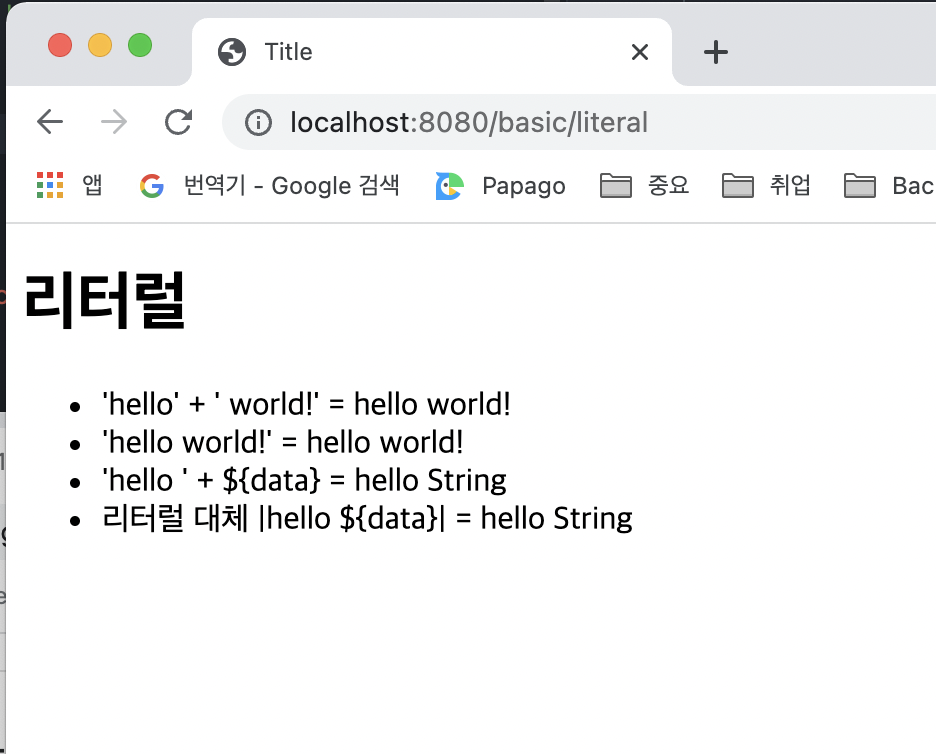
<h1>리터럴</h1>
<ul>
<!--주의! 다음 주석을 풀면 예외가 발생함-->
<!-- <li>"hello world!" = <span th:text="hello world!"></span></li>-->
<li>'hello' + ' world!' = <span th:text="'hello' + ' world!'"></span></li>
<li>'hello world!' = <span th:text="'hello world!'"></span></li>
<li>'hello ' + ${data} = <span th:text="'hello ' + ${data}"></span></li>
<li>리터럴 대체 |hello ${data}| = <span th:text="|hello ${data}|"></span></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>실행 결과
리터럴 대체 (Literal substitutions)
<span th:text="|hello ${data}|">
➡️ 마지막에 리터럴 대체 문법을 사용하면 마치 템플릿을 사용하는 것 처럼 편리하다고 합니다
9. 연산
- 타임리프 연산은 자바와 크게 다르지 않습니다
- HTML 안에서 사용하기 때문에 HTML 엔티티를 사용하는 부분만 주의하면 된다고 합니다
BasicController에 추가
@GetMapping("/operation")
public String operation(Model modeL) {
model.addAttribute("nullData", null);
model.addAtrribute("data", "Spring!");
return "basic/operation";
}/resources/templates/basic/operation.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>산술 연산
<ul>
<li>10 + 2 = <span th:text="10 + 2"></span></li>
<li>10 % 2 == 0 = <span th:text="10 % 2 == 0"></span></li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>비교 연산
<ul>
<li>1 > 10 = <span th:text="1 > 10"></span></li>
<li>1 gt 10 = <span th:text="1 gt 10"></span></li>
<li>1 >= 10 = <span th:text="1 >= 10"></span></li>
<li>1 ge 10 = <span th:text="1 ge 10"></span></li>
<li>1 == 10 = <span th:text="1 == 10"></span></li>
<li>1 != 10 = <span th:text="1 != 10"></span></li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>조건식
<ul>
<li>(10 % 2 == 0)? '짝수':'홀수' = <span th:text="(10 % 2 == 0)? '짝수':'홀수'"></span></li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>Elvis 연산자
<ul>
<li>${data}?: '데이터가 없습니다.' = <span th:text="${data}?: '데이터가 없습니다.'"></span></li>
<li>${nullData}?: '데이터가 없습니다.' = <span th:text="${nullData}?:
'데이터가 없습니다.'"></span></li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>No-Operation
<ul>
<li>${data}?: _ = <span th:text="${data}?: _">데이터가 없습니다.</span></li>
<li>${nullData}?: _ = <span th:text="${nullData}?: _">데이터가 없습니다.</span></li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>-
비교연산 : HTML 엔티티를 사용해야 하는 부분을 주의하자❗️
➡️ > (gt), < (lt), >= (ge), <= (le), ! (not), == (eq), != (neq, ne) -
조건식 : 자바의 조건식과 유사합니다
-
Elvis 연산자 : 조건식의 편의 버전
-
No-Operation : 인 경우 마치 타임리프가 실행되지 않는 것처럼 동작한다.
➡️ 이것을 잘 사용하면 HTML 의 내용 그대로 활용할 수 있다.
➡️ - ${nullData}?: = 데이터가 없습니다. 를 보면 '데이터가 없습니다.' 부분이 그대로 출력됩니다
실행 결과
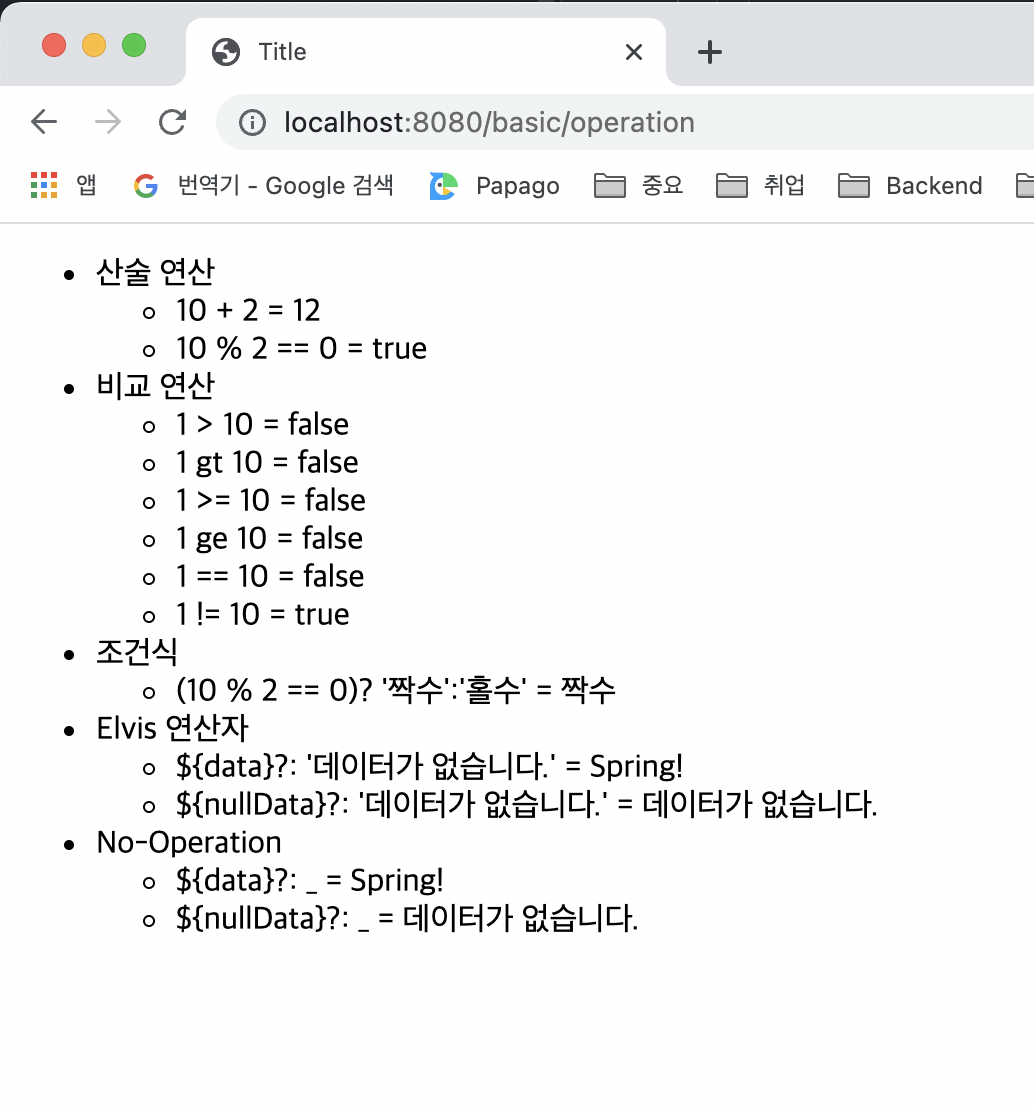
10 속성 값 설정
타임리프 태그 속성(Attribute)
- 타임리프는 주로 HTML 태그에 th:* 속성을 지정하는 방식으로 동작합니다
- th:* 로 속성을 적용하면 기존 속성을 대체합니다
- 기존 속성이 없으면 새로 만듭니다
BasicController에 추가
- 기존 속성이 없으면 새로 만듭니다
@GetMapping("/attribute")
public String attribute(){
return "basic/attribute";
}/resources/templates/basic/attribute.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
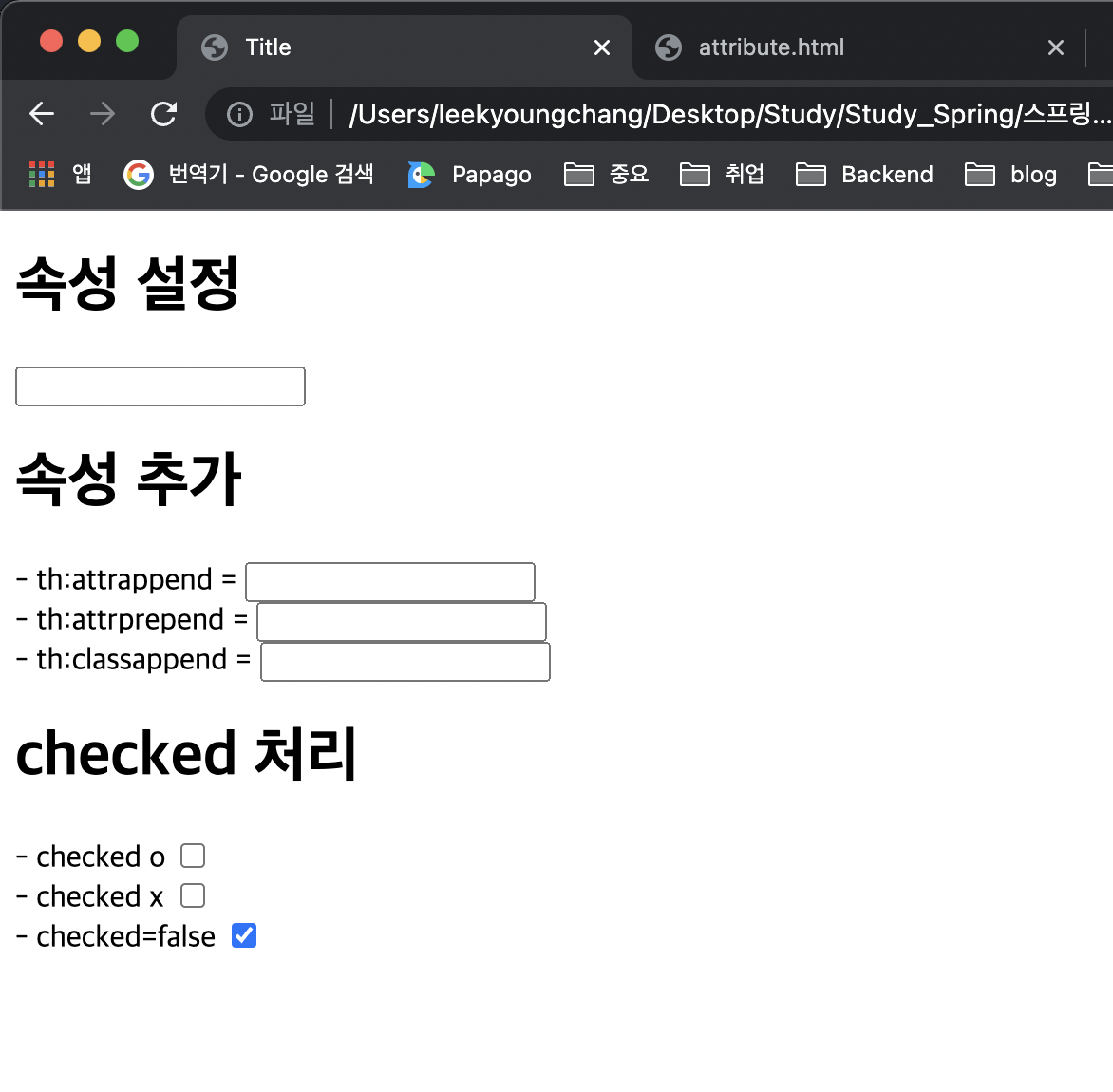
<h1>속성 설정</h1>
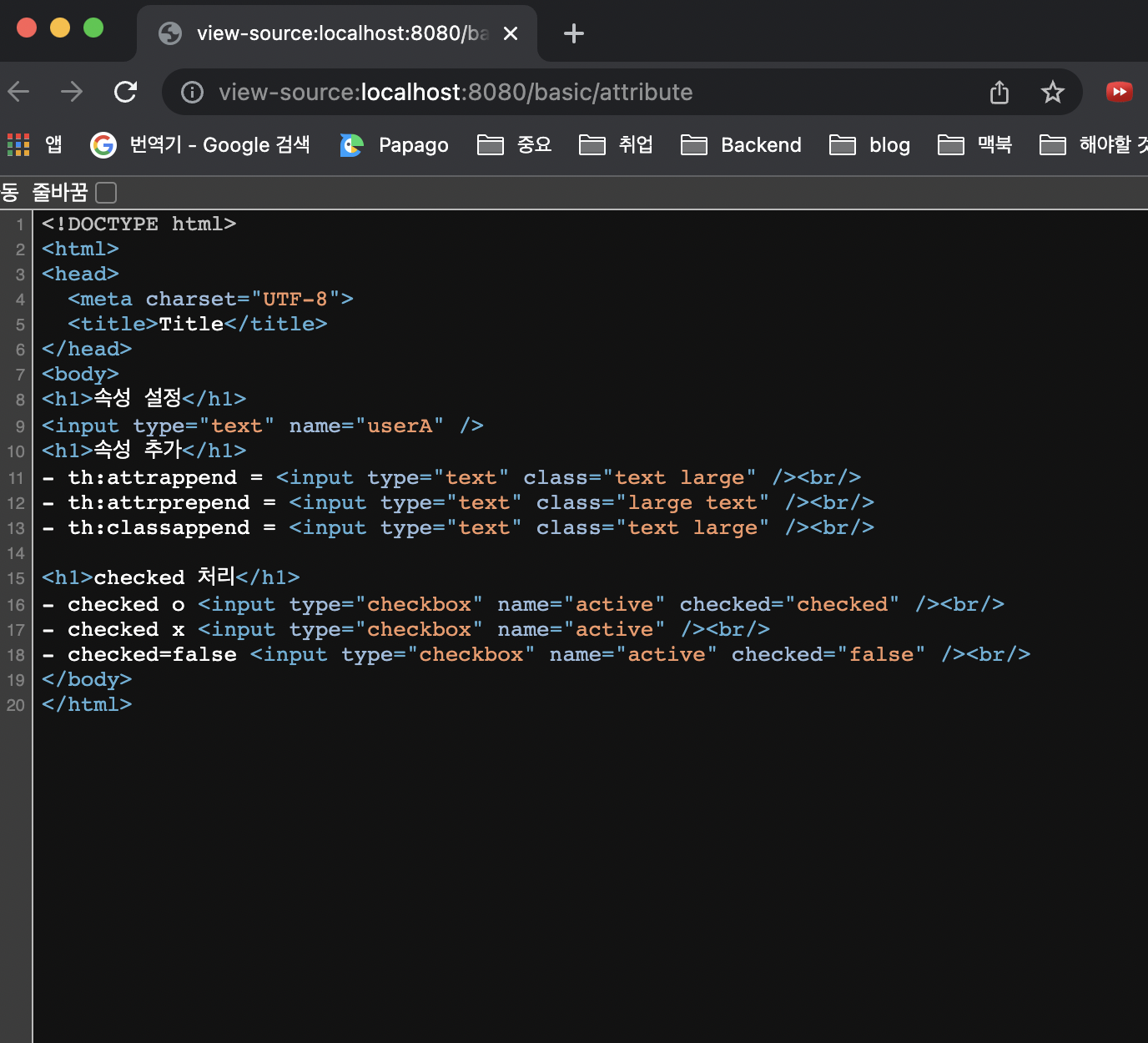
<input type="text" name="mock" th:name="userA" />
<h1>속성 추가</h1>
- th:attrappend = <input type="text" class="text" th:attrappend="class=' large'" /><br/>
- th:attrprepend = <input type="text" class="text" th:attrprepend="class='large '" /><br/>
- th:classappend = <input type="text" class="text" th:classappend="large" /><br/>
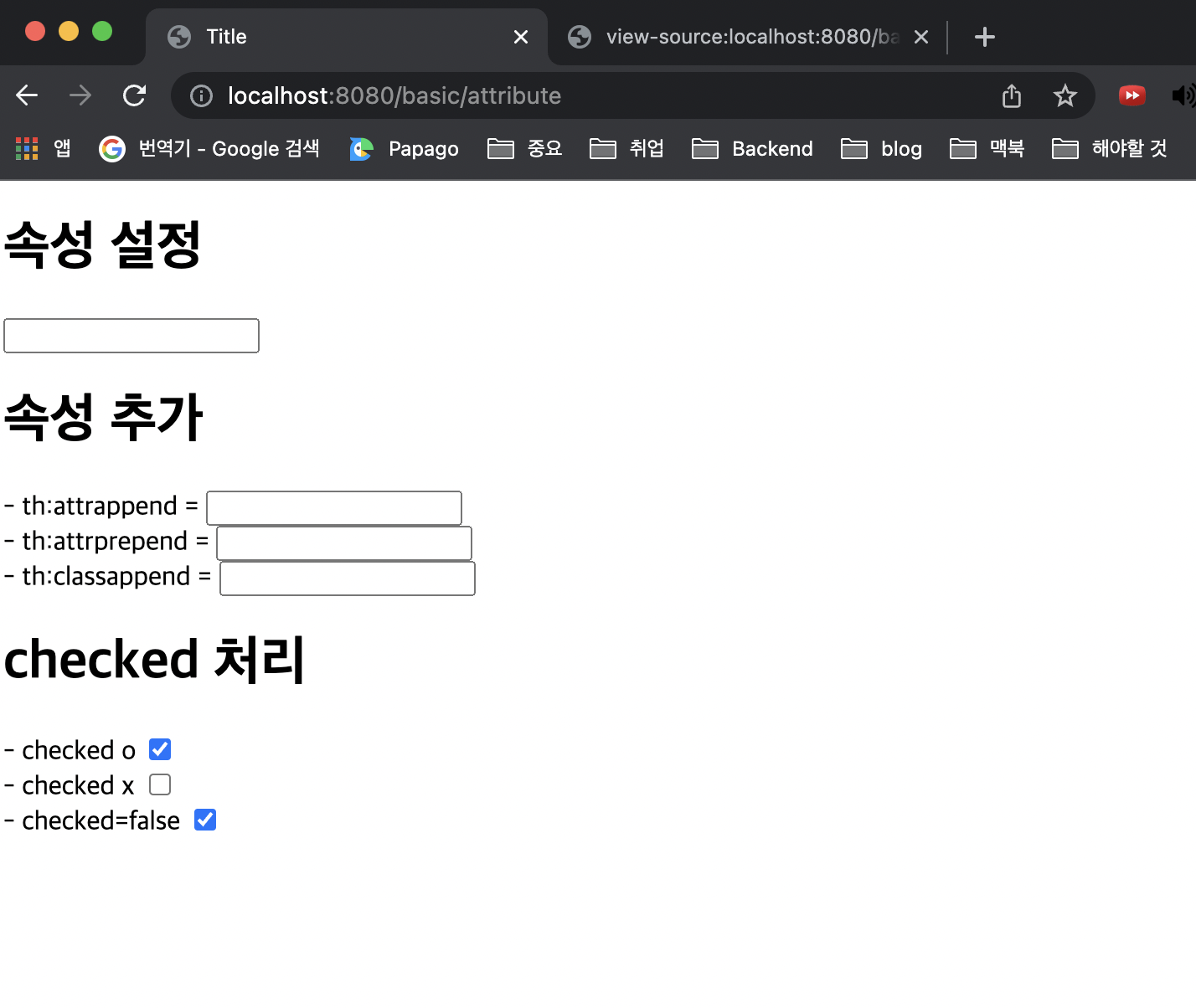
<h1>checked 처리</h1>
- checked o <input type="checkbox" name="active" th:checked="true" /><br/>
- checked x <input type="checkbox" name="active" th:checked="false" /><br/>
- checked=false <input type="checkbox" name="active" checked="false" /><br/>
</body>
</html>속성 설정
th: 속성을 지정하면 타임리프는 기존 속성을 `th:`로 지정한 속성으로 대체합니다
기존 속성이 없다면 새로 만듭니다
<input type="text" name="mock" th:name="userA" />타임리프 렌더링 후
<input type="text" name="userA" />
속성 추가
- th:attrappend : 속성 값의 뒤에 값을 추가합니다
- th:attrprepend : 속성 값의 앞에 값을 추가합니다
- th:classappend : class 속성에 자연스럽게 추가합니다
checked 처리
- HTML에서는
<input type="checkbox" name="active" checked="false" /> - 이 경우에도 checked 속성이 있기 때문에 checked 처리가 되어버립니다
HTML에서 checked 속성은 checked 속성의 값과 상관없이 checked 라는 속성만 있어도 체크가 된다. 이런 부분이 true , false 값을 주로 사용하는 개발자 입장에서는 불편합니다
th:checked="true" 는 서버를 실행하지 않았을 때는 적용되지 않습니다
th:checked="true" : 서버를 실행했을 때 적용됩니다
반복
- 타임리프에서 반복은
th:each를 사용합니다. 추가로 반복에서 사용할 수 있는 여러 상태 값을 지원합니다
BasicControlelr 추가
@GetMapping("/each")
public String each(Model model){
addUsers(model);
return "basic/each";
}
public void addUsers(Model model) {
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new User("UserA", 10));
list.add(new User("UserB", 20));
list.add(new User("UserC", 30));
model.addAttribute("users", list);
}/resources/templates/basic/each.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>기본 테이블</h1>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>username</th>
<th>age</th>
</tr>
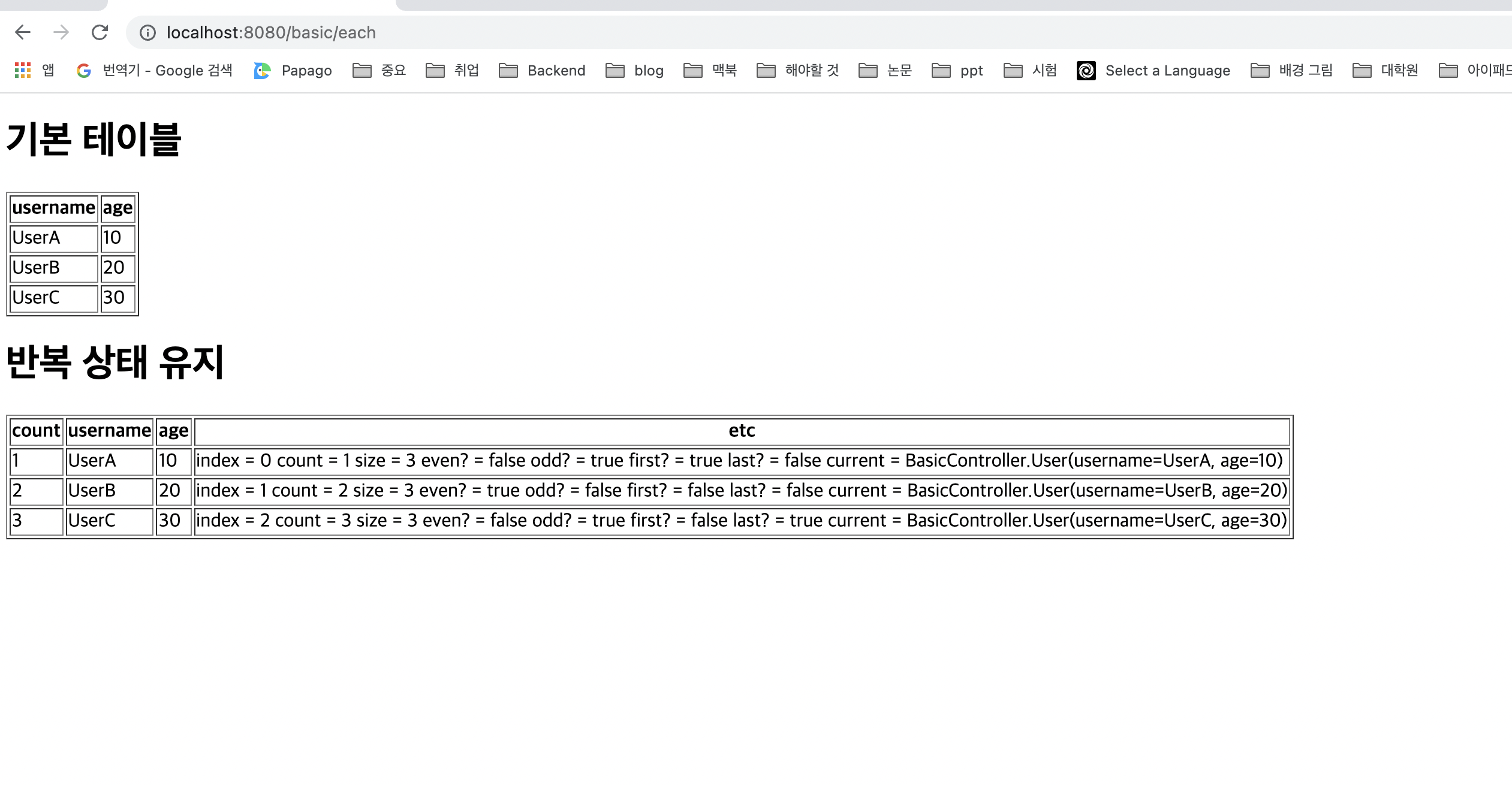
<tr th:each="user : ${users}">
<td th:text="${user.username}">username</td>
<td th:text="${user.age}">0</td>
</tr>
</table>
<h1>반복 상태 유지</h1>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>count</th>
<th>username</th>
<th>age</th>
<th>etc</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="user, userStat : ${users}">
<td th:text="${userStat.count}">username</td>
<td th:text="${user.username}">username</td>
<td th:text="${user.age}">0</td>
<td>
index = <span th:text="${userStat.index}"></span>
count = <span th:text="${userStat.count}"></span>
size = <span th:text="${userStat.size}"></span>
even? = <span th:text="${userStat.even}"></span>
odd? = <span th:text="${userStat.odd}"></span>
first? = <span th:text="${userStat.first}"></span>
last? = <span th:text="${userStat.last}"></span>
current = <span th:text="${userStat.current}"></span>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>반복 기능
<tr th:each="user : ${users}">
➡️ 반복시 오른쪽 컬렉션( ${users} )의 값을 하나씩 꺼내서 왼쪽 변수( user )에 담아서 태그를 반복 실행합니다
➡️ th:each 는 List 뿐만 아니라 배열, java.util.Iterable , java.util.Enumeration 을 구현한 모든 객체를 반복에 사용할 수 있습니다
➡️ Map 도 사용할 수 있는데 이 경우 변수에 담기는 값은 Map.Entry 입니다
반복 상태 유지
<tr th:each="user, userStat : ${users}">
➡️ 반복의 두번째 파라미터를 설정해서 반복의 상태를 확인 할 수 있습니다
➡️ 두번째 파라미터는 생략 가능한데, 생략하면 지정한 변수명 ( user ) + Stat 가 됩니다
- 여기서는 user + Stat = userStat이므로 생략 가능합니다
(usersStat는 불가능)
반복 상태 유지 기능
- index : 0부터 시작하는 값
- count : 1부터 시작하는 값
- size : 전체 사이즈
- even , odd : 홀수, 짝수 여부( boolean )
- first , last :처음, 마지막 여부( boolean )
- current : 현재 객체
실행 결과

조건부 평가
- 타임리프의 조건식
- th:if, th:unless (if의 반대)
BasicController에 추가
@GetMapping("/condition")
public String condition(Model model) {
addUsers(model);
return "basic/condition";
}/resources/templates/basic/condition.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
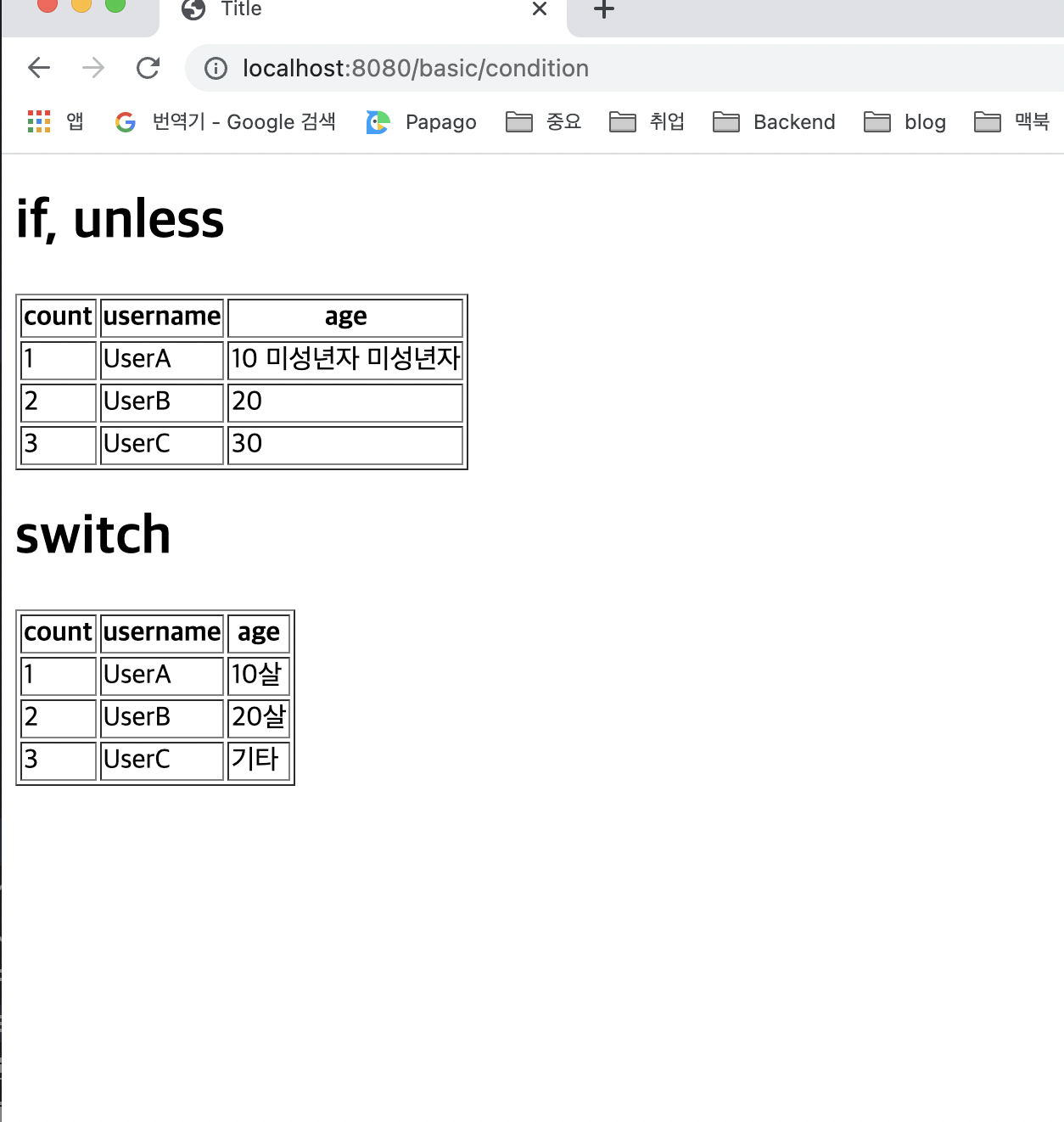
<h1>if, unless</h1>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>count</th>
<th>username</th>
<th>age</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="user, userStat : ${users}">
<td th:text="${userStat.count}">1</td>
<td th:text="${user.username}">username</td>
<td>
<span th:text="${user.age}">0</span>
<span th:text="'미성년자'" th:if="${user.age lt 20}"></span>
<span th:text="'미성년자'" th:unless="${user.age ge 20}"></span>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
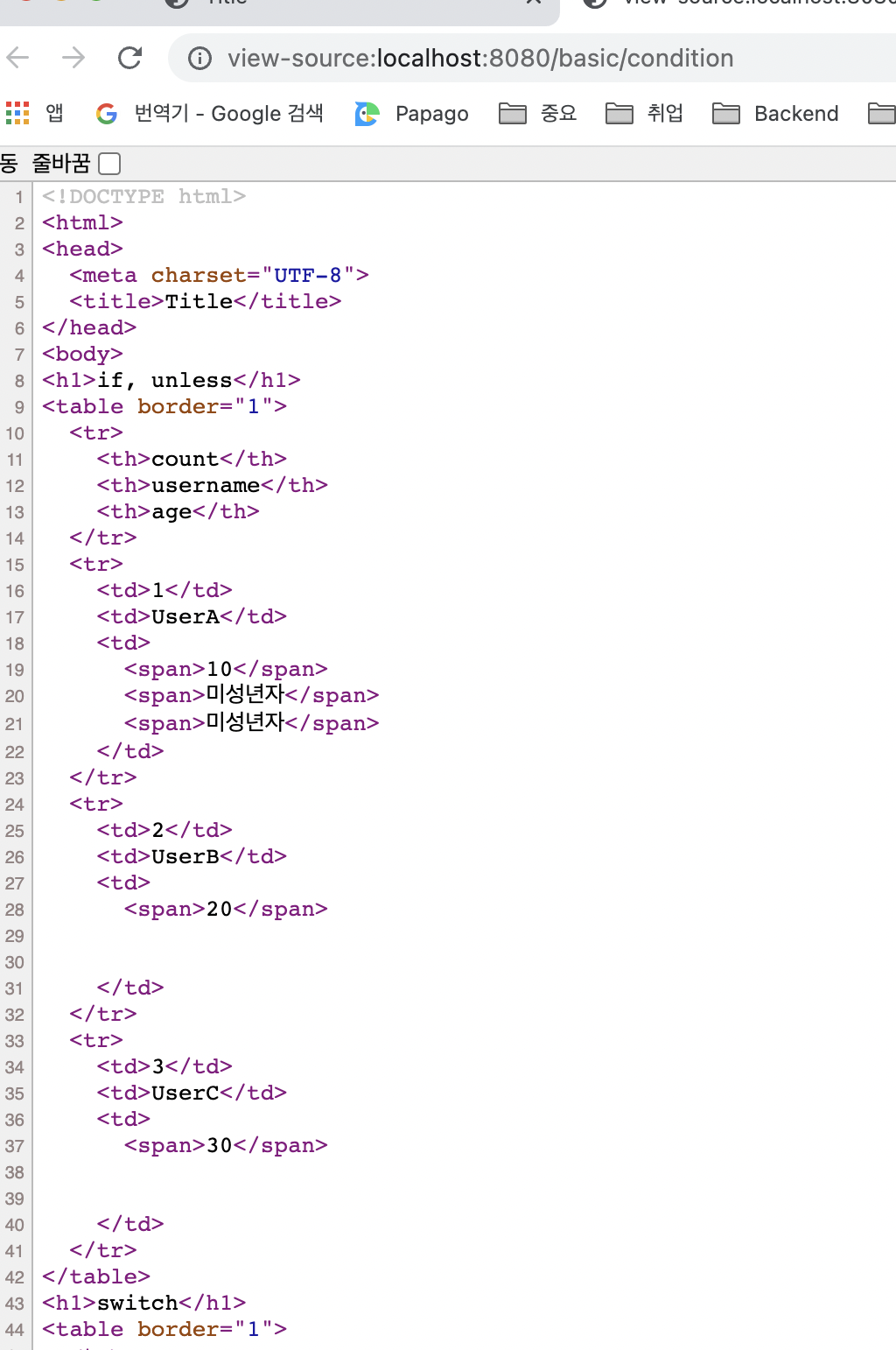
<h1>switch</h1>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>count</th>
<th>username</th>
<th>age</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="user, userStat : ${users}">
<td th:text="${userStat.count}">1</td>
<td th:text="${user.username}">username</td>
<td th:switch="${user.age}">
<span th:case="10">10살</span>
<span th:case="20">20살</span>
<span th:case="*">기타</span>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>if, unless
- 타임리프는 해당 조건이 맞지 않으면 태그 자체를 렌더링하지 않는다고 합니다
- 만약 다음 조건이 false인 경우
<span>...<span>부분 자체가 렌더링 되지 않고 사라집니다
➡️<span th:text="'미성년자'" th:if="${user.age lt 20}"></span>
switch
- th:switch를 통해 기준이 될 변수를 지정합니다
- th:case를 통해 case를 나누면 됩니다
*은 만족하는 조건이 없을 때 사용하는 디폴트입니다
<td th:switch="${user.age}">
<span th:case="10">10살</span>
<span th:case="20">20살</span>
<span th:case="*">기타</span>
</td>실행 결과
주석
BasicController에 추가
GetMapping("/comments")
public String comments(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("data", "Spring!");
return "basic/comments";
}/resources/templates/basic/comments.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>예시</h1>
<span th:text="${data}">html data</span>
<h1>1. 표준 HTML 주석</h1>
<!--
<span th:text="${data}">html data</span>
-->
<h1>2. 타임리프 파서 주석</h1>
<!--/* [[${data}]] */-->
<!--/*-->
<span th:text="${data}">html data</span>
<!--*/-->
<h1>3. 타임리프 프로토타입 주석</h1>
<!--/*/
<span th:text="${data}">html data</span>
/*/-->
</body>
</html>실행 결과
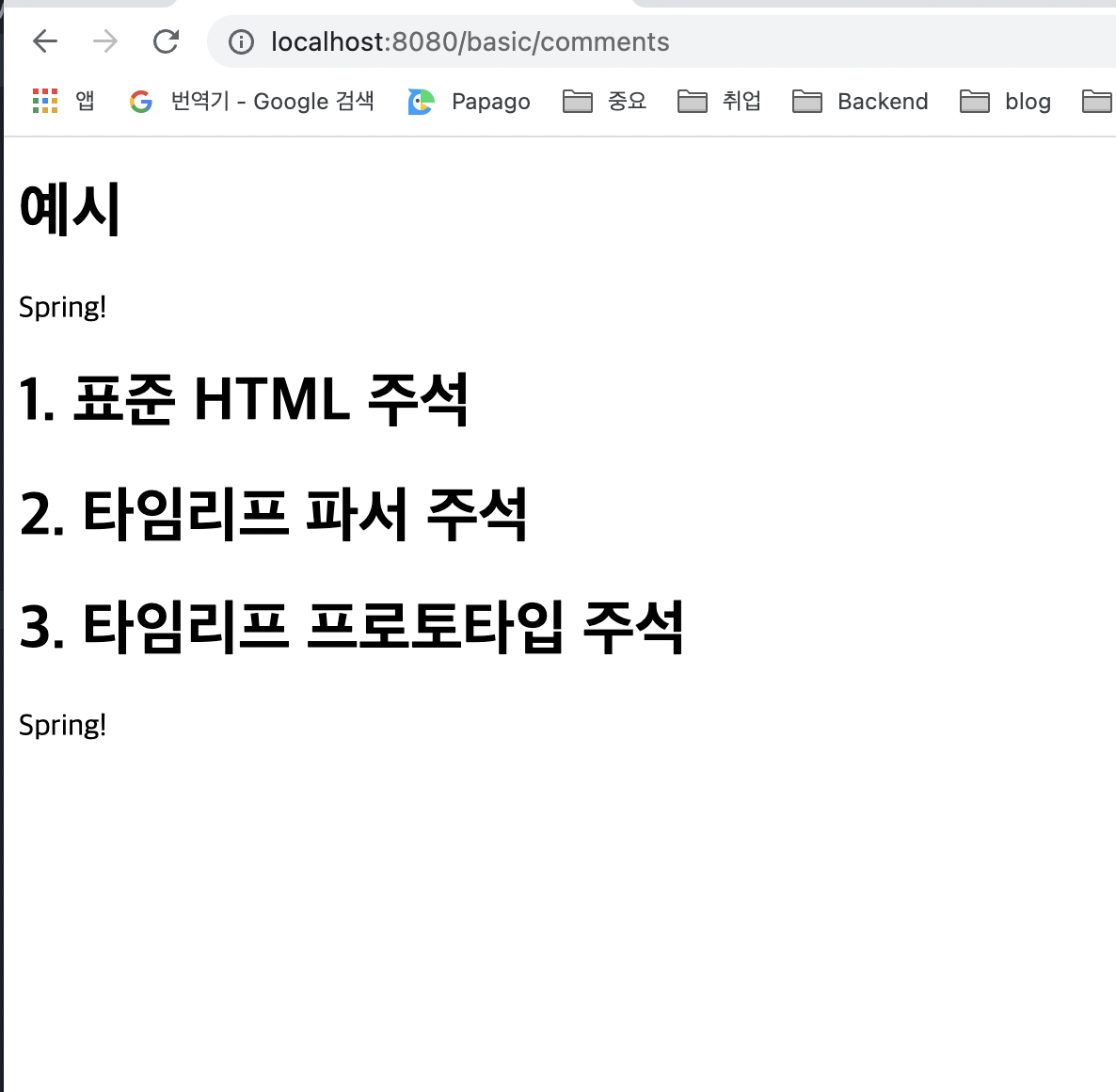
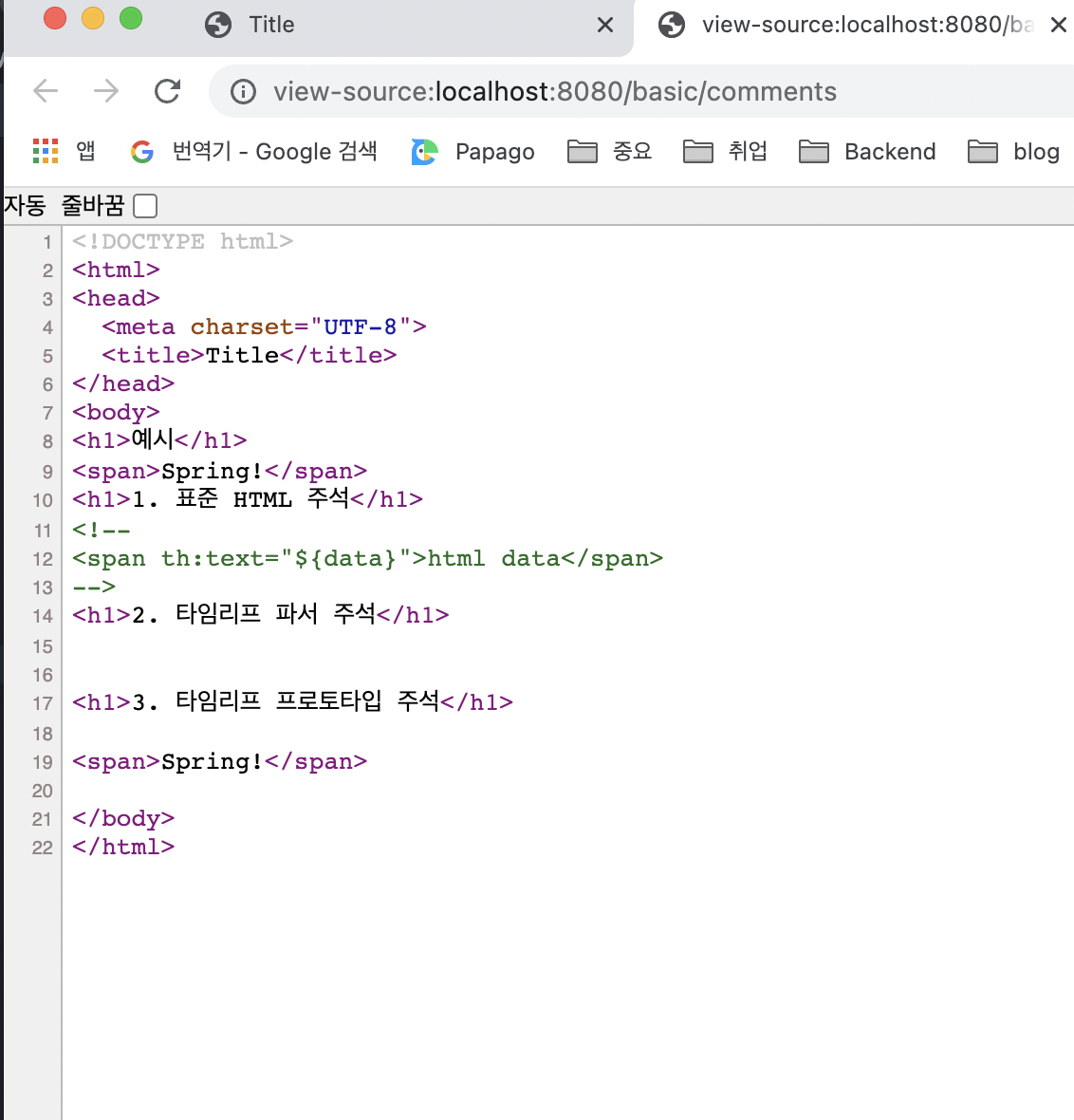
- 표준 HTML 주석만 보입니다 (이외는 보이지 않음)
A. 표준 HTML 주석
- HTML에서 사용하는 기본적인 주석 사용법과 동일
- 자바스크립트의 표준 HTML 주석은 타임리프가 렌더링 하지 않고, 그대로 남겨둡니다
- Format:
<span th:text="${data}">html data</span>
-->```
#### B. 타임리프 파서 주석
- 많이 사용되는 주석
- 타임리프 파서 주석은 타임리프의 진짜 주석이다.
- 렌더링에서 주석 부분을 제거한다.
- Format
➡️ 한 줄 : <!--/* contents */-->
➡️ 여러 줄 : <!--/*--> \n contents \n <!--*/-->
```html
<!--/* [[${data}]] */-->
<!--/*-->
<span th:text="${data}">html data</span>
<!--*/-->C. 타임리프 프로토타입 주석
- HTML 파일을 그대로 열어보면 주석처리가 되지만, 타임리프를 렌더링하는 경우에만 보이는 기능
- Format:
<!--/*/ contents /*/-->
<!--/*/ <span th:text="${data}">html data</span> /*/-->
블록
- <th:block>은 HTML 태그가 아닌 타임리프의 유일한 자체 태그입니다
- 렌더링 시 제거되며, 타임리프의 속성을 사용하기 애매한 경우 사용됩니다
- 대표적으로, th:each로 반복하고자 할 때, 한 요소가 아닌 동등한 레벨의 여러 요소를 그룹화하여 반복하고자 할 때 유용합니다
BasicController에 추가
@GetMapping("/block")
public String block(Model model){
addUsers(model);
return "basic/block";
}/resources/templates/basic/block.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<th:block th:each="user : ${users}">
<div>
사용자 이름1 <span th:text="${user.username}"></span>
사용자 나이1 <span th:text="${user.age}"></span>
</div>
<div>
요약 <span th:text="${user.username} + ' / ' + ${user.age}"></span>
</div>
</th:block>
</body>
</html>실행 결과
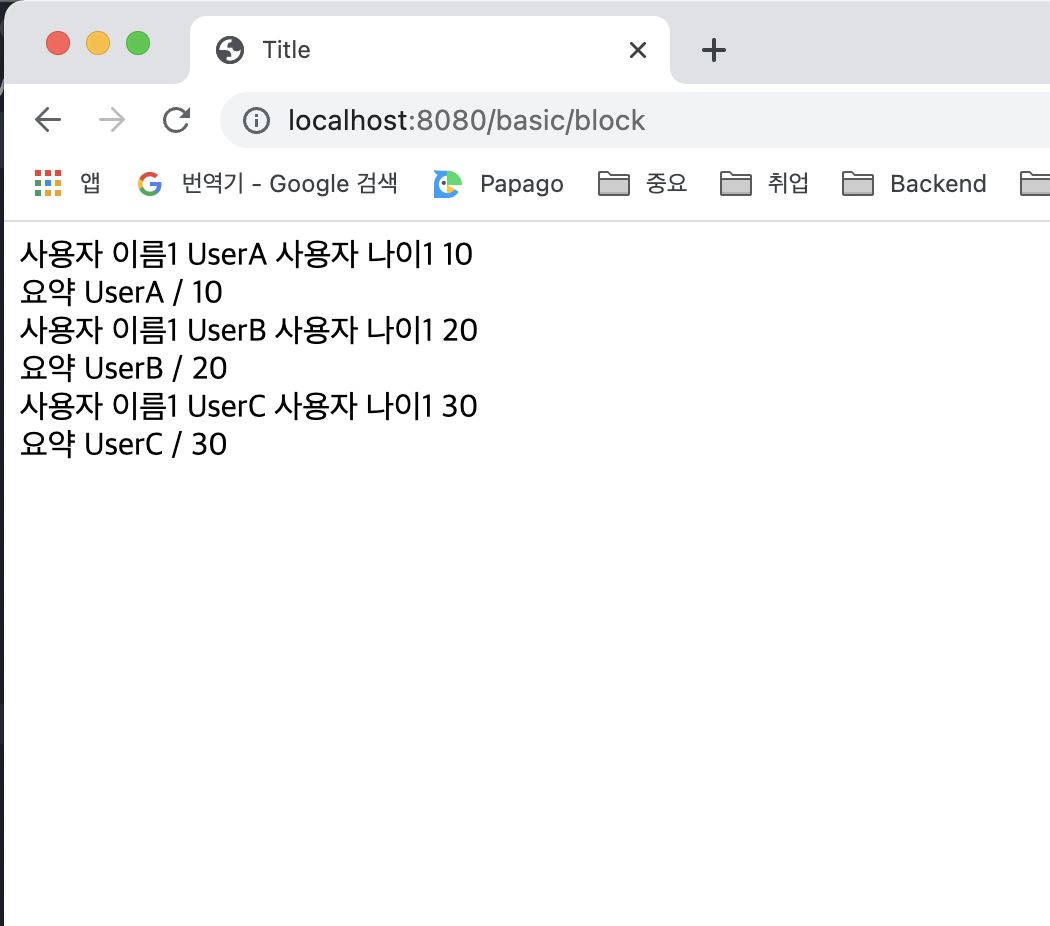
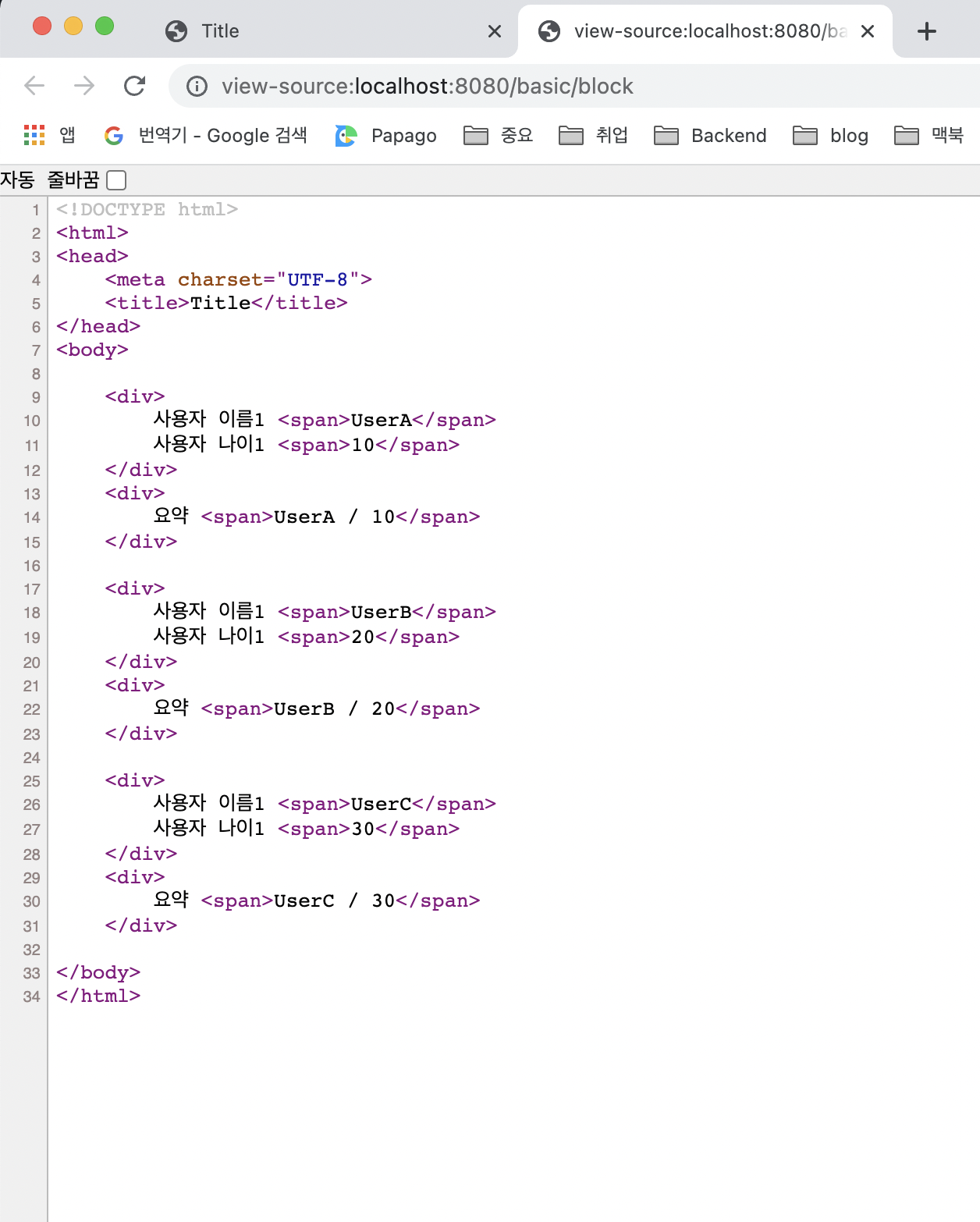
- 타임리프의 특성상 HTML 태그 안에 속성으로 기능을 정의해서 사용하는데, 위 예처럼 이렇게 사용하기 애매한 경우에 사용하면 됩니다
<th:block>은 렌더링시 제거됩니다
자바스크립트 인라인
- 타임리프는 자바스크립트에서 타임리프를 편리하게 사용할 수 있는 자바스크립트 인라인 기능을 제공합니다
<script th:inline="javascript">
이를 추가할 시, 자바스크립트 인라인 기능을 사용할 수 있습니다
BasicController 추가
@GetMapping("/javascipt")
public String javascript(Model model){
model.addAttribute("user", new User("UserA", 10));
addUsers(model);/resources/templates/basic/javascript.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 자바스크립트 인라인 사용 전 -->
<script>
var username = [[${user.username}]];
var age = [[${user.age}]];
//자바스크립트 내추럴 템플릿
var username2 = /*[[${user.username}]]*/ "test username";
//객체
var user = [[${user}]];
</script>
<!-- 자바스크립트 인라인 사용 후 -->
<script th:inline="javascript">
var username = [[${user.username}]];
var age = [[${user.age}]];
//자바스크립트 내추럴 템플릿
var username2 = /*[[${user.username}]]*/ "test username";
// username2에 /*[[${user.username}]]*/ user.username 가 삽입된다.
//객체
var user = [[${user}]];
</script>
<!-- 자바스크립트 인라인 each -->
<script th:inline="javascript">
[# th:each="user, stat : ${users}"]
var user[[${stat.count}]] = [[${user}]];
[/]
</script>
</body>
</html>자바스크립트 인라인을 사용하지 않은 경우 어떤 문제들이 있는지 알아보고, 인라인을 사용하면 해당 문제들이 어떻게 해결되는지 확인해보겠습니다
자바스크립트 인라인 사용전
<script>
var username = [[${user.username}]];
var age = [[${user.age}]];
// 자바스크립트 내추럴 템플릿
var username2 = /*[[${user.username}]]*/ "test username";
// 객체
var user = [[${user}]];
</script>텍스트 렌더링
var username = [[${user.username}]]; -> var username = userA;
- 결과를 보면
userA라는 변수 이름이 그대로 남아있습니다 - userA는 문자열인데 작은 따옴표(or 큰 따옴표)가 없어서 변수명으로 인식하여 오류가 발생합니다
자바스크립트 내추럴 템플릿
var username2 = /*[[${user.username}]]*/ "test username"; → var username2 = /*userA*/ "test username";
- 결과를 보면 정말 순수하게 그대로 해석을 해버렸습니다
- 따라서 내추럴 템플릿 기능이 동작하지 않고, 심지어 렌더링 내용이 주석처리 되어버립니다
객체
var user = [[${user}]]; -> var user = BasicController.User(username=userA, age=10);
- 객체의 toString()이 호출된 값이므로 분리해서 파싱하기 까다롭습니다
자바스크립트 인라인 사용 후
<script th:inline="javascript">
var username = [[${user.username}]];
var age = [[${user.age}]];
//자바스크립트 내추럴 템플릿
var username2 = /*[[${user.username}]]*/ "test username";
//객체
var user = [[${user}]];
</script>텍스트 렌더링
var username = [[${user.username}]]; → var username = "userA";
- 인라인 사용 후 렌더링 결과를 보면 문자 타입의 경우
"를 포함해줍니다 - 추가로 자바스크립트에서 문제가 될 수 있는 문자가 포함되어있으면 이스케이프 처리도 해줍니다
- 예
"→\"
- 예
자바스크립트 내추럴 템플릿
- 타임타임리프는 HTML 파일을 직접 열어도 동작하는 내추럴 템플릿 기능을 제공합니다
- 자바스크립트 인라인 기능을 사용하면 주석을 활용해서 이 기능을 사용할 수 있습니다
var username2 = /*[[${user.username}]]*/ "test username"; → var username2 = "userA";
- 결과를 보면 주석 부분이 제거되고, 기대한 "userA"가 정확하게 적용됩니다
객체
var user = [[${user}]]; -> `var user = {"username":"userA", "age":10};
- 타임리프의 자바스크립트의 인라인 기능을 사용하면 객체를 JSON으로 자동 변환해줍니다
실행 결과
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 자바스크립트 인라인 사용 전 -->
<script>
var username = [[${user.username}]];
var age = [[${user.age}]];
//자바스크립트 내추럴 템플릿
var username2 = /*[[${user.username}]]*/ "test username";
//객체
var user = [[${user}]];
</script>
<!-- 자바스크립트 인라인 사용 후 -->
<script th:inline="javascript">
var username = [[${user.username}]];
var age = [[${user.age}]];
//자바스크립트 내추럴 템플릿
var username2 = /*[[${user.username}]]*/ "test username";
//객체
var user = [[${user}]];
</script>
</body>
</html>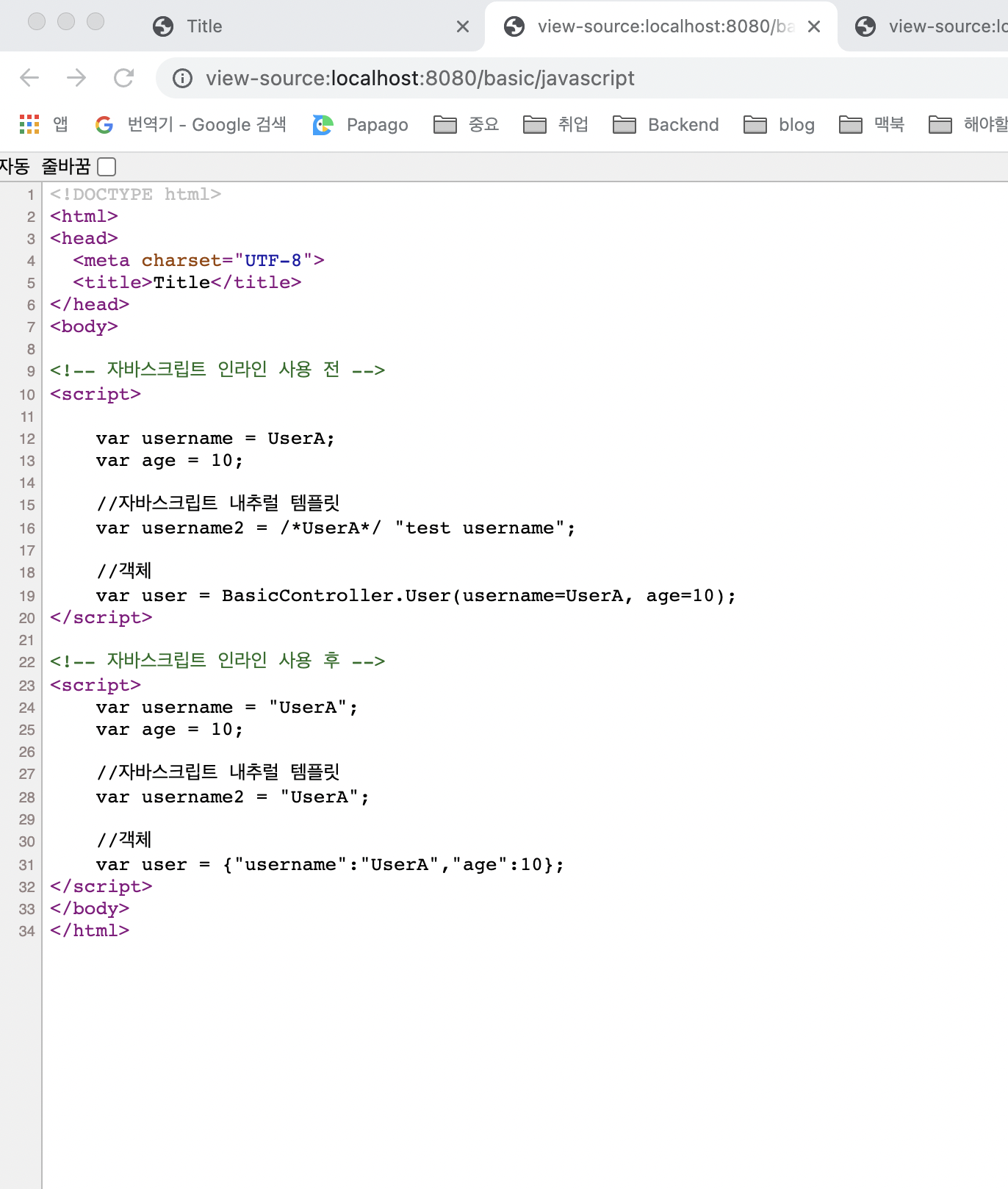
자바스크립트 인라인 each
- 자바스크립트 인라인은 each를 지원합니다
/resources/templates/basic/javascript.html에 추가
<!-- 자바스크립트 인라인 each -->
<script th:inline="javascript">
[# th:each="user, stat : ${users}"]
var user[[${stat.count}]] = [[${user}]];
[/]
</script>자바스크립트 인라인 each 결과
<script>
var user1 = {"username":"userA","age":10};
var user2 = {"username":"userB","age":20};
var user3 = {"username":"userC","age":30};
</script>전체 결과

템플릿 조각
웹 페이지 개발 시 발생하는 공통 영역에서 코드를 복사해서 사용한다면 변경시 여러 페이지를 다 수정해야 하므로 상당히 비효율적입니다
타임리프는 이런 문제들을 해결하기 위해 템플릿 조각과 레이아웃 기능을 지원합니다
package hello.thymeleaf.basic;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/template")
public class TemplateController {
@GetMapping("/fragment")
public String template(){
return "template/fragment/fragmentMain";
}
}/resources/templates/template/fragment/footer.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<body>
<footer th:fragment="copy">
푸터 자리 입니다.
</footer>
<footer th:fragment="copyParam (param1, param2)">
<p>파라미터 자리 입니다.</p>
<p th:text="${param1}"></p>
<p th:text="${param2}"></p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>- th:fragment 가 있는 태그는 다른곳에 포함되는 코드 조각으로 이해하면 됩니다
/resources/templates/template/fragment/fragmentMain.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>부분 포함</h1>
<h2>부분 포함 insert</h2>
<div th:insert="~{template/fragment/footer :: copy}"></div>
<h2>부분 포함 replace</h2>
<div th:replace="~{template/fragment/footer :: copy}"></div>
<h2>부분 포함 단순 표현식</h2>
<div th:replace="template/fragment/footer :: copy"></div>
<h1>파라미터 사용</h1>
<div th:replace="~{template/fragment/footer :: copyParam ('데이터1', '데이터2')}"></div>
</body>
</html>템플릿 조각 사용법
template/fragment/footer :: copy
: template/fragment/footer.html 템플렛에 있는 th:fragment="copy"라는 부분을 템플릿 조각으로 가져와서 사용한다는 의미
<footer th:fragment="copy">
푸터 자리 입니다.
</footer>- 부분 포함 insert
<div th:insert="~{template/fragment/footer :: copy}"></div>
th:insert를 사용하면 템플릿 조각을 현재 태그(div) 내부에 추가합니다
실행 결과
<h2>부분 포함 insert</h2>
<div>
<footer>
푸터 자리 입니다.
</footer>
</div>- 부분 포함 replace
<div th:replace="~{template/fragment/footer :: copy}"></div>
th:replace를 사용하면 템플릿 조각이 현재 태그(div)를 대체합니다
실행 결과
<h2>부분 포함 replace</h2>
<footer>
푸터 자리 입니다.
</footer>- 부분 포함 단순 표현식
<div th:replace="template/fragment/footer :: copy"></div>~{...}를 사용하는 것이 원칙이지만 템플릿 조각을 사용하는 코드가 단순하면 이 부분을 생략할 수 있습니다
실행 결과
<h2>부분 포함 단순 표현식</h2>
<footer>
푸터 자리 입니다.
</footer>- 파라미터 사용
html <div th:replace="~{template/fragment/footer :: copyParam ('데이터1', '데이터2')}"></div>
파라미터를 전달해서 동작으로 조각을 렌더링 할 수도 있습니다
실행 결과
<h1>파라미터 사용</h1>
<footer>
<p>파라미터 자리 입니다.</p>
<p>데이터1</p>
<p>데이터2</p>
</footer>footer.html의 copyParam 부분
<footer th:fragment="copyParam (param1, param2)">
<p>파라미터 자리 입니다.</p>
<p th:text="${param1}"></p>
<p th:text="${param2}"></p>
</footer>실행 결과 화면
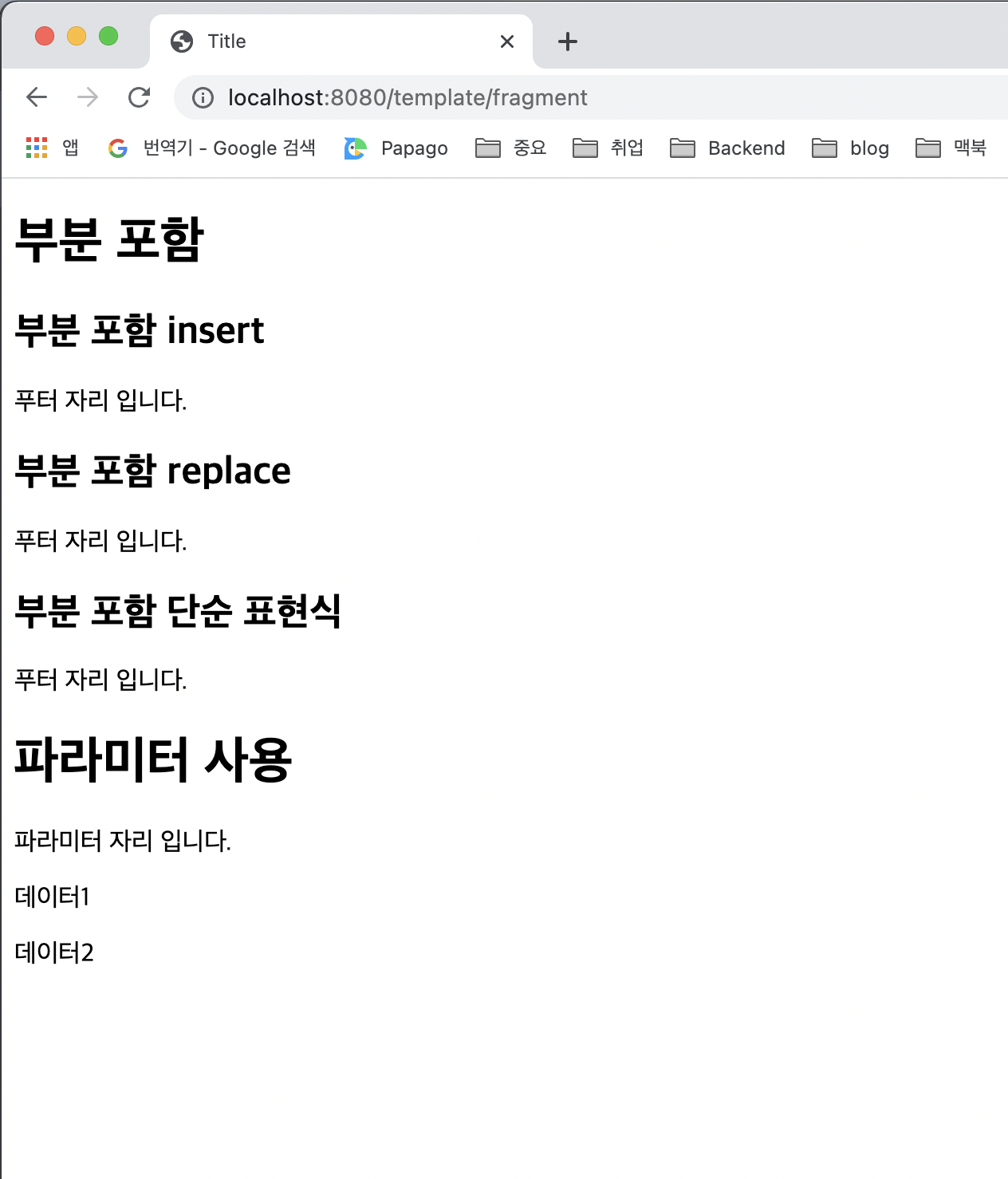
템플릿 레이아웃1
- 이전에는 일부 코드 조각을 가지고와서 사용했다면, 이번에는 개념을 더 확장해서 코드조각을 레이아웃에 넘겨 사용하는 방법에 대해 알아보겠습니다
- 예를 들어 에 공통으로 사용하는 css, javascript 같은 정보들이 있는데, 이러한 공통 정보들을 한 곳에 모아두고 공통으로 사용하지만 각 페이지마다 필요한 정보를 더 추가해서 사용하고 싶다면 다음과 같이 사용하면 됩니다
TemplateController에 추가
@GetMapping("layout")
public String layout() {
return "template/layout/layoutMain";
}/resources/templates/template/layout/base.html
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head th:fragment="common_header(title,links)">
<title th:replace="${title}">레이아웃 타이틀</title>
<!-- 공통 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" media="all" th:href="@{/css/awesomeapp.css}">
<link rel="shortcut icon" th:href="@{/images/favicon.ico}">
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/sh/scripts/codebase.js}"></script>
<!-- 추가 -->
<th:block th:replace="${links}" />
</head>/resources/templates/template/layout/layoutMain.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head th:replace="template/layout/base :: common_header(~{::title},~{::link})">
<title>메인 타이틀</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" th:href="@{/css/bootstrap.min.css}">
<link rel="stylesheet" th:href="@{/themes/smoothness/jquery-ui.css}">
</head>
<body>
메인 컨텐츠
</body>
</html>common_header(~{::title}, ~{::link})이 부분이 핵심입니다
➡️ ::title 은 현재 페이지의 title 태그들을 전달합니다
➡️ ::link 는 현재 페이지의 link 태그들을 전달합니다
실행 결과
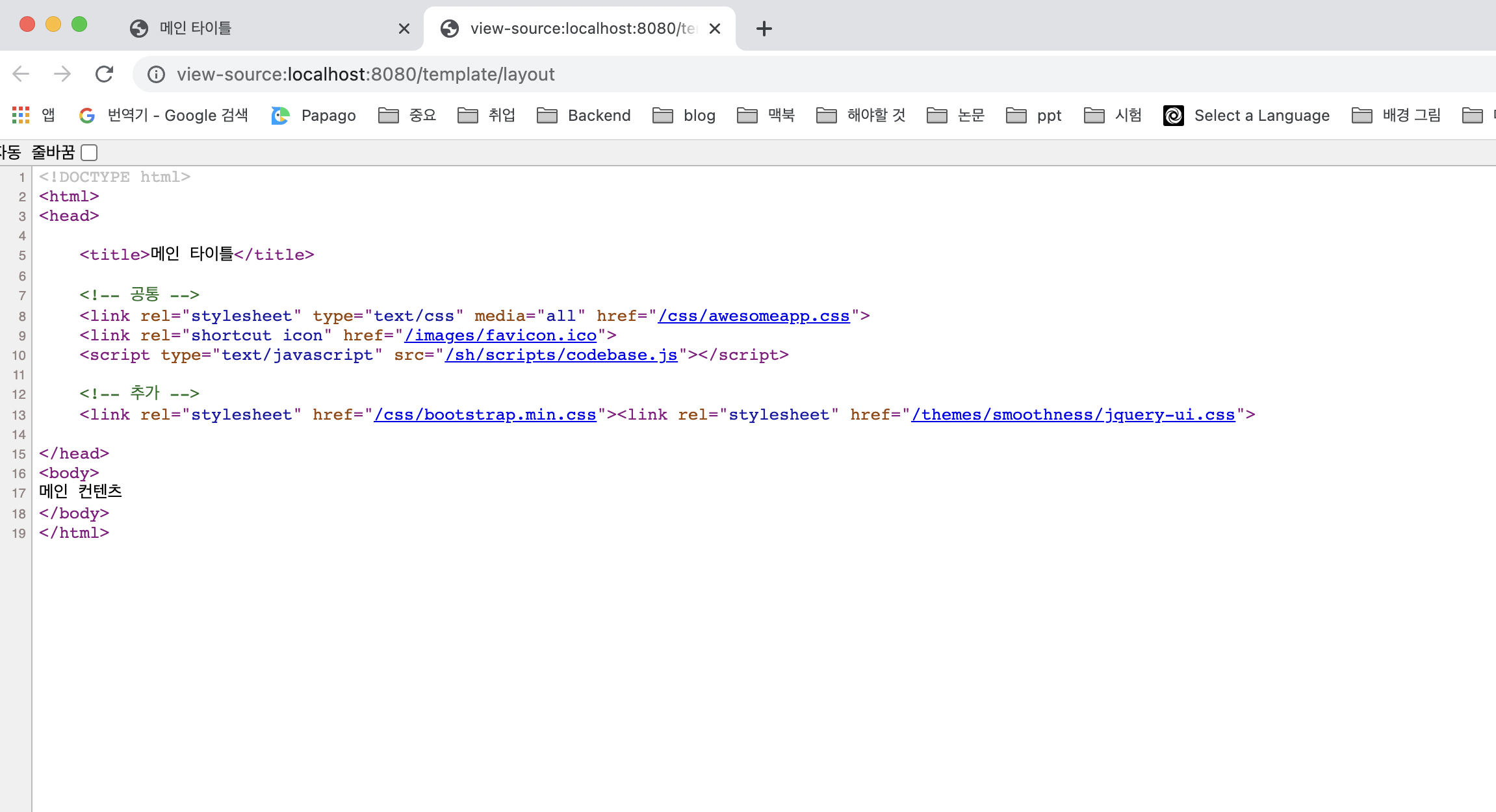
결과를 보면
- 메인 타이틀이 전달한 부분으로 교체되었습니다
- 공통 부분은 그대로 유지되고, 추가 부분에 전달한
<link>들이 포함되었습니다 - 레이아웃 개념을 두고 그 레이아웃에 필요한 코드 조각을 전달해서 완성하는 것으로 이해하면 됩니다
템플릿 레이아웃2
템플릿 레이아웃 확장
- 템플릿 레이아웃 1에서는
<head>부분만 적용했지만,<html>전체에 적용할 수도 있습니다
TemplateController에 추가
@GetMapping("/layoutExtend")
public String layoutExtend(){
return "template/layoutExtend/layoutExtendMain";
}/resources/templates/template/layoutExtend/layoutFile.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html th:fragment="layout (title, content)" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title th:replace="${title}">레이아웃 타이틀</title> </head>
<body>
<h1>레이아웃 H1</h1>
<div th:replace="${content}">
<p>레이아웃 컨텐츠</p>
</div>
<footer>
레이아웃 푸터
</footer>
</body>
</html>/resources/templates/template/layoutExtend/layoutExtendMain.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html th:replace="~{template/layoutExtend/layoutFile :: layout(~{::title}, ~{::section})}"
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>메인 페이지 타이틀</title> </head>
<body>
<section>
<p>메인 페이지 컨텐츠</p>
<div>메인 페이지 포함 내용</div> </section>
</body>
</html>실행 결과
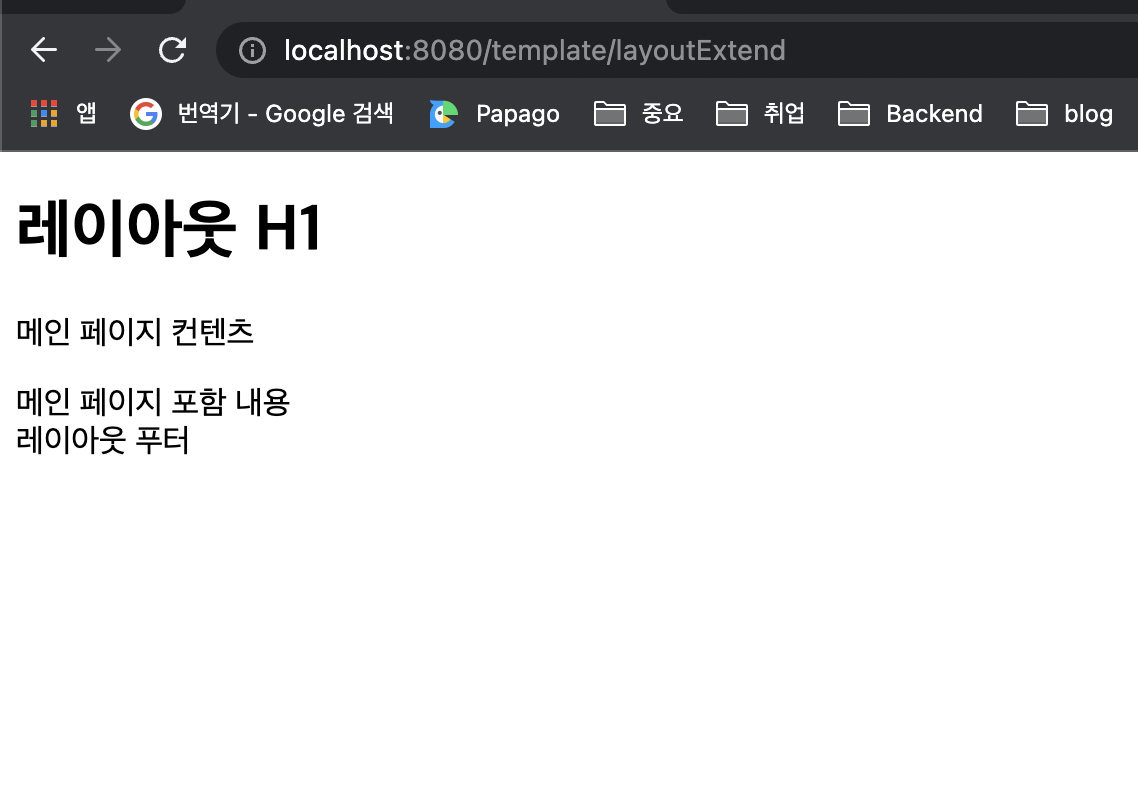
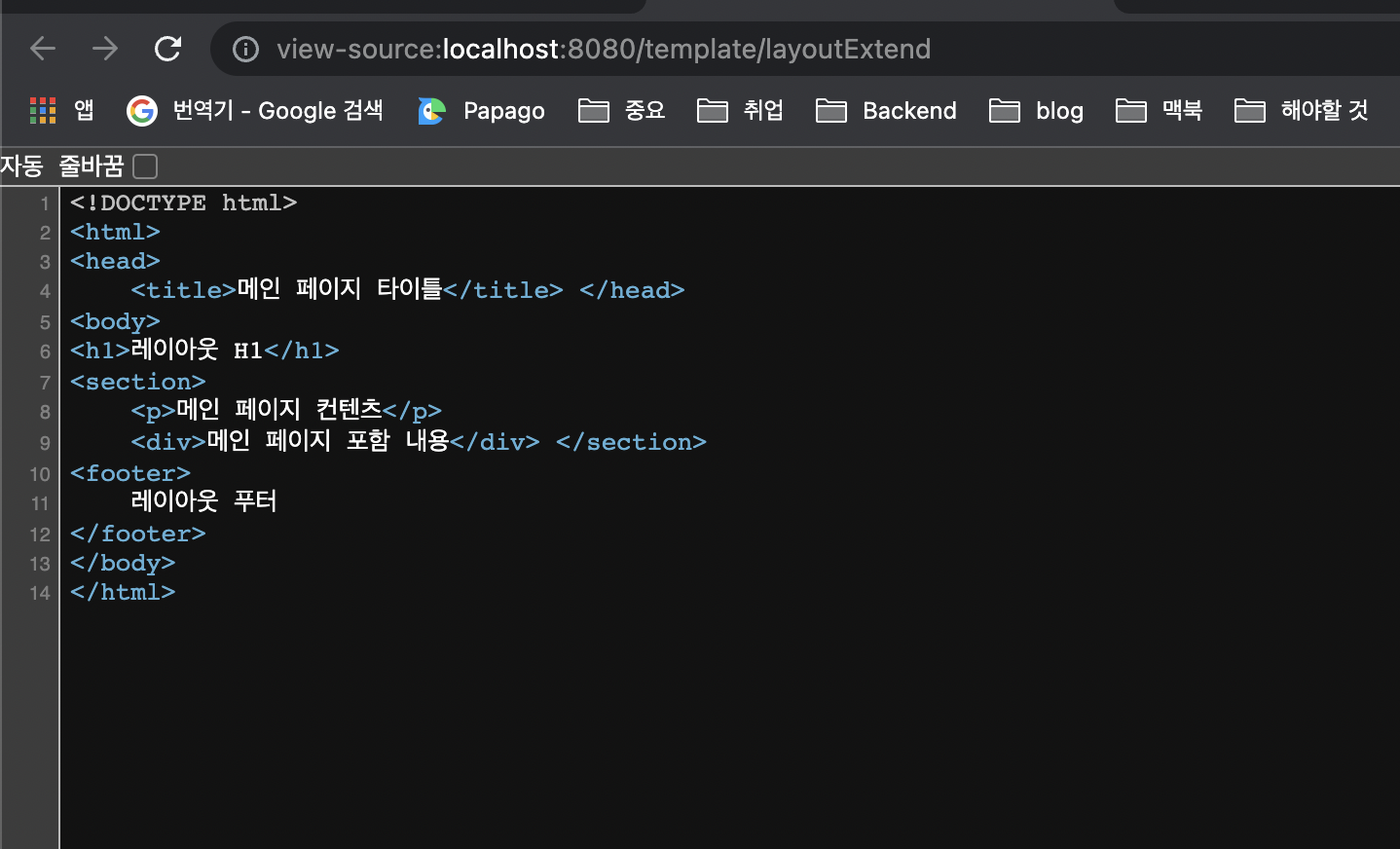
- layoutFile.html 을 보면 기본 레이아웃을 가지고 있는데, 에 th:fragment 속성이 정의되어 있습니다
- layoutFile.html을 기본으로 하고 여기에 필요한 내용을 전달해서 부분적으로 변경하는 것으로 이해하면 됩니다
- layoutExtendMain.html 는 현재 페이지인데, 자체를 th:replace 를 사용해서 변경하는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다
- 결국 layoutFile.html 에 필요한 내용을 전달하면서 자체를 layoutFile.html 로 변경합니다