[JS] 자바스크립트 bind, call, apply 메소드
이전 벨로그 - [JS] 자바스크립트 this 키워드
...
🔹함수에서의 this 사용➡window 객체 가리킴
function playAudio() {
console.log(this);
}
playAudio();🔥자바스크립트 bind, call, apply
보통 함수 안에서 this 사용하면 Window 객체를 참조하게 됨
🤔 이걸 바꿀 수 있는 방법은 있을까 ❓❓
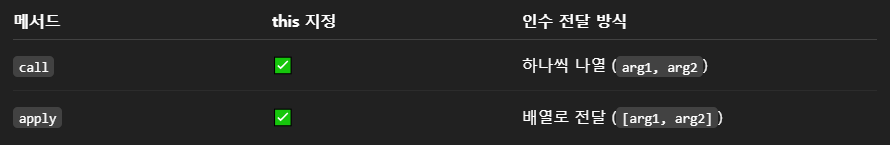
📢call - this를 지정해서 함수를 호출하는 메소드
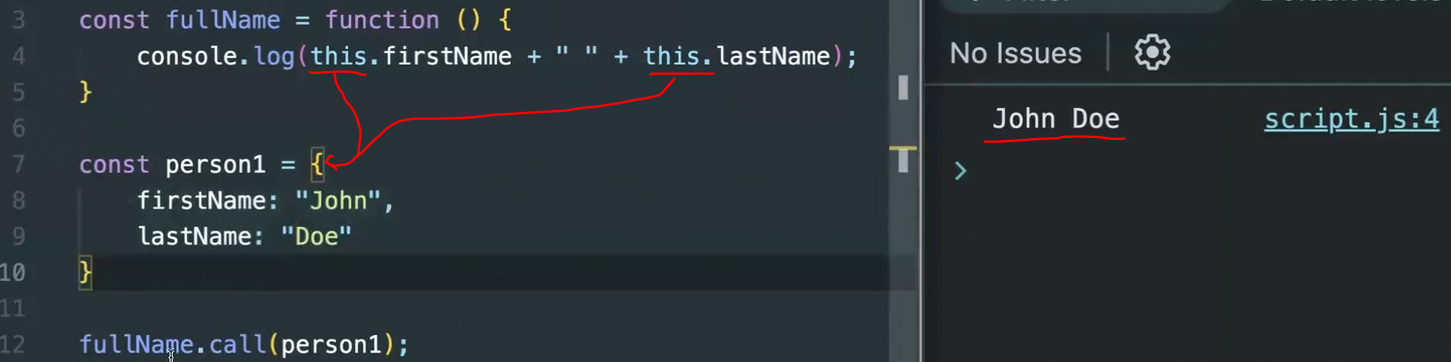
const fullName = function () {
console.log(this.firstName + " " + this.lastName);
}
const person1 = {
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Doe"
}
fullName.call(person1);원래 함수에서
this는 Window 가리켜서 둘 다undefined출력 되지만
이this가 Window가 아닌person1이 생성한 객체 가리키게 하기 위해fullName.call메소드 사용해서person1을 인수로 넣어 호출하면
이제 함수 안this는 Window가 아닌person1객체 가리키게 됨😮
call 메소드 안에 인수를 더 넣어서 함수의 매개변수로 전달 할 수도 있음
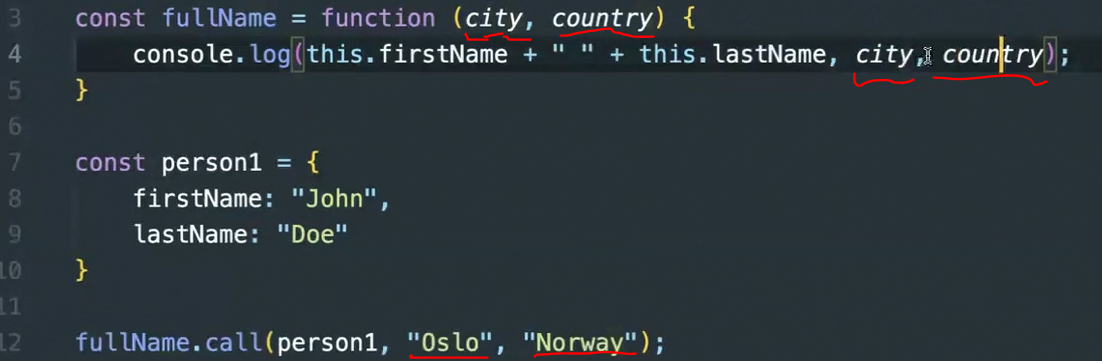
📢apply - this를 지정해서 함수를 호출하는 메소드
👉 call과 다른 점 : 인수 넣어줄 때 배열[ ]로 넣음
const fullName = function (city, country) {
console.log(this.firstName + " " + this.lastName, city, country);
}
const person1 = {
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Doe"
}
// 인수 [] 배열로 넣어주기
fullName.apply(person1, ["Oslo", "Norway"]);call( ) + 스프레드 연산자 (...) 방식
function fullName(city, country) {
console.log(this.firstName + " " + this.lastName, city, country);
}
const person1 = {
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Doe"
};
const args = ["Oslo", "Norway"];
fullName.call(person1, ...args);
// 결과: John Doe Oslo Norway요즘은 apply( )보다 스프레드(...) + call을 더 많이 씀
👉 sum.call(null, ...arr) ( 이게 더 편하고 많이 씀 )
bind - 함수를 복사해서 this를 고정시킨 새 함수를 반환하는 메소드
👉 this를 고정한 “새 함수”를 만들어서 나중에 호출할 수 있게 해줌
function func(language) {
if(language === 'kor') {
console.log(`language: ${this.korGreeting}`);
} else {
console.log(`language: ${this.engGreeting}`);
}
}
func('kor')➡️ 아무것도 바인딩하지 않으면 this는 기본적으로 전역 객체(Window)를 가리킴
undefined 출력
function func(language) {
if(language === 'kor') {
console.log(`language: ${this.korGreeting}`);
} else {
console.log(`language: ${this.engGreeting}`);
}
}
const greeting = {
korGreeting: "안녕 ",
engGreeting: "Hello "
}
// this가 greeting 객체를 참조하도록
// 바인딩이 된 함수가 반환이 된 것-> boundFunc
const boundFunc = func.bind(greeting);➡️ func 함수에 this를 greeting으로 고정(bind) 했기 때문에,
이제 boundFunc( )를 호출하면 this는 항상 greeting 객체를 가리키게 됨✅
boundFunc('kor');