Compose란?
안드로이드 최신 UI 툴킷으로 선언형으로 UI를 개발한다.
기존 뷰 시스템과는 다르게 코틀린 코드로 UI를 개발할 수 있으며
일일이 뷰를 변경해주어야 했던 명령형과 다르게 상태 값에 따라 알아서 UI를 업데이트를 해주기에 상태 관리가 중요하다.
composable
모든 Compose UI는 Composable 함수로 구성되어 있다.
Composable 함수가 화면에 구성되면 composition이 되었다고 하며
상태값이 변경되어 다시 화면에 그려지면 recomposition이 되었다고 한다.
상태
상태값에 따라 구성될 UI를 선언하는 방식이기에 상태관리가 중요하다.
상태관리를 잘못하여 불필요하게 recomposition이 많이 일어나는 것을 방지하는 것이 중요하다.
@Composable
fun WindBlownDiagonalEffect(
resourceId: Int,
) {
val configuration = LocalConfiguration.current
val density = LocalDensity.current
val screenWidthPx = with(density) {
configuration.screenWidthDp * this.density
}
val screenHeightPx = with(density) {
configuration.screenHeightDp * this.density
}
val things by remember {
mutableStateOf(
List(10) {
val x = Random.nextInt(screenWidthPx.toInt()).toFloat()
val y = Random.nextInt(screenHeightPx.toInt() / 2).toFloat()
val offset = if (Random.nextInt(2) == 1) {
Offset(x, -y)
} else {
Offset(screenWidthPx + x, y)
}
val imageSize = Random.nextInt(10, 40).dp
Leaf(offset, imageSize, Random.nextFloat() * 360)
})
}
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
while (true) {
things.forEach { thing ->
thing.update(screenSize = Size(screenWidthPx, screenHeightPx))
}
delay(16L)
}
}
val imageVector = ImageBitmap.imageResource(id = resourceId)
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.background(Color.Transparent)
) {
for (thing in things) {
thing.Draw(imageVector)
}
}
}
class Leaf(
var offset: Offset,
var size: Dp,
var rotate: Float,
) {
fun update(screenSize: Size) {
val newX = offset.x - 5f
val newY = offset.y + 5f
val offset = if (newX <= 0 || newY >= screenSize.height) {
val x = Random.nextInt(screenSize.width.toInt()).toFloat()
val y = Random.nextInt(screenSize.height.toInt() / 2).toFloat()
if (Random.nextInt(2) == 1) {
Offset(x, -y)
} else {
Offset(screenSize.width + x, y)
}
} else {
Offset(newX, newY)
}
val rotate = (rotate + 2) % 360
this.offset = offset
this.rotate = rotate
}
@Composable
fun Draw(imageVector: ImageBitmap) {
val density = LocalDensity.current
val offsetX = with(density) {
offset.x.toDp()
}
val offsetY = with(density) {
offset.y.toDp()
}
Image(
bitmap = imageVector,
contentDescription = null,
modifier = Modifier
.size(size)
.offset(
x = offsetX,
y = offsetY
)
.rotate(rotate),
colorFilter = ColorFilter.tint(color = Color(0xFFAE8B4E))
)
}
}해당 코드는 오른쪽 위 -> 왼쪽 아래로 나뭇잎이 떨어지는 것 같은 UI를 그리는 컴포저블이다.
해당 컴포저블은 16밀리초마다 위치값을 업데이트하고 있지만 실제로는 화면에 아무것도 그려지지 않는다.
그 이유는 Draw에서 뷰를 그릴 때 참고하고 있는 offset과 rotate가 state 변수가 아니라서 변경을 감지하지 못하여 recomposition을 하지 못하고 있기 때문이다.
class Leaf(
private val offset: Offset,
private var size: Dp,
private var rotate: Float,
) {
private var offsetState by mutableStateOf(offset)
private var rotateState by mutableFloatStateOf(rotate)
fun update(screenSize: Size) {
val newX = offsetState.x - 5f
val newY = offsetState.y + 5f
val offset = if (newX <= 0 || newY >= screenSize.height) {
val x = Random.nextInt(screenSize.width.toInt()).toFloat()
val y = Random.nextInt(screenSize.height.toInt() / 2).toFloat()
if (Random.nextInt(2) == 1) {
Offset(x, -y)
} else {
Offset(screenSize.width + x, y)
}
} else {
Offset(newX, newY)
}
val rotate = (rotateState + 2) % 360
this.offsetState = offset
this.rotateState = rotate
}
@Composable
fun Draw(imageVector: ImageBitmap) {
val density = LocalDensity.current
val offsetX = with(density) {
offsetState.x.toDp()
}
val offsetY = with(density) {
offsetState.y.toDp()
}
Image(
bitmap = imageVector,
contentDescription = null,
modifier = Modifier
.size(size)
.offset(
x = offsetX,
y = offsetY
)
.rotate(rotateState),
colorFilter = ColorFilter.tint(color = Color(0xFFAE8B4E))
)
}
}
다음과 같이 offsetState, rotateState를 만들어서 이를 변경하고 참조하면 이제 화면에 그려지는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
stateful
내부에서 상태를 가지고있는 컴포저블
외부 호출자가 상태 관리를 하지 않아도 되지만 해당 컴포저블은 재사용하기 힘들다.
stateless
상태를 외부 호출자가 관리하도록 하여 해당 컴포저블은 상태를 가지지 않는다.
재사용할 수 있다.
내부 상태를 외부 호출자로 끌어올리는 것을 상태 호이스팅 (state hoisting)이라고 한다.
remember
state 변수로 참조하고 있는 값이 변경되어 recomposition이 발생하면 해당 컴포저블은 다시 그려진다.
이 과정에서 state 변수도 다시 초기값으로 업데이트되어서 recomposition이 일어났지만 값이 변경되지 않는 상황이 발생한다.
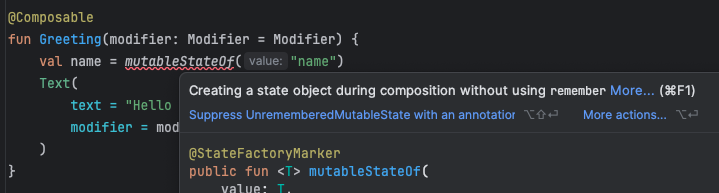
(애초에 그런 일은 일어나지 않도록 막고 있다)
remember API는 메모리에 객체를 저장하여 초기 컴포지션에 저장했다가 recomposition이 일어날 때마다 해당값을 반환하고 해당 컴포저블이 삭제되면 더 이상 기억하지 않는다.
key 매개변수값을 통해서 해당 값이 변경되었다면 다시 새로운 값을 기억하도록 할 수 있다.
val pendulum = remember(size, animation) {
Pendulum(
size = size,
animation = animation
)
}세줄요약
- 컴포즈는 상태 값에 따라 자동으로 UI를 업데이트 해주는 선언형 툴킷
- state 변수로 상태를 선언하며 remember를 통해 recomposition이 되어도 해당 값을 기억하고 있다.
- 상태 호이스팅을 통해 stateless 컴포저블을 만들어 재사용 가능하게 만들면 좋다.

