AuthenticationProvider의 이해
애플리케이션에서 여러 다른 방식의 인증을 구현해야 할 수 있다. 예를 들어 암호를 입력하는 경우, 지문 인식을 하는 경우, SMS 코드로 인증을 하는 방법 등이 있다. 스프링 시큐리티에서는 AuthenticationProvider 계약으로 모든 맞춤형 인증 논리를 정의할 수 있다.
Authentication
인증 요청 이벤트를 나타내며 애플리케이션에 접근을 요청한 엔티티의 세부 정보를 담는다.
메서드
예시 코드
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
public class AuthenticationExample {
public void printAuthenticationDetails() {
// 현재 인증 정보를 가져옴
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authentication != null) {
System.out.println("Principal: " + authentication.getPrincipal());
System.out.println("Credentials: " + authentication.getCredentials());
System.out.println("Authorities:");
for (GrantedAuthority authority : authentication.getAuthorities()) {
System.out.println("\t" + authority.getAuthority());
}
System.out.println("Is Authenticated: " + authentication.isAuthenticated());
} else {
System.out.println("현재 인증된 사용자가 없습니다.");
}
}
}
isAuthenticated() - 인증 프로세스가 끝났으면 true를 반환하고 아직 진행중이면 false를 반환한다.
getCredentials() - 인증 프로세스에 이용된 암호나 비밀을 반환한다.
getAuthorities() - 인증된 요청에 허가된 권한의 컬렉션을 반환한다.
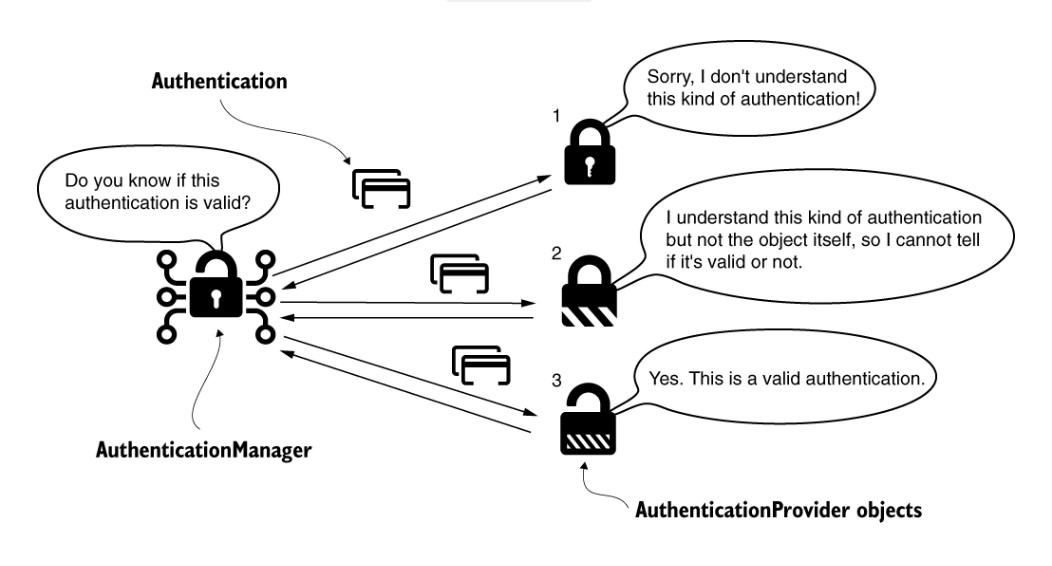
AuthenticationProvider
시스템의 사용자를 찾는 책임을 UserDetailsService에 위임하고 PasswordEncoder로 인증 프로세스에서 암호를 관리한다.
- 인증이 성공하면 Authentication 인스턴스를 반환한다.
- 인증이 실패하면 AuthenticationException을 반환한다.
인터페이스 정의
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
// 주어진 Authentication 객체를 이용해 사용자를 인증하고, 인증된 객체를 반환
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;
// 이 AuthenticationProvider가 특정 Authentication 클래스를 지원하는지 확인
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}supports - 해당 AuthenticationProvider가 특정 Authentication 클래스를 처리할 수 있는지 확인하는 역할을 한다.
예를 들어 잠금 장치를 열지 결정하는 인증 관리자이다. 인증 관리자는 결정을 위해 인증 공급자에게 작업을 위임하여 카드가 유효한지 확인할 수 있다. 이것이 supports() 메서드의 목적이다.
SecurityContext
AuthenticationManager는 인증 프로세스를 성공적으로 완료한 후 요청이 유지되는 동안 Authentication 인스턴스를 저장한다. Authentication 객체를 저장하는 인스턴스를 SecurityContext라고 한다.
예를 들어 인증이 끝난 후에도 사용자의 이름이나 권한과 같은 정보를 참조하기 위해 사용한다.
SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContext의 주 책임은 Authentication 객체를 저장하는 것이다.
SecurityContext는 SecurityContextHolder로 관리하며 세 가지 전략을 제공한다.
-
MODE_THREADLOCAL
각 스레드가 SecurityContext에 각자의 세부 정보를 저장할 수 있게 한다.
SecurityContext를 관리하는 기본 전략이다. -
MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL
비동기 메서드의 경우 SecurityContext를 다음 스레드로 복사하도록 한다.
비동기 처리가 필요한 애플리케이션에서 유용하며, 예를 들어, 비동기 방식으로 작업을 처리하는 스프링의 @Async 어노테이션을 사용할 때 유용하다. -
MODE_GLOBAL
모든 스레드가 같은 SecurityContext를 보게 한다.
비동기호출을 위한 전략
@Async 어노테이션을 통해 엔드포인트가 비동기가 되면 스레드가 달라지기 때문에 context.getAuthentication()을 하면 NullPointerException이 투척된다.
이 경우 MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL를 이용하여 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
DeligatingSecurityContextRunnable
새로운 스레드로 보안 컨텍스트가 올바르게 전파되도록 돕는다. 보안 데이터를 처리하는 자바 애플리케이션에서 멀티 스레딩을 사용할 때, 스레드 간에 보안 컨텍스트를 유지하는 것이 중요하다.
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.concurrent.DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable;
public class SecurityContextExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Runnable 작업 정의
Runnable task = () -> {
System.out.println("현재 사용자: " + SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getName());
};
// 보안 컨텍스트를 새 스레드로 전달
Runnable secureTask = new DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable(task);
// 스레드 시작
new Thread(secureTask).start();
}
}비동기적으로 실행하는 작업을 장식하고 구현이 새로 생성된 스레드로의 SecurityContext를 전달한다.
SecurityContext의 동시성 지원과 관련된 클래스
-
DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable: 이 객체는 Runnable 인터페이스를 구현한 태스크를 래핑하며, 태스크 실행 전후로 보안 컨텍스트를 설정하고 복원한다다. 기본적으로 실행 중인 스레드의 보안 컨텍스트를 이용하거나 명시적으로 전달된 컨텍스트를 사용할 수 있다.
-
DelegatingSecurityContextCallable: Callable 인터페이스를 구현한 태스크를 래핑하는 객체로, DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable과 유사하게 작동하지만 반환 값이 있는 태스크에 사용된다. 이 객체도 태스크 실행 전후로 보안 컨텍스트를 설정하고 복원한다.
-
DelegatingSecurityContextExecutor: Executor 인터페이스를 구현하는 객체로, 제출된 모든 태스크에 대해 보안 컨텍스트를 적용한다. 이 객체는 스레드 풀 내의 모든 태스크 실행에 보안 컨텍스트를 전파하는 데 사용된다.
-
DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService: ExecutorService 인터페이스를 확장한 객체로, 이 역시 스레드 풀을 사용하여 다양한 태스크를 관리할 때 보안 컨텍스트를 유지한다. 이 서비스를 사용하면 복잡한 스레드 관리 시나리오에서도 보안 컨텍스트의 일관성을 보장할 수 있다.
-
DelegatingSecurityContextScheduledExecutorService: ScheduledExecutorService 인터페이스를 구현하는 객체로, 주기적인 태스크 실행을 스케줄링할 때 사용된다. 이 객체를 통해 예약된 모든 태스크에 보안 컨텍스트를 적용하면서 타이밍을 관리할 수 있다.
이 구간은 이해가 잘 안된다... 너무어렵다....
HttpBasic 양식 기반 로그인으로 인증 구현
HttpSecurity 매개 변수의 httpBasic()대신 formLogin()매서드를 호출한다.
예시코드
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login") // 사용자 정의 로그인 페이지 URL
.permitAll() // 모든 사용자가 로그인 페이지 접근 허용
.and()
.logout()
.permitAll();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth
.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("user").password("{noop}password").roles("USER"); // 인메모리 사용자 정의
}
}AuthenticationSuccessHandler, AuthenticationFailureHandler를 이용해서 인증이 성공했을때와 실패했을 때의 논리를 구성할 수 있다.
요청식별자
인증에 실패했을 경우 401 권한 없은 외에 HTTP상태 코드나 본문을 추가하는 경우 요청 식별자를 보낸다. 요청을 역추적하기 위한 고유한 값이며 민감한 데이터를 시스템 외부로 보내지 않기 위한 용도로도 사용한다.
