1. 백업을 위해 오라클 싱글 머신에 Catalog 인스턴스 추가, 디렉토리 생성
1. 백업을 위한 디스크 추가
- Virtual Box에서 Disk 추가 (20 GiB), 설정 -> 저장소 -> 컨트롤러(SATA) 추가
2. 가상머신에서 백업위치에 디스크 마운트
1. 가상머신 부팅 후 fdisk -l 로 디스크 디바이스 이름 및 용량 확인
[root@edu ~]
Disk /dev/sda: 34.4 GB, 34359738368 bytes, 67108864 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x000ca538
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 2099200 67108863 32504832 83 Linux
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/centos-root: 31.1 GB, 31134318592 bytes, 60809216 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/centos-swap: 2147 MB, 2147483648 bytes, 4194304 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
2. 디스크 파티션, 리눅스 파일시스템 생성 및 마운트
[root@edu ~]
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Device does not contain a recognized partition table
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x005c9df4.
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
First sector (2048-41943039, default 2048):
Using default value 2048
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-41943039, default 41943039):
Using default value 41943039
Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 20 GiB is set
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[root@edu ~]
3. 마운트 상태 확인
[root@edu ~]
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x005c9df4
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 41943039 20970496 83 Linux
[root@edu ~]
4. 파일시스템 생성
[root@edu ~]
mke2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
1310720 inodes, 5242624 blocks
262131 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=2153775104
160 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
[root@edu ~]
5. 백업 디렉토리 생성 및 디스크 마운트
1. 백업 디렉토리 생성
mkdir /backup
2. 디스크 마운트
nano /etc/fstab
/dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=f8727e35-38d4-489e-ac72-b97d2e1533da /boot xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
/dev/sdb1 /backup ext4 defaults 0 0
3. reboot 후 /backup 에 /dev/sdb1 마운트 확인
[root@edu ~]
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 8115988 0 8115988 0% /dev
tmpfs 8133000 0 8133000 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 8133000 9816 8123184 1% /run
tmpfs 8133000 0 8133000 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 30394368 15945580 14448788 53% /
/dev/sdb1 20510288 45080 19400300 1% /backup
/dev/sda1 1038336 246584 791752 24% /boot
tmpfs 1626604 8 1626596 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs 1626604 20 1626584 1% /run/user/0
[root@edu ~]
6. 백업을 위해 /backup 하위 디렉토리 생성
[root@edu ~]
[root@edu ~]
[root@edu ~]
/backup
├── close
├── lost+found
├── open
└── rman
├── arch
├── cont
└── database
7 directories, 0 files
[root@edu ~]
2. 복원의 두 단계
1. Restore
2. Recover
- 백업 파일을 이용해 복구
- 아카이브 로그와 리두 로그를 참조해 SCN 을 맞추는 작업을 통해 DB Open 상태로 만들어줌
3. 백업 대상
1. Data File
SQL> col name for a50
select name, status from v$datafile;

tempfiles
- 백업 대상에서는 제외되나 백업 및 복구 가능
- 실제 서비스에서는 백업은 받지 않으며, 복구시 temp 테이블 스페이스를 새롭게 생성해줌
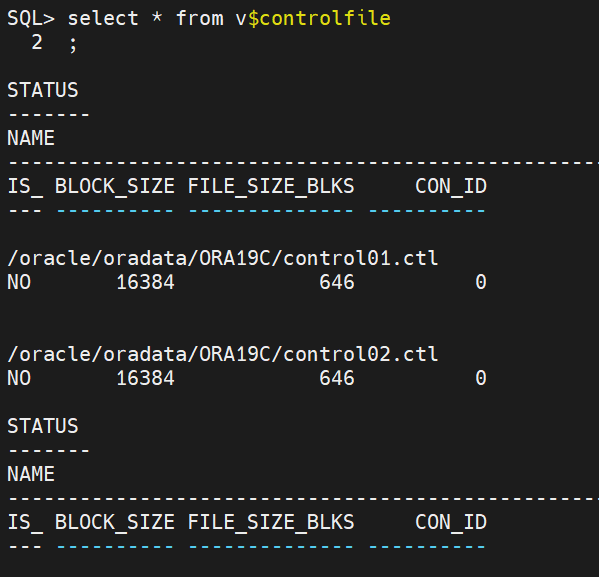
2. Control file
SQL> select * from v$controlfile;
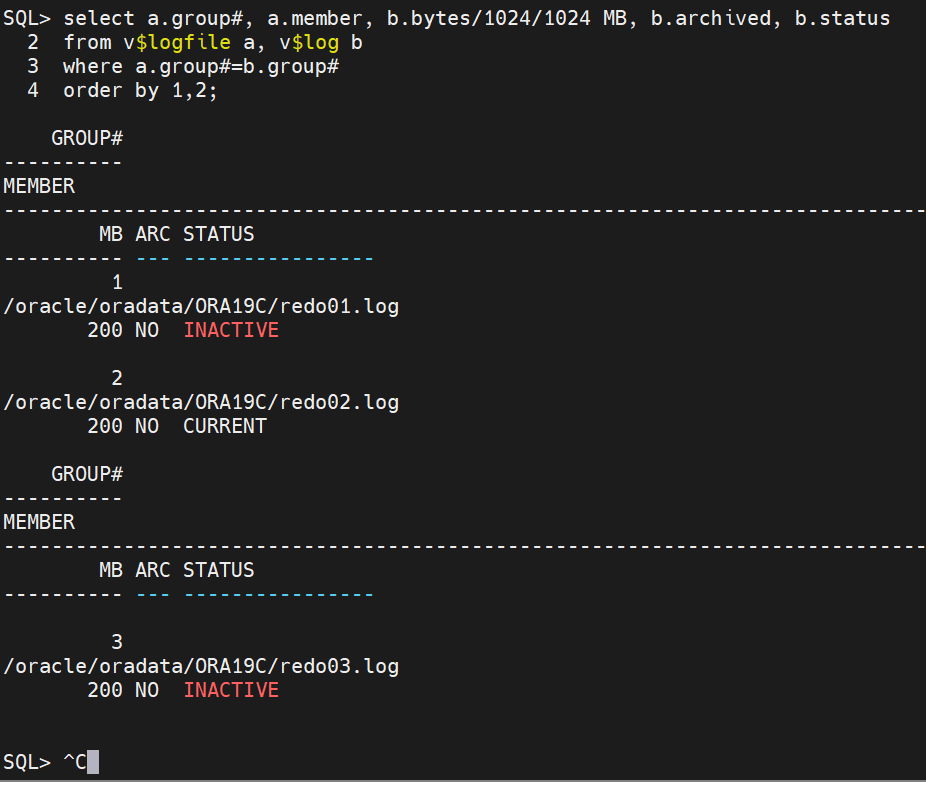
3. Redo Log file
select a.group
from v$logfile a, v$log b
where a.group
order by 1,2;
4. Parameter file & Password file
oracle> cd $ORACLE_HOME/dbs
oracle> ls

4. 백업의 종류
1. Closed Backup(cold backup)
1. root에서 /backup 하위 디렉토리 생성 및 권한 설정
mkdir -p /backup/close
mkdir -p /backup/open
chown -R oracle:dba /backup
2. Open Backup(hot backup / begin end backup)
참고자료




