배열(Array)
배열(Array) 기초
1) 배열이란
- 동일한 타입의 데이터를 한 곳에 모아서 순차적으로 처리할 목적으로 사용되는 순차적 자료 구조이다.
- 인데스 연산자[]를 이용하여 빠른 참조가 가능하다.
- 물리적 위치와 논리적 위치가 동일하다
- 배열의 순선는 0부터 시작한다.
- 자바에서는 객체 배열을 구현한 ArrayList를 많이 활용한다.
2) 배열 선언과 초기화
- 배열 선언하기
// 데이터타입[] 참조변수 = new 데이터타입[배열크기]
int[] arr1 = new int[10]3) 배열 사용하기
배열의 참조변수를 이용하면 배열객체가 생성된 메모리까지 접근할 수 있다.
public class ArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] scoreList = new int[5];
scoreList[0] = 76;
scoreList[1] = 92;
scoreList[2] = 49;
System.out.println("scoreList[0] : " + scoreList[0]); // 76출력
System.out.println("scoreList[1] : " + scoreList[1]); // 92출력
System.out.println("scoreList[2] : " + scoreList[2]); // 49출력
}
}배열객체를 생성하면서 동시에 초기화까지 처리할 수있다.
int[] scoreList = {76,92,49,83,100);일반적으로 배열에 들어있는 값들을 순차적으로 처리할때는 for문이나 향상된 for문을 사용한다.
<for문 사용>
public class ArrayTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] scoreList = {76, 92, 49, 83, 100};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("scoreList[" + i + "] : " + scoreList[i]);
}
}
}<향상된 for문 사용>
public class ArrayTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] scoreList = {76, 92, 49, 83, 100};
// for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// System.out.println("scoreList[" + i + "] : " + scoreList[i]);
// }
for (int score : scoreList) {
System.out.println("score : " + score);
}
}
}4. 배열의 크기와 length변수
length 변수는 배열객체의 길이를 확인할때 사용한다.
public class ArrayTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] scoreList = {76, 92, 49, 83, 100};
System.out.println(scoreList.length); // 배열의 길이인 5가 출력된다.
}
}5. 배열의 형변환
배열은 형변환이 가능한 경우 다른 타입의 데이터도 저장할 수 있다.
다차원 배열
- 이차원 이상으로 구현된 배열을 말한다.
- 평면(이차원 배열) 이나 공간(삼차원 배열)을 활용한 프로그램 구현에 사용된다.
1) 2차원배열의 선언과 객체생성
2차원배열은
데이터타입[행][렬] 배열이름 이라고 생각하면 된다.
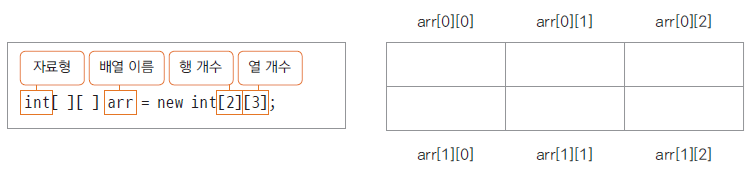
데이터타입[][] 배열변수
int[][] scoreList
